
What is the major product (s) when 2-methyl-2-butene reacts with (i) ${{O}_{3}}$ (ii) $Zn/C{{H}_{3}}COOH(aq)$?
I
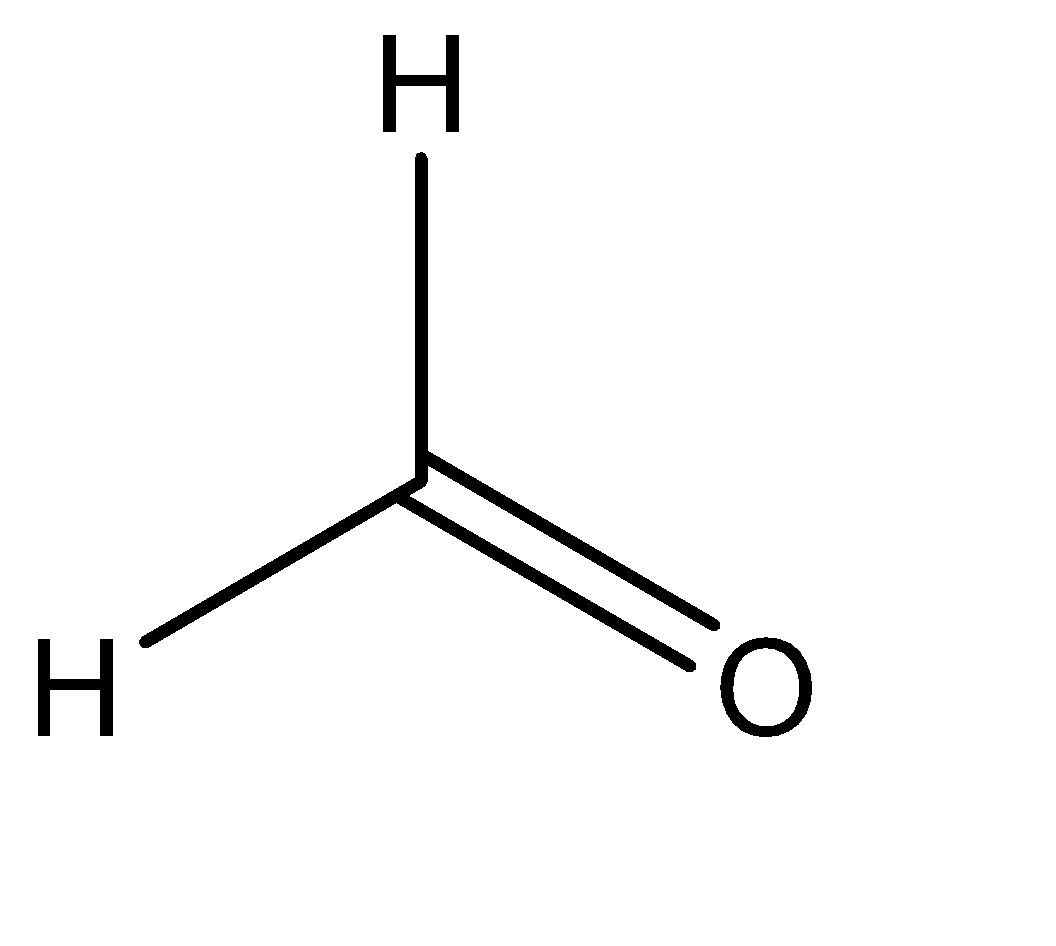
II
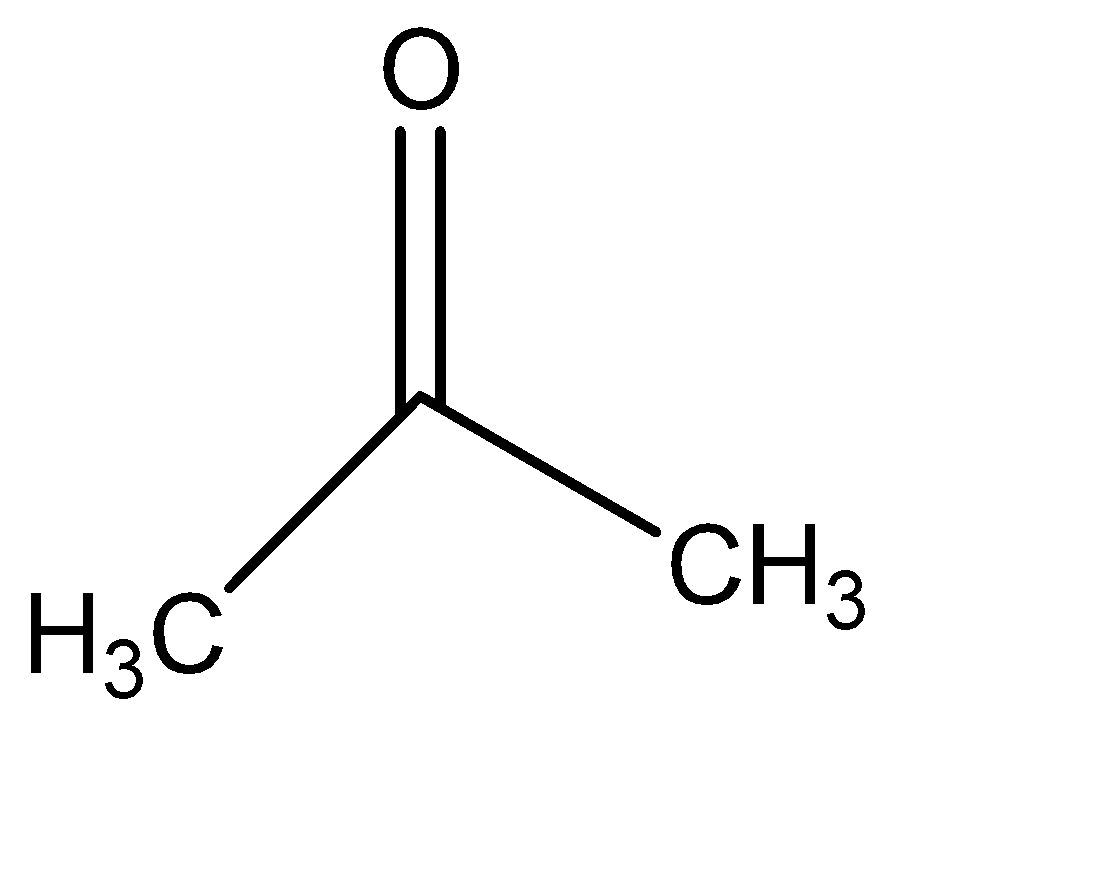
III
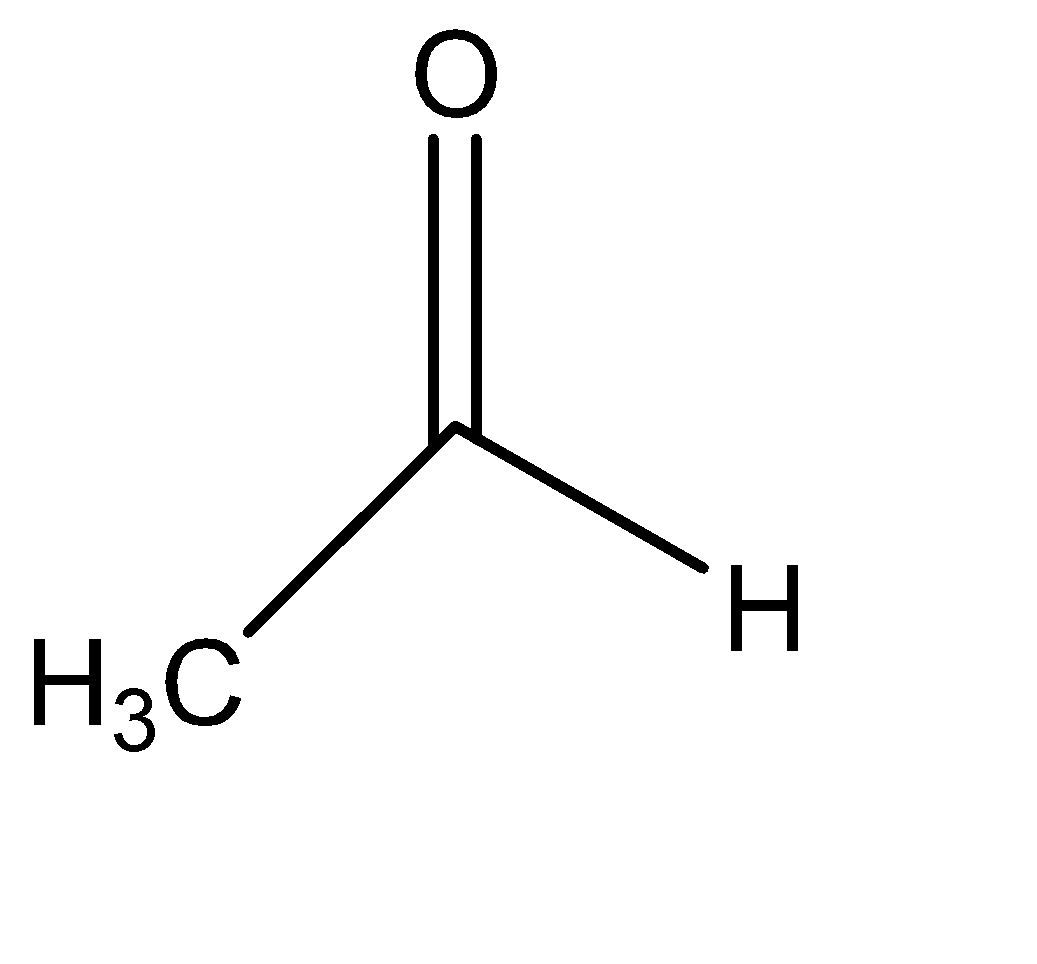
IV
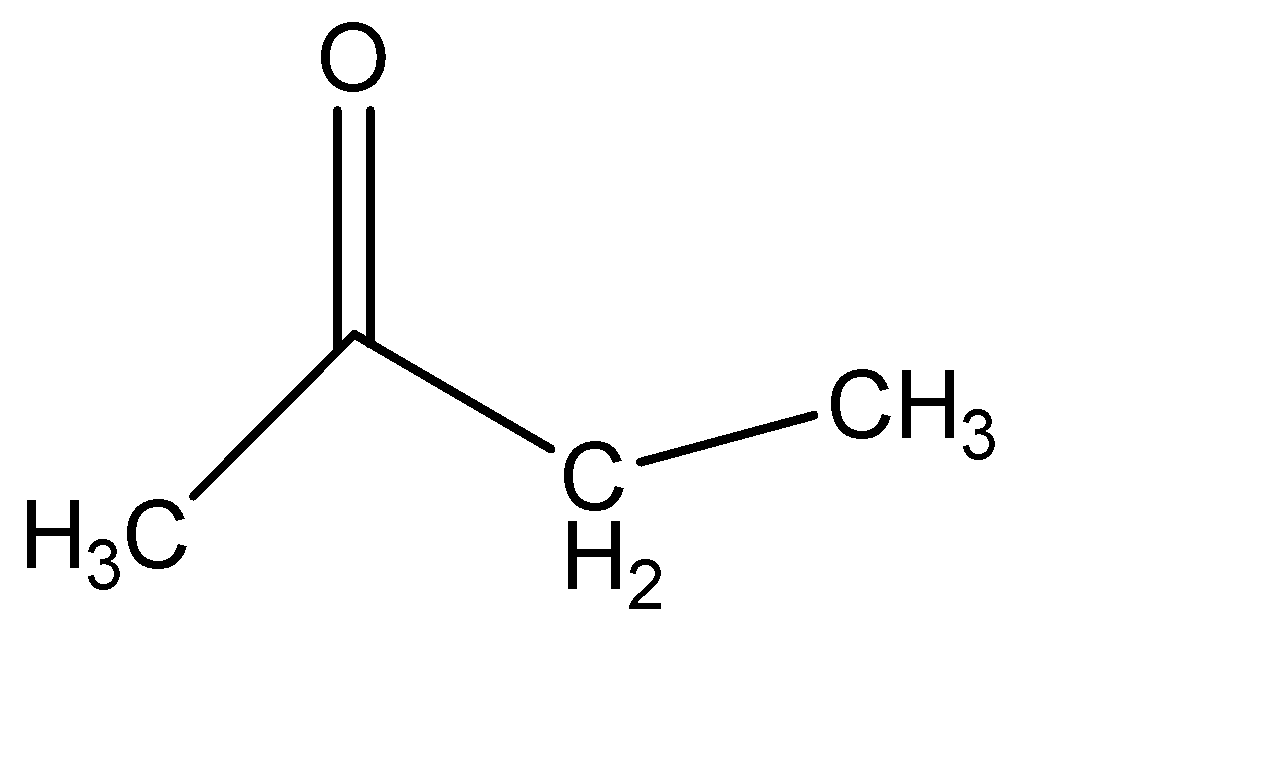
(a) I + II
(b) II + III
(c) III + IV
(d) II




Answer
531.3k+ views
Hint: As we can see that the reagents provided in the question directs us toward the process of ozonolysis which is the oxidative cleavage of alkenes’ double bond with the help of ozone and zinc dust so as to form aldehyde and ketone as product. So we will solve this question by the process of Ozonolysis.
Complete answer:
Let us first understand the process of Ozonolysis:-
-Ozonolysis is a reaction in which the unsaturated bonds of alkenes, alkynes or compounds containing azo groups are cleaved with ozone. Alkenes and alkynes generally form compounds in which the multiple carbon–carbon bonds get replaced by a carbonyl group whereas azo compounds form nitrosamines. The outcome of this reaction actually depends on the type of multiple bonds being oxidized and the work-up conditions provided as reagents.
-Ozonolysis of 2-methyl-2-butene:-
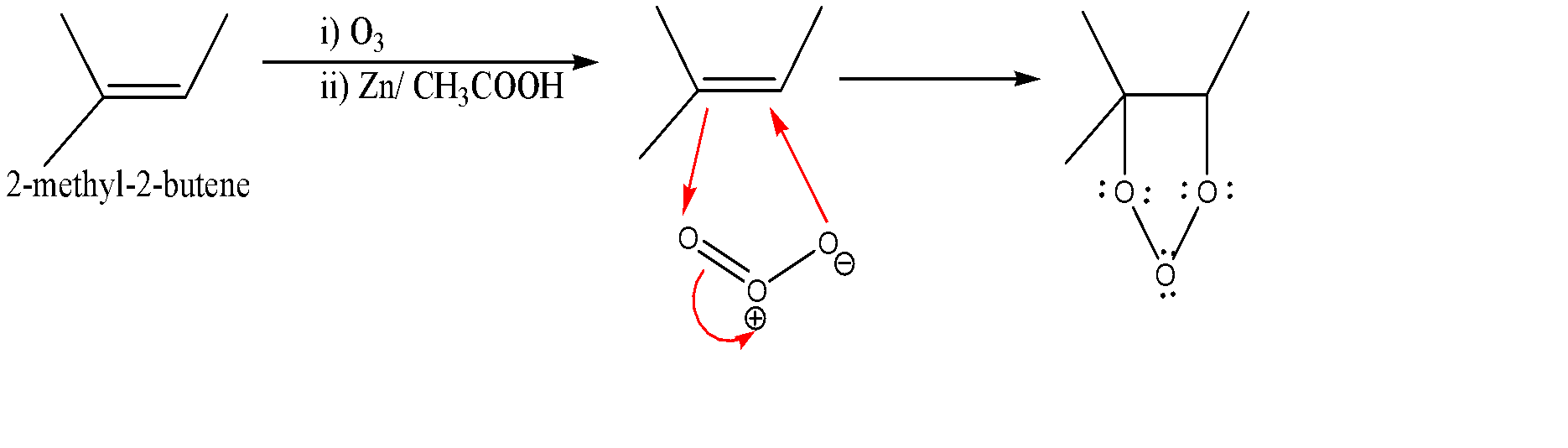

-When an alkene reacts with an ozone molecule, 1, 3 dipolar reaction takes place. Here alkene gets reduced and attaches itself to the oxygen atoms as shown in the above diagram.

-Since the entire oxygen atoms present carry lone pairs along with it, so repulsion starts creating between them which leads to the breaking of the molecule due to which carbonyl molecule and a dipolar ion are formed. Now the negative part of the ion attacks the electrophilic part of the carbonyl compound which further attacks the dipolar ion.
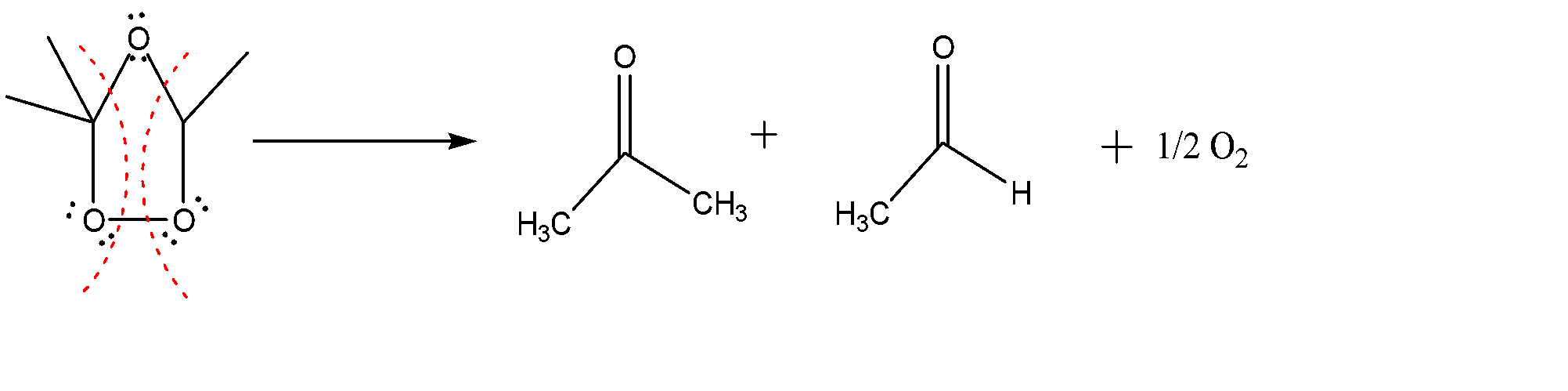
-The molecule formed is again full of repulsions due to which it breaks apart and we get following carbonyl compounds as product: ketone + aldehyde.
Hence the major products are: (b) II + III
Note:
$Zn/C{{H}_{3}}COOH(aq)$ is used because when oxygen gas (${{O}_{2}}$) is formed it reacts with ${{H}_{2}}O$ to form ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ which acts like an oxidizing agent. The ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ oxidizes the aldehyde product and further converts it into carboxylic acid. So to stop this further oxidation, we require zinc dust to convert ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ to zinc oxide and water.
Hence in ozonolysis, the last work-up decides the nature of the product formed.
Complete answer:
Let us first understand the process of Ozonolysis:-
-Ozonolysis is a reaction in which the unsaturated bonds of alkenes, alkynes or compounds containing azo groups are cleaved with ozone. Alkenes and alkynes generally form compounds in which the multiple carbon–carbon bonds get replaced by a carbonyl group whereas azo compounds form nitrosamines. The outcome of this reaction actually depends on the type of multiple bonds being oxidized and the work-up conditions provided as reagents.
-Ozonolysis of 2-methyl-2-butene:-

-When an alkene reacts with an ozone molecule, 1, 3 dipolar reaction takes place. Here alkene gets reduced and attaches itself to the oxygen atoms as shown in the above diagram.

-Since the entire oxygen atoms present carry lone pairs along with it, so repulsion starts creating between them which leads to the breaking of the molecule due to which carbonyl molecule and a dipolar ion are formed. Now the negative part of the ion attacks the electrophilic part of the carbonyl compound which further attacks the dipolar ion.

-The molecule formed is again full of repulsions due to which it breaks apart and we get following carbonyl compounds as product: ketone + aldehyde.
Hence the major products are: (b) II + III
Note:
$Zn/C{{H}_{3}}COOH(aq)$ is used because when oxygen gas (${{O}_{2}}$) is formed it reacts with ${{H}_{2}}O$ to form ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ which acts like an oxidizing agent. The ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ oxidizes the aldehyde product and further converts it into carboxylic acid. So to stop this further oxidation, we require zinc dust to convert ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ to zinc oxide and water.
Hence in ozonolysis, the last work-up decides the nature of the product formed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




