
What is meant by bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals? Give number of electron which occupy bonding orbital in $H_2^ + ,{H_2}$ and ${H_{{e_{2 - }}}}$
Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint: An anti-bonding orbital is a molecular orbital containing an electron outside the region between the two nuclei. Whereas bonding molecular orbitals contain an electron inside a region between two nuclei.
Complete step by step answer:
As the two atoms approach each other, their electrons begin to overlap. This overlap forms a molecular bond between the two atoms with its own molecular orbital shape. These orbitals follow Pauli’s exclusion principle in the same way as the atomic orbitals. No two electrons in an orbital have the same quantum state. If the original atom contains electrons where a bond would violate the higher energy anti-bonding orbital.
Anti-bonding orbital and Bonding orbital:
Bonding orbitals are denoted by $'\sigma '$ is the bonding orbital with sigma bond and $\pi $ is the bonding orbital with a pi orbital.
Anti-bonding orbitals are denoted by an asterisk symbol next to the associated type of molecular orbital. $\sigma *$ is the anti-bonding orbitals associated with sigma orbital and $\pi *$ is the anti-bonding orbitals associated with pi orbital.
When pronouncing these orbitals the word star is added to the end of the orbital name. $\sigma *$ - sigma star
Summing up
Bonding orbital formed by constructive addition of wave functions and has less energy which has more stability anti-bonding molecular orbital is formed by destructive addition has more energy and less stability.
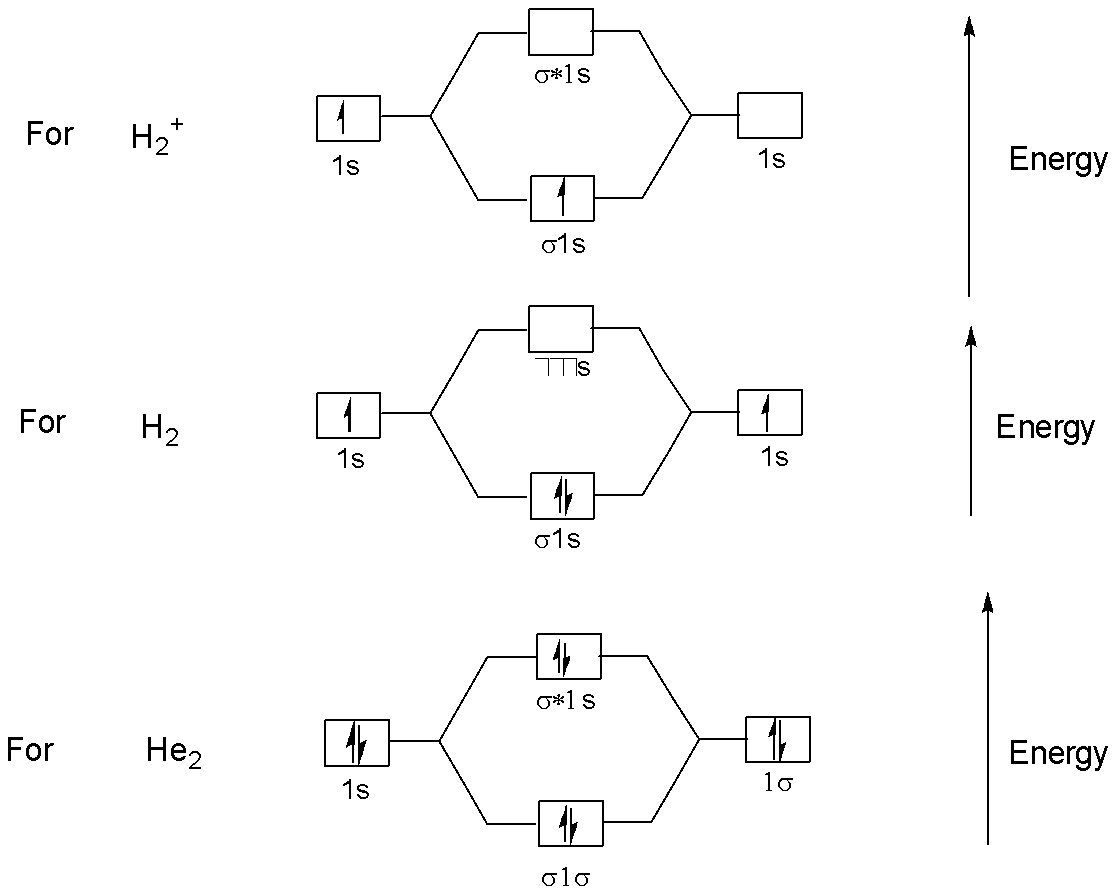
No. of electrons in bonding orbitals of:
$H_2^ + $ is $1$ bonding ${e^ - }$
${H_2}$ is $2$ bonding ${e^ - }$
$H{e_2}$ is $2$ bonding ${e^ - }$
This can be understood by the following energy diagram:
Note:
Electrons in a bonding orbital stabilize the molecule because they are between the nuclei Antibonding electrons destabilize the molecule because they are outside molecules and place less electron density between the nuclei.
They have high energy as they are net closer to the nuclei.
Complete step by step answer:
As the two atoms approach each other, their electrons begin to overlap. This overlap forms a molecular bond between the two atoms with its own molecular orbital shape. These orbitals follow Pauli’s exclusion principle in the same way as the atomic orbitals. No two electrons in an orbital have the same quantum state. If the original atom contains electrons where a bond would violate the higher energy anti-bonding orbital.
Anti-bonding orbital and Bonding orbital:
Bonding orbitals are denoted by $'\sigma '$ is the bonding orbital with sigma bond and $\pi $ is the bonding orbital with a pi orbital.
Anti-bonding orbitals are denoted by an asterisk symbol next to the associated type of molecular orbital. $\sigma *$ is the anti-bonding orbitals associated with sigma orbital and $\pi *$ is the anti-bonding orbitals associated with pi orbital.
When pronouncing these orbitals the word star is added to the end of the orbital name. $\sigma *$ - sigma star
Summing up
Bonding orbital formed by constructive addition of wave functions and has less energy which has more stability anti-bonding molecular orbital is formed by destructive addition has more energy and less stability.
No. of electrons in bonding orbitals of:
$H_2^ + $ is $1$ bonding ${e^ - }$
${H_2}$ is $2$ bonding ${e^ - }$
$H{e_2}$ is $2$ bonding ${e^ - }$
This can be understood by the following energy diagram:

Note:
Electrons in a bonding orbital stabilize the molecule because they are between the nuclei Antibonding electrons destabilize the molecule because they are outside molecules and place less electron density between the nuclei.
They have high energy as they are net closer to the nuclei.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




