
Maleic acid is stronger than fumaric acid because? (This question has multiple correct answers)
(a)- Fumaric acid shows intermolecular H-bonding
(b)- Fumaric acid shows intermolecular ionic bonding
(c)- Maleic acid is dibasic acid
(d)- Maleic acid shows chelation or intermolecular H-bonding
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Intermolecular H-bonding is caused when hydrogen bonding is formed between many molecules. Intramolecular H-bonding is caused when hydrogen bonding is formed within the molecule. Butenedioic acid has two forms, cis-form known as maleic acid and trans-form known as fumaric acid.
Complete step by step answer:
Maleic acid is also known as the cis-form of Butenedioic acid. The cis-form in which both the carboxylic group is on the same side of the molecule.
The structure of maleic acid is given below:
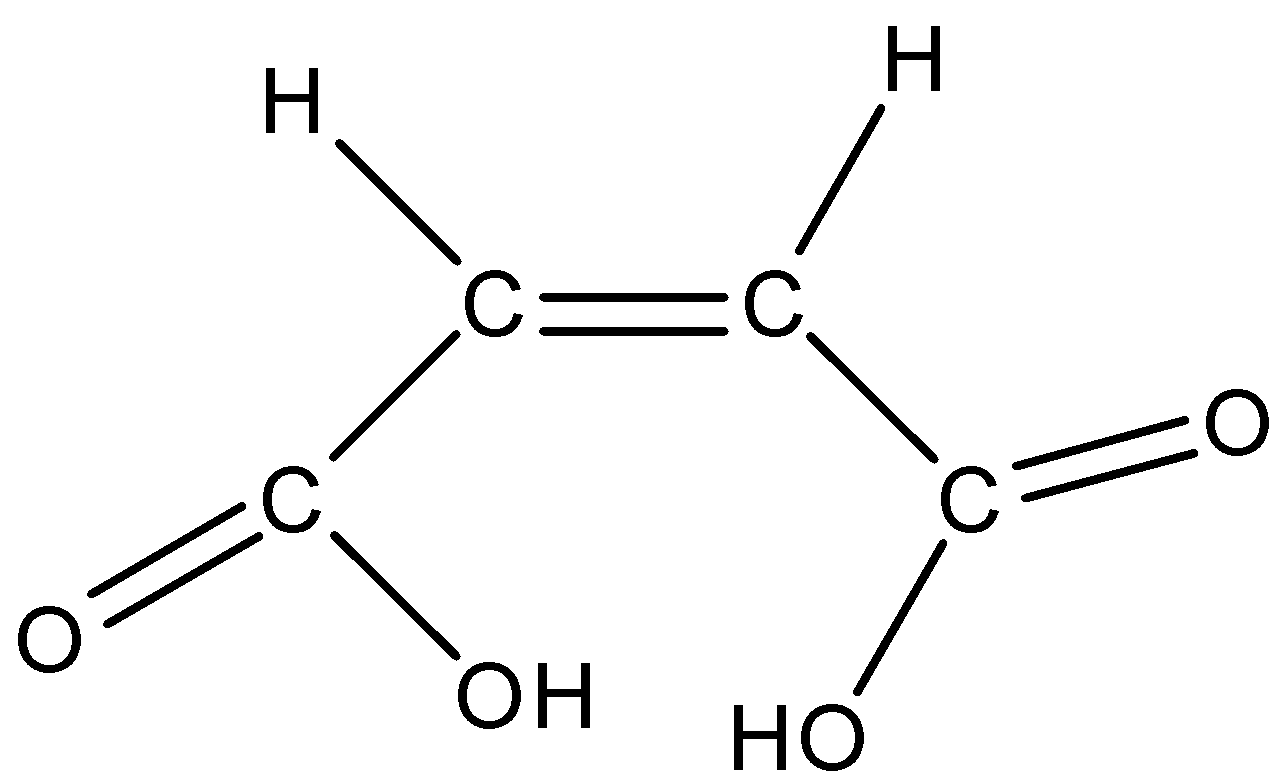
So according to this structure, the maleic acid has the ability to form intramolecular H-bonding. This happens when the maleic acid removes one hydrogen atom from one of the carboxylic groups the intramolecular Hydrogen-bonding is formed as shown in below:
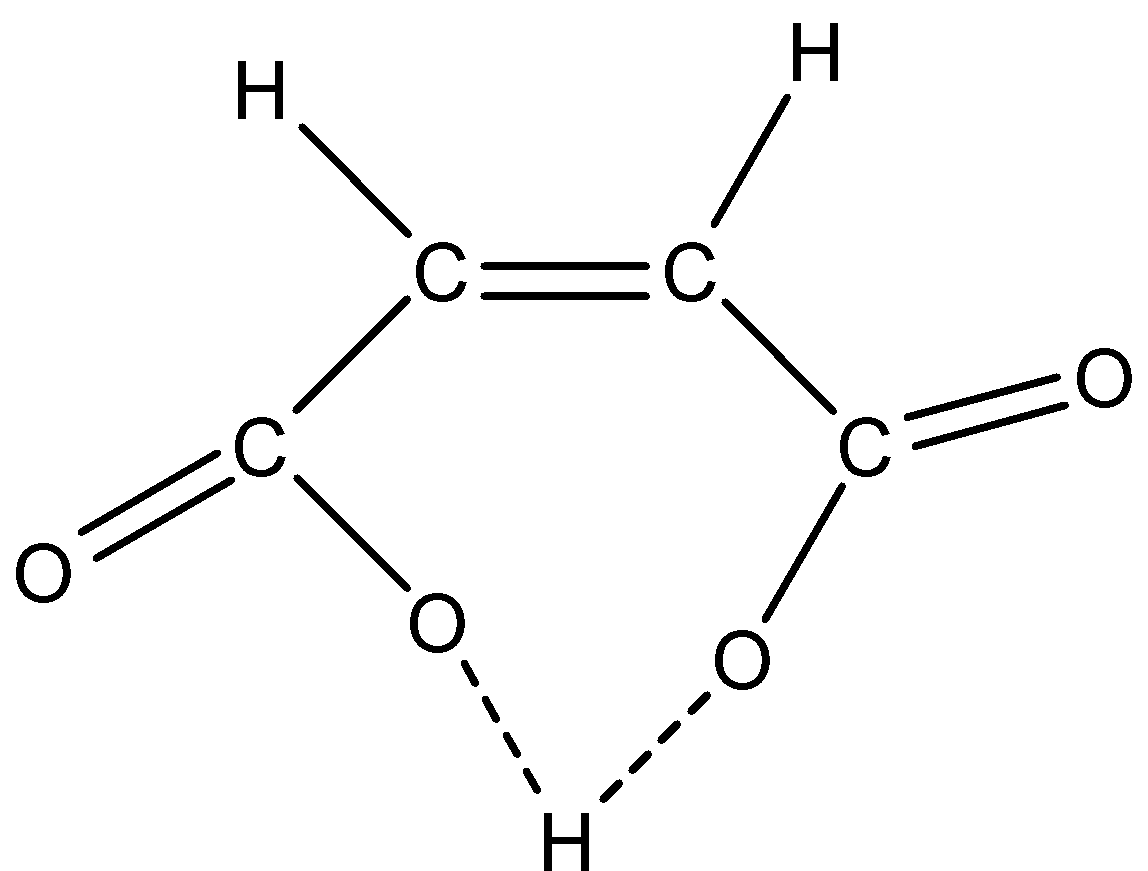
This is not possible in fumaric acid, this can be explained as:
Fumaric acid is also known as the trans form of butenedioic acid. The trans form is when both the carboxylic groups are on the opposite side. The structure is given below:
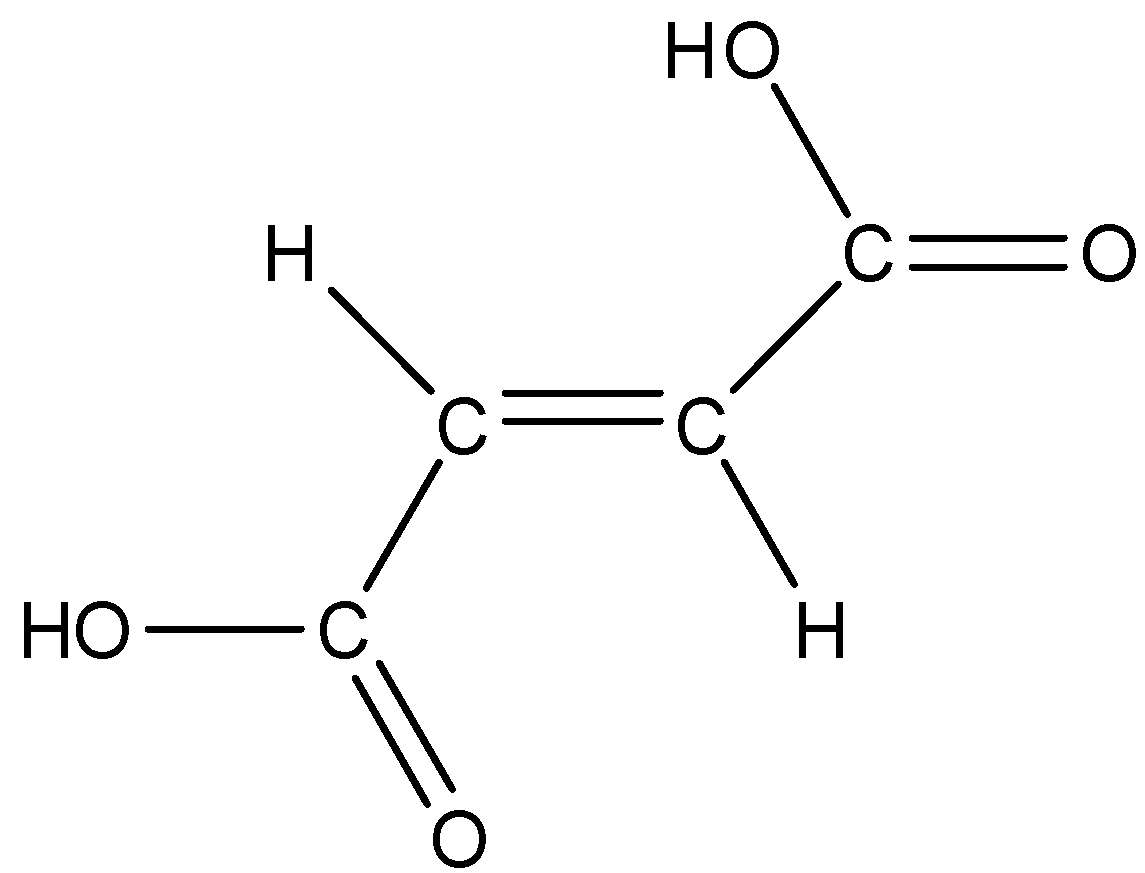
So, according to this structure fumaric acid cannot for intramolecular H-bonding, else it forms intermolecular H-bonding as shown below:
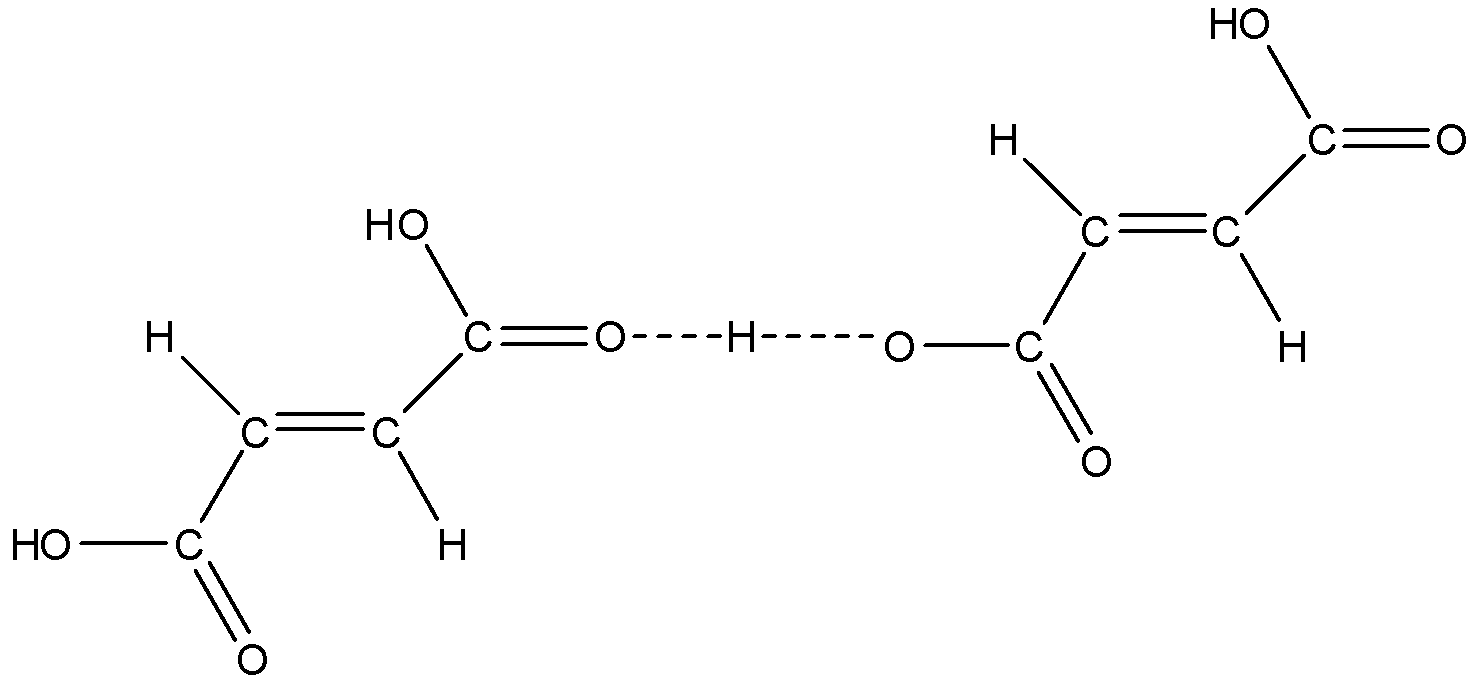
Therefore, the correct answers are an option (a)- Fumaric acid shows intermolecular H-bonding and (d)- Maleic acid shows chelation or intermolecular H-bonding.
Note: The maleic acid or the cis-form of butenedioic acid is less stable than the Fumaric acid or the trans form of butenedioic acid. Maleic acid is soluble in water but Fumaric acid is not soluble in water.
Complete step by step answer:
Maleic acid is also known as the cis-form of Butenedioic acid. The cis-form in which both the carboxylic group is on the same side of the molecule.
The structure of maleic acid is given below:

So according to this structure, the maleic acid has the ability to form intramolecular H-bonding. This happens when the maleic acid removes one hydrogen atom from one of the carboxylic groups the intramolecular Hydrogen-bonding is formed as shown in below:

This is not possible in fumaric acid, this can be explained as:
Fumaric acid is also known as the trans form of butenedioic acid. The trans form is when both the carboxylic groups are on the opposite side. The structure is given below:

So, according to this structure fumaric acid cannot for intramolecular H-bonding, else it forms intermolecular H-bonding as shown below:

Therefore, the correct answers are an option (a)- Fumaric acid shows intermolecular H-bonding and (d)- Maleic acid shows chelation or intermolecular H-bonding.
Note: The maleic acid or the cis-form of butenedioic acid is less stable than the Fumaric acid or the trans form of butenedioic acid. Maleic acid is soluble in water but Fumaric acid is not soluble in water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




