
What is meant by diffraction of light?
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: Diffraction of light refers to the phenomena that occur when a wave of light encounters an obstacle or a slit generally. It is defined as the bending of waves at the edges of an obstacle or through a slit into the region of geometrical shadow of the obstacle or slit.
Complete step by step answer:
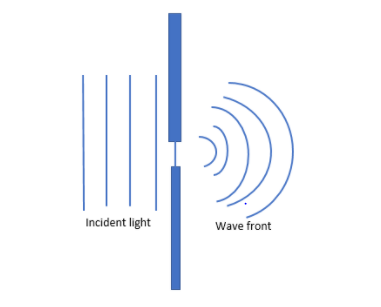
Diffraction of light is a phenomenon in which a light wave passes by a corner or edge of an obstacle through an opening called as a slit that is approximately having the size in order of or even smaller than that wavelength of light.
There are so many daily life examples for this.it can be performed by holding our hand in front of a light source and slowly closing two fingers while observing the transmitted light in between them. As the fingers become close to each other we can see a series of dark lines parallel to the fingers. These kinds of parallel lines are the diffraction patterns. A good daily life example of this is the diffraction of sunlight by clouds that are often called by us as silver lining. Sometimes we can observe pastel shades of blue, pink, purple, and green in clouds that are formed due diffraction of light from water droplets in the clouds. The amount of diffraction depends on so many factors like the wavelength of fallen light. Larger the wavelengths being diffracted, lesser will be the angle of diffracted light.
Note:
To observe the diffraction of light we need a narrow slit width. In daily life diffraction is not so common because we observe the slit width comparable to the wavelength of sound waves as compared to light waves. Therefore the diffraction of sound waves is clearer in daily life than the case of light waves.
Complete step by step answer:
Diffraction of light is a phenomenon in which a light wave passes by a corner or edge of an obstacle through an opening called as a slit that is approximately having the size in order of or even smaller than that wavelength of light.
There are so many daily life examples for this.it can be performed by holding our hand in front of a light source and slowly closing two fingers while observing the transmitted light in between them. As the fingers become close to each other we can see a series of dark lines parallel to the fingers. These kinds of parallel lines are the diffraction patterns. A good daily life example of this is the diffraction of sunlight by clouds that are often called by us as silver lining. Sometimes we can observe pastel shades of blue, pink, purple, and green in clouds that are formed due diffraction of light from water droplets in the clouds. The amount of diffraction depends on so many factors like the wavelength of fallen light. Larger the wavelengths being diffracted, lesser will be the angle of diffracted light.

Note:
To observe the diffraction of light we need a narrow slit width. In daily life diffraction is not so common because we observe the slit width comparable to the wavelength of sound waves as compared to light waves. Therefore the diffraction of sound waves is clearer in daily life than the case of light waves.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




