
Match the following. Identify the correct match between Set-I and Set-II.
Set-I Set-II A) Stichonematic I) Flagellum has two or more rows of lateral appendages B) Pantonematic II) Flagellum has no lateral appendages and terminal filament C) Acronematic III) Flagellum bears one row of lateral appendages D) Anematic IV) Flagellum does not lateral appendages and terminal part of the acroneme is naked
A. A-III, B-I, C-IV-D-II
B. A-IV, B-I, C-III-D-II
C. A-III, B-II, C-IV-D-I
D. A-II, B-I, C-III-D-IV
| Set-I | Set-II |
| A) Stichonematic | I) Flagellum has two or more rows of lateral appendages |
| B) Pantonematic | II) Flagellum has no lateral appendages and terminal filament |
| C) Acronematic | III) Flagellum bears one row of lateral appendages |
| D) Anematic | IV) Flagellum does not lateral appendages and terminal part of the acroneme is naked |
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: There are different types of flagella. For example, stichonematic flagella is present in euglena and they have only one-row mastigonemes.
Step by step answer:
Flagella are the microscopic hair-like structures that are involved in the locomotion of a cell. The flagella have whip-like appearances that help a cell to move through the liquid. Some special flagella are used in a few organisms as sensory organs which can sense changes in pH and temperature of the surroundings. Flagella have the small hair-like structures which are called mastigonemes. There are different types of flagella.
-If the flagella have mastigonemes on only one side or row, then they are called stichonematic flagella. Such a type of flagella is found in euglena.
-If flagella have two rows of mastigonemes, then they are called pantonematic flagella.
-If there are no mastigonemes present in flagella, then they are called acronematic flagella. This type of flagella is found in Chlamydomonas.
-If there are no mastigonemes and the distal ends of the flagella end as a naked, axial filament, then they are called anemic. Such a type of flagella is found in cryptomonas.
So, the correct option is option A
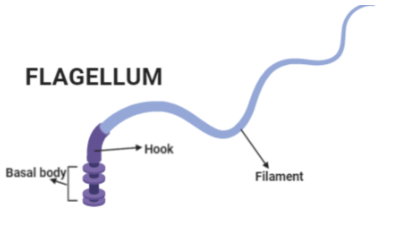
Note: The flagella possess a helical structure composed of a protein called flagellin. The flagella structure comprises three parts: basal body, hook, and filament. Each has its own function.
Step by step answer:
Flagella are the microscopic hair-like structures that are involved in the locomotion of a cell. The flagella have whip-like appearances that help a cell to move through the liquid. Some special flagella are used in a few organisms as sensory organs which can sense changes in pH and temperature of the surroundings. Flagella have the small hair-like structures which are called mastigonemes. There are different types of flagella.
-If the flagella have mastigonemes on only one side or row, then they are called stichonematic flagella. Such a type of flagella is found in euglena.
-If flagella have two rows of mastigonemes, then they are called pantonematic flagella.
-If there are no mastigonemes present in flagella, then they are called acronematic flagella. This type of flagella is found in Chlamydomonas.
-If there are no mastigonemes and the distal ends of the flagella end as a naked, axial filament, then they are called anemic. Such a type of flagella is found in cryptomonas.
So, the correct option is option A
| Set-I | Set-II |
| A) Stichonematic | III) Flagellum bears one row of lateral appendages |
| B) Pantonematic | I) Flagellum has two or more rows of lateral appendages |
| C) Acronematic | IV) Flagellum does not lateral appendages and the terminal part of the acroneme is naked |
| D) Anematic | II) Flagellum has no lateral appendages and terminal filament |
Note: The flagella possess a helical structure composed of a protein called flagellin. The flagella structure comprises three parts: basal body, hook, and filament. Each has its own function.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




