
What is meant by the judiciary? Describe its composition. What powers does the Supreme Court exercise?
Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint: The Supreme Court is the highest court of the Indian democracy. Judiciary, the third organ of the government has an important role to play in governance. India has a single unified judicial system and that is the Supreme court the highest court in India.
Complete answer:
There are three organs of the government as shown in the diagram
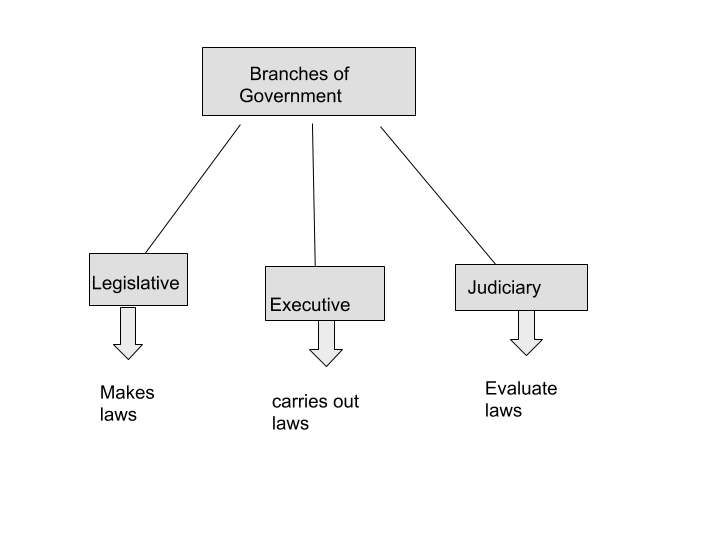
The federal court was established under the Government of India Act.
Composition: The chief justice and other judges of the Supreme court have been appointed by the President of India. The original Constitution of 1950 envisaged a supreme court with a chief justice and 7 other judges.-leaving it to the parliament to increase this number. The Supreme Court which at its inception began with 8 judges which grew to a strength of 34 Judges.
High Court: Article 214 of the constitution provides that there shall be a high court for each state.
After the Supreme Court at the district level, it is the high court.
Subordinate court: Article 233 to 237 in Part VI of the constitution provides the organization of subordinate court.
Powers of Supreme Court:
1.Guardian of the Constitution
2.Original Jurisdiction
3.Review (Revisory Jurisdiction)
4.Power of Judicial Review
5.Advisory Jurisdiction
Court of Records
Note:On 28 January 1950 the Supreme court came into being. Indian Judiciary has also taken reforms to instill transparency in the Indian judicial system. However, the Indian judiciary should strike to balance between transparency and accountability and to maintain the Independence of the judiciary.
Complete answer:
There are three organs of the government as shown in the diagram

The federal court was established under the Government of India Act.
Composition: The chief justice and other judges of the Supreme court have been appointed by the President of India. The original Constitution of 1950 envisaged a supreme court with a chief justice and 7 other judges.-leaving it to the parliament to increase this number. The Supreme Court which at its inception began with 8 judges which grew to a strength of 34 Judges.
High Court: Article 214 of the constitution provides that there shall be a high court for each state.
After the Supreme Court at the district level, it is the high court.
Subordinate court: Article 233 to 237 in Part VI of the constitution provides the organization of subordinate court.
Powers of Supreme Court:
1.Guardian of the Constitution
2.Original Jurisdiction
3.Review (Revisory Jurisdiction)
4.Power of Judicial Review
5.Advisory Jurisdiction
Court of Records
Note:On 28 January 1950 the Supreme court came into being. Indian Judiciary has also taken reforms to instill transparency in the Indian judicial system. However, the Indian judiciary should strike to balance between transparency and accountability and to maintain the Independence of the judiciary.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




