
What is the main difference between atomic orbital and molecular orbital?
Answer
507.6k+ views
Hint :The name itself suggests that the atomic orbitals are orbitals associated with individual atoms in their free state and the molecular orbitals are orbitals associated with molecules that contain two or more atoms in a bonded state.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The orbitals according to Bohr’s atomic model or Schrodinger's model represent the three dimensional spaces around the nucleus where the probability of finding electrons is high. Mathematically, orbitals can be treated as wave functions that help us in doing various quantum mechanical calculations on them.
The atom in a free state has a uniformly distributed electron cloud around its nucleus resulting in its overall symmetry. When two or more atoms approach each other, their electron clouds are pulled by a force of attraction from each other’s nuclei. This pull results in the distortion of electron clouds disturbing the symmetry of the orbitals of the atoms.
When two atoms approach each other, their orbitals also come closer and the wave functions can experience a constructive or destructive overlap when the orbitals overlap to form a bond. The bonded electrons have a high electron density in between the two nuclei rather than a uniformly distributed electron cloud.
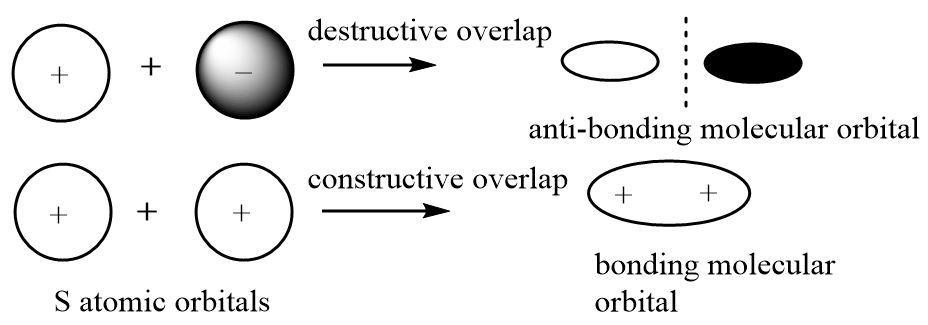
Thus atomic orbitals represent spaces with maximum electron density associated with individual atoms but molecular orbitals represent spaces of high electron density (bonding MO) between the nuclei of two atoms linked through a bond and also spaces where there is zero probability of finding shared pairs of electron in a molecule (non-bonding MO).
Note :
The overlap between two atomic orbitals can result in a variety of bonds. A head-on overlap between two orbitals results in the formation of a sigma \[\sigma \] bond between atoms and the sidewise overlap results in a \[\pi \] bond.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The orbitals according to Bohr’s atomic model or Schrodinger's model represent the three dimensional spaces around the nucleus where the probability of finding electrons is high. Mathematically, orbitals can be treated as wave functions that help us in doing various quantum mechanical calculations on them.
The atom in a free state has a uniformly distributed electron cloud around its nucleus resulting in its overall symmetry. When two or more atoms approach each other, their electron clouds are pulled by a force of attraction from each other’s nuclei. This pull results in the distortion of electron clouds disturbing the symmetry of the orbitals of the atoms.
When two atoms approach each other, their orbitals also come closer and the wave functions can experience a constructive or destructive overlap when the orbitals overlap to form a bond. The bonded electrons have a high electron density in between the two nuclei rather than a uniformly distributed electron cloud.

Thus atomic orbitals represent spaces with maximum electron density associated with individual atoms but molecular orbitals represent spaces of high electron density (bonding MO) between the nuclei of two atoms linked through a bond and also spaces where there is zero probability of finding shared pairs of electron in a molecule (non-bonding MO).
Note :
The overlap between two atomic orbitals can result in a variety of bonds. A head-on overlap between two orbitals results in the formation of a sigma \[\sigma \] bond between atoms and the sidewise overlap results in a \[\pi \] bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




