
Match the label of the diagrams with the correct cellular structure given above.
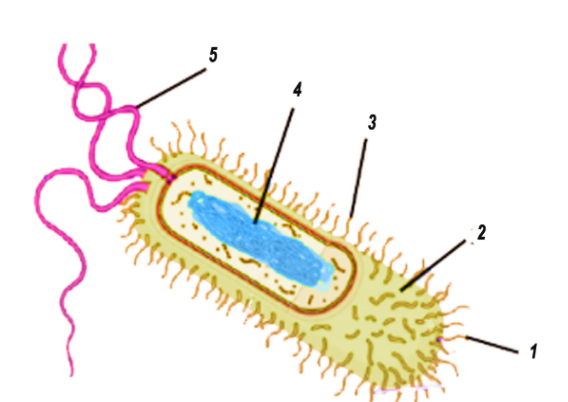
(A)Flagellum-V, Pilus-I, Cytoplasm-II, Nucleoid-III
(B)Flagellum-III, Pilus-V, Cytoplasm-IV, Nucleoid-I
(C)Flagellum-V, Pilus-III, Cytoplasm-IV, Nucleoid-II
(D)Flagellum-IV, Pilus-II, Cytoplasm-V, Nucleoid-III
(E)Flagellum-V, Pilus-III, Cytoplasm-II, Nucleoid-IV

Answer
570k+ views
Hint: It's an easy, single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. It's found during a focal area of the cell called the nucleoid, and it regularly comprises one huge circle called a circular chromosome.
Complete answer:
The diagram is of a prokaryotic bacterial cell. The microorganisms have various limbs or pili (Label III) on its surface for connection to the substrate. It also features a single polar flagellum (Label V) attached to at least one end. As only one flagellum is present, it's a monotrichous bacteria. The bacterium is motile and rod-shaped. The prokaryotic cells possess cytoplasm (Label II). They lack a well-developed nucleus. The central part of a prokaryotic cell that contains a bacterial chromosome and isn't limited by a nuclear layer is called a Nucleoid (Label IV).
Additional Information: Most bacteria are, however, surrounded by a rigid cell membrane made out of peptidoglycan, a polymer composed of linked carbohydrates and little proteins. The cell film gives an extra layer of security, enables the cell to keep up its shape, and forestalls parchedness. Numerous microorganisms even have the farthest layer of starches called the capsule. The capsule is clingy and encourages the cell to append to surfaces in its current circumstance.
So the correct answer is ‘Flagellum-V, Pilus-III, Cytoplasm-II, Nucleoid-IV’.
Note: Fimbriae are various, hair-like structures that are utilized for connection to have cells and different surfaces. Microbes can likewise have bar-like structures alluded to as pili, which are accessible to various assortments.
Regular prokaryotic cells range from 0.1 to 5.0 micrometers (μm) in measurement and are essentially more modest than eukaryotic cells, which typically have widths beginning from 10 to 100 μm.
Complete answer:
The diagram is of a prokaryotic bacterial cell. The microorganisms have various limbs or pili (Label III) on its surface for connection to the substrate. It also features a single polar flagellum (Label V) attached to at least one end. As only one flagellum is present, it's a monotrichous bacteria. The bacterium is motile and rod-shaped. The prokaryotic cells possess cytoplasm (Label II). They lack a well-developed nucleus. The central part of a prokaryotic cell that contains a bacterial chromosome and isn't limited by a nuclear layer is called a Nucleoid (Label IV).
Additional Information: Most bacteria are, however, surrounded by a rigid cell membrane made out of peptidoglycan, a polymer composed of linked carbohydrates and little proteins. The cell film gives an extra layer of security, enables the cell to keep up its shape, and forestalls parchedness. Numerous microorganisms even have the farthest layer of starches called the capsule. The capsule is clingy and encourages the cell to append to surfaces in its current circumstance.
So the correct answer is ‘Flagellum-V, Pilus-III, Cytoplasm-II, Nucleoid-IV’.
Note: Fimbriae are various, hair-like structures that are utilized for connection to have cells and different surfaces. Microbes can likewise have bar-like structures alluded to as pili, which are accessible to various assortments.
Regular prokaryotic cells range from 0.1 to 5.0 micrometers (μm) in measurement and are essentially more modest than eukaryotic cells, which typically have widths beginning from 10 to 100 μm.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




