
Match the following
Set I (Cl-O bond length) Set II $({{\text{A}}^{\text{o}}})$ A. ${\text{HClO}}$ 1. $1.64$ B. ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ 2. $1.70$ C. ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_3}$ 3. $1.45$ D. ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_4}$ 4. $1.57$
The correct matching is:
A. A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4
B. A-2, B-3, C-4, D-1
C. A-2, B-1, C-4, D-3
D. A-2, B-1, C-3, D-4
| Set I (Cl-O bond length) | Set II $({{\text{A}}^{\text{o}}})$ |
| A. ${\text{HClO}}$ | 1. $1.64$ |
| B. ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ | 2. $1.70$ |
| C. ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_3}$ | 3. $1.45$ |
| D. ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_4}$ | 4. $1.57$ |
Answer
570k+ views
Hint:Bond length depends upon the bond strength and bond order. As the bond strength or bond
order increases the bond length decreases. We will determine the bond strength order. The acid having the highest Cl-O bond strength will correspond to the smallest Cl-O bond length value.
Complete answer:As the bond order increases the bond strength increases which in turn decreases the bond length.
So, the relations in bond length, bond order, and bond strength are as follows:
${\text{B}}{\text{.L}}{\text{.}} \propto \dfrac{1}{{{\text{B}}{\text{.O}}{\text{.}}}} \propto \dfrac{1}{{{\text{B}}{\text{.S}}{\text{.}}}}$
Where, B.L. is the bond length, B.O. is the bond order and B.S. is the bond strength.
The structures of all the acids are as follows:
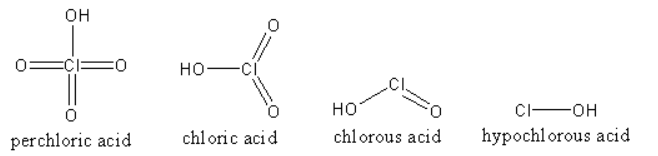
The oxidation state of chlorine in ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_4}$ is $ + 7$ so, it has high tendency to attract the electrons of Cl-O bond towards itself so, Cl-O bond is strongest in ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_4}$. Similarly the oxidation state of chlorine in ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_3}$ is $ + 5$ so, it also has high tendency to attract the electrons of Cl-O bond towards itself but less than ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_4}$. Similarly the oxidation state of chlorine is ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is $ + 3$ and in ${\text{HClO}}$ is $ + 1$.
So, ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_4}$ has the strongest Cl-O bond and ${\text{HClO}}$ has the weakest Cl-O bond.
So, the decreasing order of Cl-O bond strength or is as follows:
${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_4}$>${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_3}$>${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$>${\text{HClO}}$
The increasing order of bond length is as follows:
${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_4}$<${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_3}$<${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$<${\text{HClO}}$
Therefore, option (C) A-2, B-1, C-4, D-3, is correct.
Note:
Bond strength is directly proportional to the positive charge of the central element or the oxidation state of the central element. The molecular orbital diagram is used to determine the bond order for homo or hetero diatomic species. Formula to determine the bond order is as follows: ${\text{Bond}}\,{\text{order}}\, = \,\dfrac{{{\text{Bonding}}\,{\text{electron}} - {\text{Antibonding}}\,\,{\text{electron}}}}{2}$
order increases the bond length decreases. We will determine the bond strength order. The acid having the highest Cl-O bond strength will correspond to the smallest Cl-O bond length value.
Complete answer:As the bond order increases the bond strength increases which in turn decreases the bond length.
So, the relations in bond length, bond order, and bond strength are as follows:
${\text{B}}{\text{.L}}{\text{.}} \propto \dfrac{1}{{{\text{B}}{\text{.O}}{\text{.}}}} \propto \dfrac{1}{{{\text{B}}{\text{.S}}{\text{.}}}}$
Where, B.L. is the bond length, B.O. is the bond order and B.S. is the bond strength.
The structures of all the acids are as follows:

The oxidation state of chlorine in ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_4}$ is $ + 7$ so, it has high tendency to attract the electrons of Cl-O bond towards itself so, Cl-O bond is strongest in ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_4}$. Similarly the oxidation state of chlorine in ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_3}$ is $ + 5$ so, it also has high tendency to attract the electrons of Cl-O bond towards itself but less than ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_4}$. Similarly the oxidation state of chlorine is ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is $ + 3$ and in ${\text{HClO}}$ is $ + 1$.
So, ${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_4}$ has the strongest Cl-O bond and ${\text{HClO}}$ has the weakest Cl-O bond.
So, the decreasing order of Cl-O bond strength or is as follows:
${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_4}$>${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_3}$>${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$>${\text{HClO}}$
The increasing order of bond length is as follows:
${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_4}$<${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_3}$<${\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$<${\text{HClO}}$
Therefore, option (C) A-2, B-1, C-4, D-3, is correct.
Note:
Bond strength is directly proportional to the positive charge of the central element or the oxidation state of the central element. The molecular orbital diagram is used to determine the bond order for homo or hetero diatomic species. Formula to determine the bond order is as follows: ${\text{Bond}}\,{\text{order}}\, = \,\dfrac{{{\text{Bonding}}\,{\text{electron}} - {\text{Antibonding}}\,\,{\text{electron}}}}{2}$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




