
What is meant by the aufbau principle?
Answer
502.5k+ views
Hint: The Aufbauprinzip (building-up principle), often known as the aufbau rule, says that in the ground state of an atom or ion, electrons fill atomic orbitals of the lowest possible energy levels before moving on to higher levels. The 1s subshell, for example, is occupied before the 2s subshell. An atom's or ion's electrons construct the most stable electron configuration feasible in this fashion.
Complete answer:
The Aufbau principle governs how electrons are filled in an atom's atomic orbitals while it is in its ground state. According to this theory, electrons are filled into atomic orbitals in sequence of increasing orbital energy level. According to the Aufbau principle, the lowest energy atomic orbitals are occupied first, followed by the higher energy levels. The word 'Aufbau' has German roots and essentially translates to 'build up' or 'construct.' The sequence in which atomic orbitals are filled is depicted in the diagram below. The main quantum number is ‘n,' while the azimuthal quantum number is ‘l.' The Aufbau principle may be used to figure out where electrons are in an atom and what energy levels they correspond to. Carbon, for example, has six electrons and has the electrical structure\[~1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{2}}\]. It's crucial to remember that each orbital can only carry two electrons (as per the Pauli exclusion principle). In addition, the way electrons are filled into orbitals in a single subshell must adhere to Hund's rule, which states that every orbital in a given subshell must be single-occupied by electrons before any two electrons couple up in an orbital.
The Aufbau principle states that electrons will inhabit the lowest-energy orbitals first. This means that electrons can only enter higher-energy orbitals after lower-energy orbitals have been entirely filled. The (n+l) rule may be used to identify the sequence in which the energy of orbitals rises, with the sum of the primary and azimuthal quantum numbers determining the orbital energy level. Lower orbital energies correlate to lower (n+l) values. When two orbitals have the same (n+l) values, the orbital with the lower n value is said to have less energy.
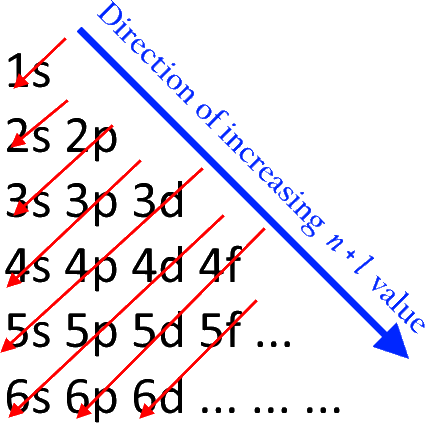
1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d, 7p, and so on are the orders in which the orbitals are filled with electrons.
Note:
Other atomic physics concepts, such as Hund's rule and the Pauli exclusion principle, help to explain electron behaviour. If numerous orbitals of the same energy are accessible, electrons will occupy various orbitals singly before any are occupied twice, according to Hund's rule. If double occupancy occurs, the Pauli exclusion principle dictates that electrons in the same orbital have distinct spins (+1/2 and 1/2).
Complete answer:
The Aufbau principle governs how electrons are filled in an atom's atomic orbitals while it is in its ground state. According to this theory, electrons are filled into atomic orbitals in sequence of increasing orbital energy level. According to the Aufbau principle, the lowest energy atomic orbitals are occupied first, followed by the higher energy levels. The word 'Aufbau' has German roots and essentially translates to 'build up' or 'construct.' The sequence in which atomic orbitals are filled is depicted in the diagram below. The main quantum number is ‘n,' while the azimuthal quantum number is ‘l.' The Aufbau principle may be used to figure out where electrons are in an atom and what energy levels they correspond to. Carbon, for example, has six electrons and has the electrical structure\[~1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{2}}\]. It's crucial to remember that each orbital can only carry two electrons (as per the Pauli exclusion principle). In addition, the way electrons are filled into orbitals in a single subshell must adhere to Hund's rule, which states that every orbital in a given subshell must be single-occupied by electrons before any two electrons couple up in an orbital.
The Aufbau principle states that electrons will inhabit the lowest-energy orbitals first. This means that electrons can only enter higher-energy orbitals after lower-energy orbitals have been entirely filled. The (n+l) rule may be used to identify the sequence in which the energy of orbitals rises, with the sum of the primary and azimuthal quantum numbers determining the orbital energy level. Lower orbital energies correlate to lower (n+l) values. When two orbitals have the same (n+l) values, the orbital with the lower n value is said to have less energy.

1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d, 7p, and so on are the orders in which the orbitals are filled with electrons.
Note:
Other atomic physics concepts, such as Hund's rule and the Pauli exclusion principle, help to explain electron behaviour. If numerous orbitals of the same energy are accessible, electrons will occupy various orbitals singly before any are occupied twice, according to Hund's rule. If double occupancy occurs, the Pauli exclusion principle dictates that electrons in the same orbital have distinct spins (+1/2 and 1/2).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




