
What is meant by limiting friction?
Answer
487.2k+ views
Hint: In Physics, we define force as a push or pull. When two objects interact with each other they apply force on each other. When they get separated from each other, no longer they experience this force but the impact of force lasts for some time. This means either the object comes to rest or starts moving and the reason for this we will discuss here.
Complete answer:
We know when objects interact with each other they apply force on each other.
Similarly, when two surfaces slide against each other they produce a force called frictional force which opposes their relative motion.
We categorize frictions mainly in two categories, static friction, and kinetic friction. As the name suggests, in static friction the object does not move and in kinetic friction, the object starts moving.
Limiting friction comes under static friction. So, we will discuss static friction now. Static friction keeps an object at rest. When we try to move a stationary object on a surface, before it starts moving, it experiences static friction. We can say that static friction balances the applied force.
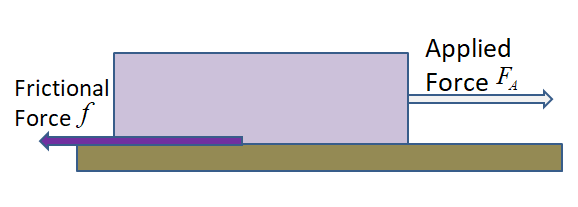
But we also know after applying a certain amount of force the object starts moving. So, the highest value of static friction which opposes the applied force when the object is just about to move is called limiting friction. For example, suppose limiting friction is \[2N\] , this means if we apply the force of \[1N\] or \[2N\] it will be balanced by the static friction. But if the applied force is \[3N\] , greater than the limiting friction object will start moving.
So, limiting friction is the maximum value of static friction which comes to play when the object is just about to move on the surface.
Note:
The frictional force depends on the texture of surfaces, i.e., rough surfaces produce more friction. Limiting friction does not depend on the area of contact and always acts tangentially.
Complete answer:
We know when objects interact with each other they apply force on each other.
Similarly, when two surfaces slide against each other they produce a force called frictional force which opposes their relative motion.
We categorize frictions mainly in two categories, static friction, and kinetic friction. As the name suggests, in static friction the object does not move and in kinetic friction, the object starts moving.
Limiting friction comes under static friction. So, we will discuss static friction now. Static friction keeps an object at rest. When we try to move a stationary object on a surface, before it starts moving, it experiences static friction. We can say that static friction balances the applied force.

But we also know after applying a certain amount of force the object starts moving. So, the highest value of static friction which opposes the applied force when the object is just about to move is called limiting friction. For example, suppose limiting friction is \[2N\] , this means if we apply the force of \[1N\] or \[2N\] it will be balanced by the static friction. But if the applied force is \[3N\] , greater than the limiting friction object will start moving.
So, limiting friction is the maximum value of static friction which comes to play when the object is just about to move on the surface.
Note:
The frictional force depends on the texture of surfaces, i.e., rough surfaces produce more friction. Limiting friction does not depend on the area of contact and always acts tangentially.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




