
What is meant by crystal field splitting energy? On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration of ${{\text{d}}^{\text{4}}}$ in terms of ${{\text{t}}_{{\text{2g}}}}$ and ${{\text{e}}_{\text{g}}}$ in an octahedral field when
A. ${\Delta _0} > {\text{P}}$
B. ${\Delta _0} < {\text{P}}$
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: ${\Delta _0}$ is the crystal field splitting energy and ${\text{P}}$ is the pairing energy. When ${\Delta _0} > {\text{P}}$, it is a strong field ligand. When ${\Delta _0} < {\text{P}}$, it is a weak field ligand.
Complete step by step answer:
The theory that explains the structure and the stability of the coordination complexes is known as the crystal field theory.
The assumptions of crystal field theory are as follows:
1. The metal ion is considered to be a positive charge.
2. The ligands are considered to be a negative charge.
The elements of the d-block of the periodic table have variable oxidation states and variable coordination number. Thus, the coordination complexes are formed by the d-block elements of the periodic table.
The d-subshell has five degenerate orbitals.
When the ligand bonds to the metal ion, the energy of the degenerate d-orbitals increases.
As the energy of the degenerate d-orbitals increases, the degenerate orbitals split into ${{\text{t}}_{{\text{2g}}}}$ and ${{\text{e}}_{\text{g}}}$ orbitals.
The difference in the energies of the ${{\text{t}}_{{\text{2g}}}}$ and ${{\text{e}}_{\text{g}}}$ orbitals is known as the crystal field splitting energy (CFSE). It is denoted by ${\Delta _0}$.
The splitting of degenerate d-orbitals is shown in the diagram below:
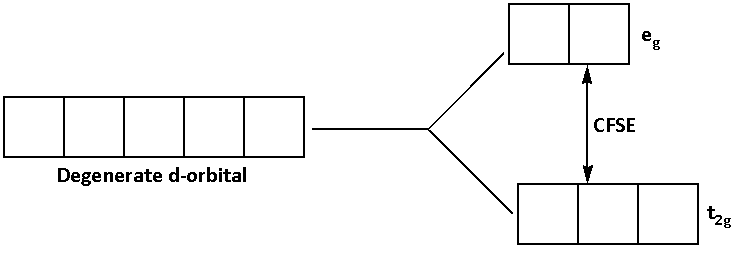
The splitting of the energy depends on the type of the ligand. If the ligand is a strong field ligand its splitting energy is high and if the ligand is a weak field ligand its splitting energy is low.
Write the electronic configuration of ${{\text{d}}^{\text{4}}}$ in terms of ${{\text{t}}_{{\text{2g}}}}$ and ${{\text{e}}_{\text{g}}}$ in an octahedral field when ${\Delta _0} > {\text{P}}$ as follows:
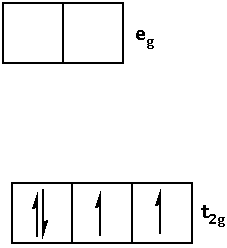
1.When ${\Delta _0} > {\text{P}}$ i.e. crystal field splitting energy is greater than the pairing energy, the ligand is a strong field ligand. When the ligand is a strong field ligand, the fourth electron pairs in the ${{\text{t}}_{{\text{2g}}}}$ orbital.
Thus, the electronic configuration is as follows:
Write the electronic configuration of ${{\text{d}}^{\text{4}}}$ in terms of ${{\text{t}}_{{\text{2g}}}}$ and ${{\text{e}}_{\text{g}}}$ in an octahedral field when ${\Delta _0} < {\text{P}}$ as follows:
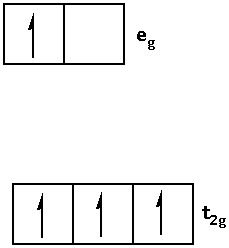
2.When ${\Delta _0} < {\text{P}}$ i.e. crystal field splitting energy is smaller than the pairing energy, the ligand is a weak field ligand. When the ligand is a weak field ligand, the fourth electron jumps in the ${{\text{e}}_{\text{g}}}$ orbital.
Thus, the electronic configuration is as follows:
Note:
Strong field ligands form low spin complexes. The examples of strong field ligands are ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}^ - }$, ${\text{C}}{{\text{N}}^ - }$. Weak field ligands form high spin complexes. The examples of weak field ligands are ${{\text{F}}^ - }$, ${\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ - }$.
Complete step by step answer:
The theory that explains the structure and the stability of the coordination complexes is known as the crystal field theory.
The assumptions of crystal field theory are as follows:
1. The metal ion is considered to be a positive charge.
2. The ligands are considered to be a negative charge.
The elements of the d-block of the periodic table have variable oxidation states and variable coordination number. Thus, the coordination complexes are formed by the d-block elements of the periodic table.
The d-subshell has five degenerate orbitals.
When the ligand bonds to the metal ion, the energy of the degenerate d-orbitals increases.
As the energy of the degenerate d-orbitals increases, the degenerate orbitals split into ${{\text{t}}_{{\text{2g}}}}$ and ${{\text{e}}_{\text{g}}}$ orbitals.
The difference in the energies of the ${{\text{t}}_{{\text{2g}}}}$ and ${{\text{e}}_{\text{g}}}$ orbitals is known as the crystal field splitting energy (CFSE). It is denoted by ${\Delta _0}$.
The splitting of degenerate d-orbitals is shown in the diagram below:

The splitting of the energy depends on the type of the ligand. If the ligand is a strong field ligand its splitting energy is high and if the ligand is a weak field ligand its splitting energy is low.
Write the electronic configuration of ${{\text{d}}^{\text{4}}}$ in terms of ${{\text{t}}_{{\text{2g}}}}$ and ${{\text{e}}_{\text{g}}}$ in an octahedral field when ${\Delta _0} > {\text{P}}$ as follows:
1.When ${\Delta _0} > {\text{P}}$ i.e. crystal field splitting energy is greater than the pairing energy, the ligand is a strong field ligand. When the ligand is a strong field ligand, the fourth electron pairs in the ${{\text{t}}_{{\text{2g}}}}$ orbital.
Thus, the electronic configuration is as follows:

Write the electronic configuration of ${{\text{d}}^{\text{4}}}$ in terms of ${{\text{t}}_{{\text{2g}}}}$ and ${{\text{e}}_{\text{g}}}$ in an octahedral field when ${\Delta _0} < {\text{P}}$ as follows:
2.When ${\Delta _0} < {\text{P}}$ i.e. crystal field splitting energy is smaller than the pairing energy, the ligand is a weak field ligand. When the ligand is a weak field ligand, the fourth electron jumps in the ${{\text{e}}_{\text{g}}}$ orbital.
Thus, the electronic configuration is as follows:

Note:
Strong field ligands form low spin complexes. The examples of strong field ligands are ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}^ - }$, ${\text{C}}{{\text{N}}^ - }$. Weak field ligands form high spin complexes. The examples of weak field ligands are ${{\text{F}}^ - }$, ${\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ - }$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




