
Match the columns and find correct options
Column I Column II a Basal p Dianthus b Free central q pea C Parietal r Lemon D Axile s Marigold E Marginal t Argemone
(a) a-p, b-q, c-r, d-s, e-t
(b) a-s, b-p, c-t, d-r, e-q
(c) a-q, b-r, c-s, d-t, e-p
(d) a-t, b-s, c-r, d-q, e-p
(e) a-s, b-r, c-t, d-p, e-q
| Column I Column II | |||
| a | Basal | p | Dianthus |
| b | Free central | q | pea |
| C | Parietal | r | Lemon |
| D | Axile | s | Marigold |
| E | Marginal | t | Argemone |
Answer
605.7k+ views
Hint: The placenta is a special type of tissue in flowering plants that connects the ovules to the ovary.
Complete answer:
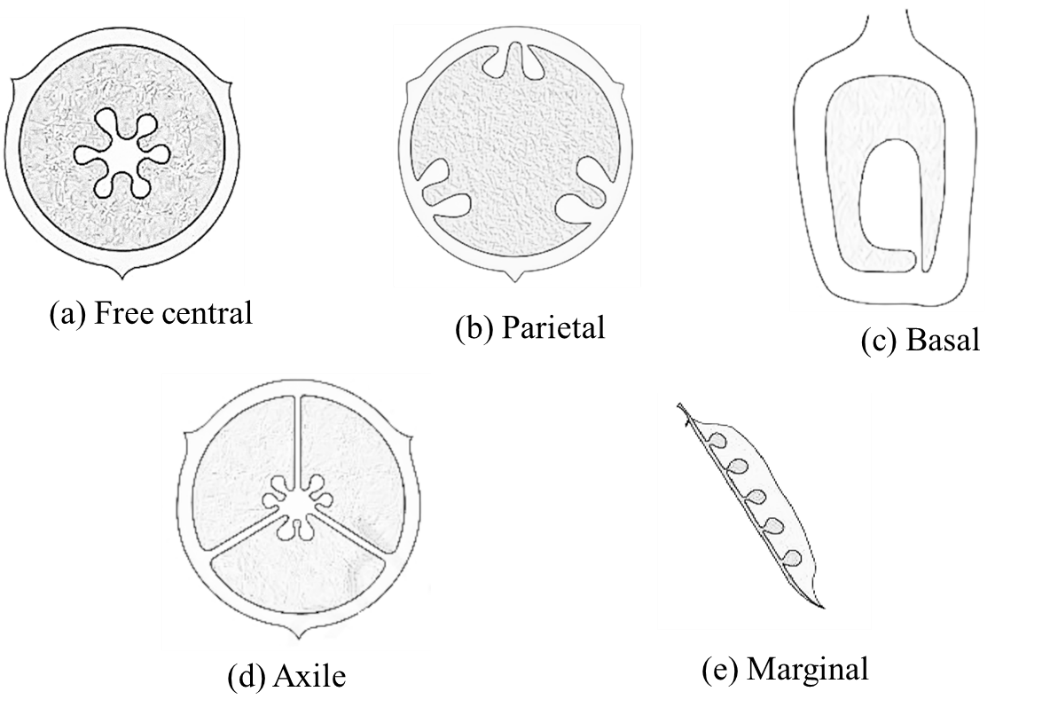
Placentation can be described as the mode of arrangement of ovules on the placenta inside the ovary. There are different types of placentation in plants that include basal, parietal, axile, free central, and marginal.
Types of placentation:
- Axile: This type of placentation is found in bicarpellary to multicarpellary syncarpous ovary. The carpel fuse forms a central axis and ovules are arranged on this axis. Examples of axile placentation include Hibiscus, lemon, tomato, lilly.
- Basal: This type of placenta is found in mono to multicarpellary, syncarpous ovary. The placenta develops at the base of the ovary and generally, a single ovule is attached to it. Examples are sunflower, daisy, marigold.
- Marginal: It is found in the mainly monocarpellary unilocular ovary. In this type, the placenta forms a ridge along the ventral side of the ovary and the ovules are arranged on this ridge forming two rows. An example includes pea.
- Parietal: This type of placenta is found in bicarpellary to multicarpellary syncarpous ovary. A false septum divided the ovary into two chambers. Example: mustard.
- Free central: In this type of placenta, ovules are arranged on the central axis due to the degradation of the false septum. Example: dianthus.
So, the correct answer is ‘a-s, b-p, c-t, d-r, e-q’
Note:
- In the apocarpous ovary, there is typically a single line of placentation in each ovary and more than one free carpel is present.
- In the syncarpous ovary, the lines of placentation can be regularly spaced along the wall of the ovary or near the center of the ovary. In this ovary, more than one carpel is found which are fused.
Complete answer:
Placentation can be described as the mode of arrangement of ovules on the placenta inside the ovary. There are different types of placentation in plants that include basal, parietal, axile, free central, and marginal.
Types of placentation:
- Axile: This type of placentation is found in bicarpellary to multicarpellary syncarpous ovary. The carpel fuse forms a central axis and ovules are arranged on this axis. Examples of axile placentation include Hibiscus, lemon, tomato, lilly.
- Basal: This type of placenta is found in mono to multicarpellary, syncarpous ovary. The placenta develops at the base of the ovary and generally, a single ovule is attached to it. Examples are sunflower, daisy, marigold.
- Marginal: It is found in the mainly monocarpellary unilocular ovary. In this type, the placenta forms a ridge along the ventral side of the ovary and the ovules are arranged on this ridge forming two rows. An example includes pea.
- Parietal: This type of placenta is found in bicarpellary to multicarpellary syncarpous ovary. A false septum divided the ovary into two chambers. Example: mustard.
- Free central: In this type of placenta, ovules are arranged on the central axis due to the degradation of the false septum. Example: dianthus.
So, the correct answer is ‘a-s, b-p, c-t, d-r, e-q’
Note:
- In the apocarpous ovary, there is typically a single line of placentation in each ovary and more than one free carpel is present.
- In the syncarpous ovary, the lines of placentation can be regularly spaced along the wall of the ovary or near the center of the ovary. In this ovary, more than one carpel is found which are fused.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




