
Maximum number of unpaired electrons in $ 3d $ orbital?
Answer
490.5k+ views
Hint: Elements which have an atomic number from $ 21 $ to $ 30 $ are known as first transition series or $ 3d $ series. This series has ten elements which are $ Sc $ , $ Ti $ , $ V $ , $ Cr $ , $ Mn $ , $ Fe $ , $ Co $ , $ Ni $ , $ Cu $ and $ Zn $ . They all filled electrons in the $ 3d $ subshell.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
According to the Aufbau principle, electrons first of all fill in the lowest energy orbitals. After filling the lower energy orbitals completely, it moves up to higher energy orbitals. Also, by Hund’s first rule electrons will first fill each empty orbital before pairing with an electron.
$ d $ subshell has five orbitals. Maximum number of electrons filled in the $ 3d $ subshell is ten electrons whereas the maximum number of unpaired electrons in the $ 3d $ subshell is five electrons. When we talk about the single $ 3d $ orbital the maximum number of electrons in the single $ 3d $ orbital is two and maximum number of unpaired electrons in the single $ 3d $ orbital is one. Here is the diagram to show the filling of electron in $ 3d $ subshell:
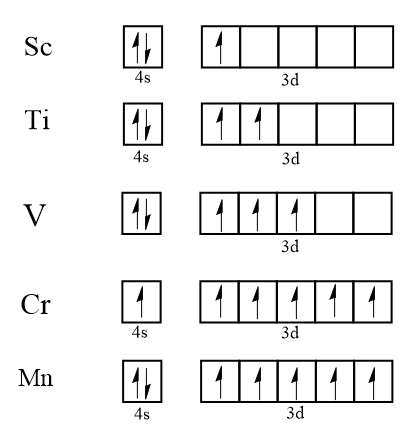
By this diagram it is clear that the maximum number of unpaired electrons in the $ 3d $ subshell is five as in case of $ Mn $ and $ Cr $ whereas the maximum number of unpaired electrons in the $ 3d $ single-orbital is one only.
Thus, the maximum number of unpaired electrons in $ 3d $ subshell is five and in the $ 3d $ single-orbital is one.
Note:
The second rule of Hund states that unpaired electrons in an orbital which are single will have the same spins. If the spins are opposite then the repulsive force increases and thus due to which electrons will separate. If they are in the same direction then they will meet less due to which repulsive force will be less.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
According to the Aufbau principle, electrons first of all fill in the lowest energy orbitals. After filling the lower energy orbitals completely, it moves up to higher energy orbitals. Also, by Hund’s first rule electrons will first fill each empty orbital before pairing with an electron.
$ d $ subshell has five orbitals. Maximum number of electrons filled in the $ 3d $ subshell is ten electrons whereas the maximum number of unpaired electrons in the $ 3d $ subshell is five electrons. When we talk about the single $ 3d $ orbital the maximum number of electrons in the single $ 3d $ orbital is two and maximum number of unpaired electrons in the single $ 3d $ orbital is one. Here is the diagram to show the filling of electron in $ 3d $ subshell:

By this diagram it is clear that the maximum number of unpaired electrons in the $ 3d $ subshell is five as in case of $ Mn $ and $ Cr $ whereas the maximum number of unpaired electrons in the $ 3d $ single-orbital is one only.
Thus, the maximum number of unpaired electrons in $ 3d $ subshell is five and in the $ 3d $ single-orbital is one.
Note:
The second rule of Hund states that unpaired electrons in an orbital which are single will have the same spins. If the spins are opposite then the repulsive force increases and thus due to which electrons will separate. If they are in the same direction then they will meet less due to which repulsive force will be less.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




