
What is meant by resonance in an LCR circuit?
Answer
536.6k+ views
Hint: LCR circuit is a circuit with three elements. These three elements are Inductor, Resistor and Capacitor. These elements can be connected in series or in parallel. This problem can be solved using the impedance formula for LCR circuit. At resonance, impedance is equal to resonance. Substitute this relation in impedance formula for the LCR circuit and then calculate the resonant frequency.
Complete answer:
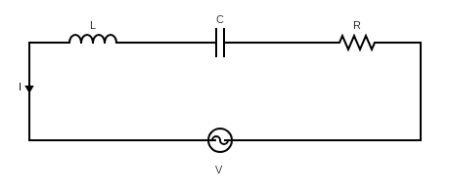
Resonance is the phenomenon in the circuit when the output of that electric circuit is maximum at one particular frequency. In an LCR circuit, this frequency is determined by the values of inductance, conductance, and resistance. If the inductor, capacitor and resistor are connected in series then the circuit is called a Series resonance circuit. But, if they are connected in parallel, then the circuit is called Parallel Resonance circuit.
In LCR series circuits, resonance occurs when the value of inductive and capacitive reactances have equal magnitude but have a phase difference of $180°$. Thus, they cancel each other.
Impedance of a LCR circuit is given by,
$Z=\sqrt{{R}^{2}+{({X}_{L}-{X}_{C})}^{2}}$. ...(1)
Where, R is the resistance
${X}_{L}$ is the inductive resonance
${X}_{C}$ is the capacitive resonance
At resonance,
Z=R
$\therefore{X}_{L}={X}_{C}$
Substituting values in above expression we get,
$\omega L =\dfrac{1}{\omega C}$
$\therefore {\omega}^{2}=\dfrac {1}{LC}$
$\therefore \omega= \dfrac {1}{\sqrt{LC}}$ ...(2)
But, we know $f=\dfrac{\omega}{2\pi}$
Rearranging the above expression we get,
$\omega= f× 2\pi$ ...(3)
Substituting equation (3) in equation. (2) we get,
$f× 2\pi= \dfrac {1}{\sqrt{LC}}$
$\therefore f= \dfrac {1}{2\pi \sqrt{LC}}$
This is known as the resonance frequency of a series LCR circuit.
The graph below shows the resonance frequency of the series LCD circuit. Where, f is in Hertz, L is in Henry and C is in Farad.
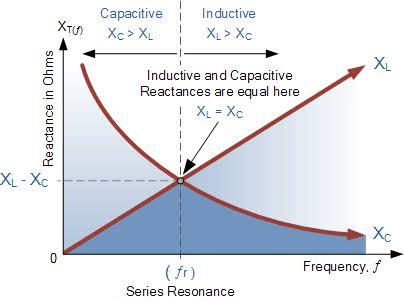
Resonant frequency for a series circuit as well as parallel circuit is the same.
Note:
In LCR series, Impedance is minimum at resonance. Thus, ${Z}_{min}=R$.
From Ohm's law, we know resistance is inversely proportional to current.
Thus, as the resistance is minimum in series LCR circuit, at the resonance, current will be maximum.
When ${X}_{L}>{X}_{C}$, the LCR circuit is inductive.
When ${X}_{L}<{X}_{C}$, the LCR circuit is capacitive.
The circuit impedance at resonance is called Dynamic Impedance of the circuit.
Complete answer:

Resonance is the phenomenon in the circuit when the output of that electric circuit is maximum at one particular frequency. In an LCR circuit, this frequency is determined by the values of inductance, conductance, and resistance. If the inductor, capacitor and resistor are connected in series then the circuit is called a Series resonance circuit. But, if they are connected in parallel, then the circuit is called Parallel Resonance circuit.
In LCR series circuits, resonance occurs when the value of inductive and capacitive reactances have equal magnitude but have a phase difference of $180°$. Thus, they cancel each other.
Impedance of a LCR circuit is given by,
$Z=\sqrt{{R}^{2}+{({X}_{L}-{X}_{C})}^{2}}$. ...(1)
Where, R is the resistance
${X}_{L}$ is the inductive resonance
${X}_{C}$ is the capacitive resonance
At resonance,
Z=R
$\therefore{X}_{L}={X}_{C}$
Substituting values in above expression we get,
$\omega L =\dfrac{1}{\omega C}$
$\therefore {\omega}^{2}=\dfrac {1}{LC}$
$\therefore \omega= \dfrac {1}{\sqrt{LC}}$ ...(2)
But, we know $f=\dfrac{\omega}{2\pi}$
Rearranging the above expression we get,
$\omega= f× 2\pi$ ...(3)
Substituting equation (3) in equation. (2) we get,
$f× 2\pi= \dfrac {1}{\sqrt{LC}}$
$\therefore f= \dfrac {1}{2\pi \sqrt{LC}}$
This is known as the resonance frequency of a series LCR circuit.
The graph below shows the resonance frequency of the series LCD circuit. Where, f is in Hertz, L is in Henry and C is in Farad.

Resonant frequency for a series circuit as well as parallel circuit is the same.
Note:
In LCR series, Impedance is minimum at resonance. Thus, ${Z}_{min}=R$.
From Ohm's law, we know resistance is inversely proportional to current.
Thus, as the resistance is minimum in series LCR circuit, at the resonance, current will be maximum.
When ${X}_{L}>{X}_{C}$, the LCR circuit is inductive.
When ${X}_{L}<{X}_{C}$, the LCR circuit is capacitive.
The circuit impedance at resonance is called Dynamic Impedance of the circuit.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




