
What is the major product P in the above reaction?
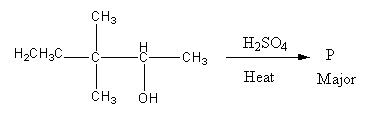
A)
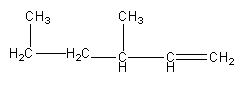
B)
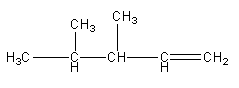
C)
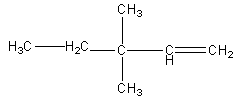
D)
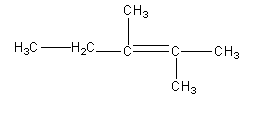





Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: Concentrated sulphuric acid is a dehydrating agent. The dehydrating agent removes water from the compounds. The major product depends upon the stability of the formed carbocation.
Complete answer:
Concentrated sulphuric acid works as a dehydrating agent, so it discards water molecules from the compound and thus dehydrates the compound. These reactions are known as dehydration reactions and the substance which causes dehydration is known as a dehydrating agent.
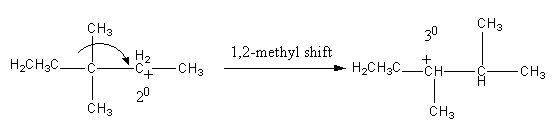
The lone pair of electrons of the hydroxyl group of the reactant attacks on the sulphuric acid and gets protonated. Then the water molecule removes forming a carbocation. The carbocation is ${2^ \circ }$. Which will convert into ${3^ \circ }$ carbocation because ${3^ \circ }$ carbocation is more stable than ${2^ \circ }$ carbocation.
The conversion of ${2^ \circ }$ carbocation to ${3^ \circ }$ carbocation takes place by 1,2 - methyl shift.
The methyl shifting is shown as follows:
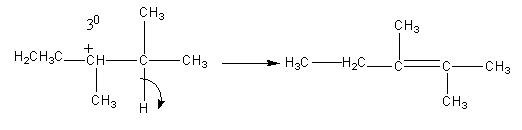
After the methyl shifting, proton from nearby carbon is removed to form an alkene.
Therefore, option (D) is correct.
Note: When a carbon is attached with only one other carbon, the carbon is known as ${1^ \circ }$. If the carbon is attached with two other carbons, the carbon is known as ${2^ \circ }$ carbon similarly the ${3^ \circ }$ carbon is attached with three other carbons. The order of stability of carbocation is: ${3^ \circ } > {2^ \circ } > {1^ \circ }$. As the number of methyl groups increases the $ + {\text{I}}$ effect increases, so the stability of the carbocation increases. Concentrated sulphuric acid is a strong oxidizing agent and also a dehydrating agent.
Complete answer:
Concentrated sulphuric acid works as a dehydrating agent, so it discards water molecules from the compound and thus dehydrates the compound. These reactions are known as dehydration reactions and the substance which causes dehydration is known as a dehydrating agent.
The lone pair of electrons of the hydroxyl group of the reactant attacks on the sulphuric acid and gets protonated. Then the water molecule removes forming a carbocation. The carbocation is ${2^ \circ }$. Which will convert into ${3^ \circ }$ carbocation because ${3^ \circ }$ carbocation is more stable than ${2^ \circ }$ carbocation.
The conversion of ${2^ \circ }$ carbocation to ${3^ \circ }$ carbocation takes place by 1,2 - methyl shift.
The methyl shifting is shown as follows:

After the methyl shifting, proton from nearby carbon is removed to form an alkene.

Therefore, option (D) is correct.
Note: When a carbon is attached with only one other carbon, the carbon is known as ${1^ \circ }$. If the carbon is attached with two other carbons, the carbon is known as ${2^ \circ }$ carbon similarly the ${3^ \circ }$ carbon is attached with three other carbons. The order of stability of carbocation is: ${3^ \circ } > {2^ \circ } > {1^ \circ }$. As the number of methyl groups increases the $ + {\text{I}}$ effect increases, so the stability of the carbocation increases. Concentrated sulphuric acid is a strong oxidizing agent and also a dehydrating agent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




