
What is meant by the term ‘fission’ as used in biology?
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint:A type of division that occurs during the process of reproduction in several lower organisms like bacteria.
Complete answer:In biology, fission is stated as the division of a single unit or cell into two or more parts. These parts regenerate to form a complete structure and resemble their parents. It is used mainly about the cell, but sometimes may also be used for organisms, species, etc.
The fission is an asexual reproduction which is of two types:
1. Binary fission – It is a type of fission in which the cell is split into two parts, and each part produces a complete organism identical to its parents.
2. Multiple fission – It is a type of fission in which the cell is split into two or more than two parts, and each part will result in the formation of a complete organism which is identical to its parents.
Additional information:Binary fission is usually found in Bacteria but it is also present in a few eukaryotic organisms. It is of various types depending upon the direction of the fission. It may be irregular (fission takes place at any plane), longitudinal (fission occurs along the longitudinal axis), transverse (fission occurs along a transverse axis), and oblique (fission occurs obliquely). Multiple fission is usually found in protists.
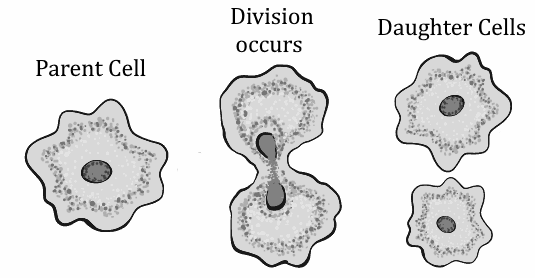
Fig.- Binary fission
Note: Fragmentation is a method of cloning where the organisms formed will be an exact copy of their parents. In the case of echinoderms, this process of cloning is generally called fissiparity. In some protozoans, the process of fission is called plasmotomy where a multinucleate parent after fission will produce two daughter cells that are also multinucleate.
Complete answer:In biology, fission is stated as the division of a single unit or cell into two or more parts. These parts regenerate to form a complete structure and resemble their parents. It is used mainly about the cell, but sometimes may also be used for organisms, species, etc.
The fission is an asexual reproduction which is of two types:
1. Binary fission – It is a type of fission in which the cell is split into two parts, and each part produces a complete organism identical to its parents.
2. Multiple fission – It is a type of fission in which the cell is split into two or more than two parts, and each part will result in the formation of a complete organism which is identical to its parents.
Additional information:Binary fission is usually found in Bacteria but it is also present in a few eukaryotic organisms. It is of various types depending upon the direction of the fission. It may be irregular (fission takes place at any plane), longitudinal (fission occurs along the longitudinal axis), transverse (fission occurs along a transverse axis), and oblique (fission occurs obliquely). Multiple fission is usually found in protists.

Fig.- Binary fission
Note: Fragmentation is a method of cloning where the organisms formed will be an exact copy of their parents. In the case of echinoderms, this process of cloning is generally called fissiparity. In some protozoans, the process of fission is called plasmotomy where a multinucleate parent after fission will produce two daughter cells that are also multinucleate.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




