
What is meant by power of a lens. Define its S.I unit. You have two lenses A and B of focal length \[+10\text{ cm}\] and \[-10\text{ cm}\]respectively. State the nature and power of each lens. Which of the two lenses will form a virtual and magnified image of an object placed 8 cm from the lens? Draw a ray diagram to Justify your answer.
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: Power of a lens is the visibility to converge or diverge the light ray falling on it. Power of the lens is the reciprocal of its focal length.
Complete step by step answer:
Power of Lens: The Degree of convergence or divergence of light rays achieved by a lens is expressed in terms of power. The power of a lens is defined as the reciprocal of its focal length. It is represented by P.
The power of a lens is related to focal length as below,
\[\text{Power of a lens}=\dfrac{1}{\text{Focal length in meter}}\]
The SI unit of power is dioptre.
The power of a convex lens is positive, the power of a concave lens is negative as a concave lens has a negative focal length.
In the given question lens A is having Focal length \[+10\text{ cm}\]and lens B is having Focal length\[-10\text{ cm}\]. Hence, Lens A is convex and Lens B is concave. Convex lenses form virtual and magnified images of an object placed between F and O.
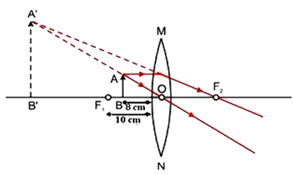
A virtual, erect and enlarged image is formed at the same side of Lens, when an object is placed between Principal focus \[\left( {{F}_{i}} \right)\] and optical center \[\left( O \right)\] of a convex lens.
Note:
There are various possibilities to form various (different) types of image at positioning the objects at different positions. For convex lenses there is only one possibility to form Image which is virtual, erect and enlarged.
Complete step by step answer:
Power of Lens: The Degree of convergence or divergence of light rays achieved by a lens is expressed in terms of power. The power of a lens is defined as the reciprocal of its focal length. It is represented by P.
The power of a lens is related to focal length as below,
\[\text{Power of a lens}=\dfrac{1}{\text{Focal length in meter}}\]
The SI unit of power is dioptre.
The power of a convex lens is positive, the power of a concave lens is negative as a concave lens has a negative focal length.
In the given question lens A is having Focal length \[+10\text{ cm}\]and lens B is having Focal length\[-10\text{ cm}\]. Hence, Lens A is convex and Lens B is concave. Convex lenses form virtual and magnified images of an object placed between F and O.

A virtual, erect and enlarged image is formed at the same side of Lens, when an object is placed between Principal focus \[\left( {{F}_{i}} \right)\] and optical center \[\left( O \right)\] of a convex lens.
Note:
There are various possibilities to form various (different) types of image at positioning the objects at different positions. For convex lenses there is only one possibility to form Image which is virtual, erect and enlarged.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




