
Main axis of a diatomic molecule is Z. The orbitals $ {p_x} $ and $ {p_y} $ overlap to form :
A) $ \pi - $ molecular orbital
B) $ \sigma - $ molecular orbital
C) $ \delta - $ molecular orbital
D) No bond is formed
Answer
481.5k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we will have to remember the concept of sigma bond formation by mixing of orbitals. The + and – refers to the electron density dispersion across the orbitals. The formation of covalent bonds happens on collision of orbitals. Some lead to constructive interference and some destructive.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
According to the VSEPR theory there are two types of bonds that can be formed by collision of orbitals:
1. Sigma Bond
2. Pi Bond
The formation of sigma bonds occurs due to head-to-head collision of the orbitals that lie in the same plane or are coaxial/collinear. By definition, a sigma bond is formed by overlapping atomic orbitals that are in line with the internuclear axis. The s-orbital is spherical in shape and is said to be non-directional. P- orbitals have a dumbbell shape, and in order to form a sigma bond, p-orbital must lie on the internuclear axis. A pi bond is formed if there are two same p-orbitals, that are perpendicular to the axis. The lateral overlap leads to the formation of the pi bond.
The axis given to us is the Z axis. All the three p-orbitals are perpendicular to each other. On the z axis, $ {p_x} $ and $ {p_y} $ will surely be perpendicular to the axis, but also will be perpendicular to each other. Both have different symmetry and the shoulder-to-shoulder overlap will not occur. The overlap can be shown as below:
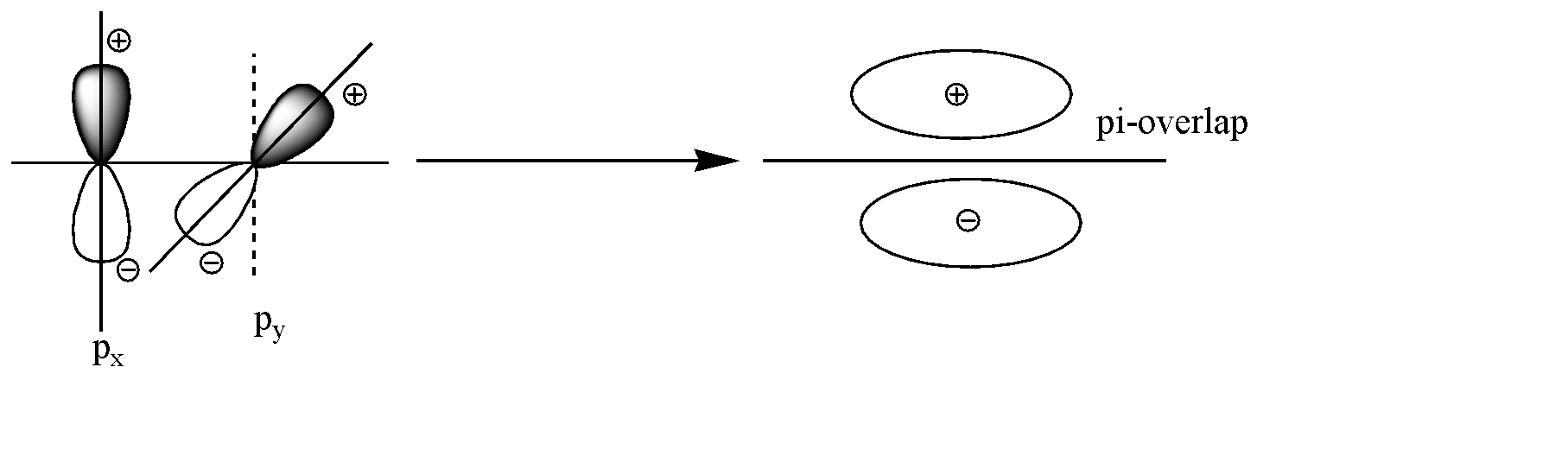
Hence as we can see no overlap occurs, because of the dissimilar symmetry.
The correct answer is option (D).
Note:
If s orbital combines with a p orbital perpendicular to the plane, no bond formation takes place and this forms a NBMO (non-bonding molecular orbital). Similarly with two p-orbitals, one in axis and one perpendicular to the axis, for example $ {p_x}\& {p_y} $ orbitals on x-axis, will lead to a formation of NBMO.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
According to the VSEPR theory there are two types of bonds that can be formed by collision of orbitals:
1. Sigma Bond
2. Pi Bond
The formation of sigma bonds occurs due to head-to-head collision of the orbitals that lie in the same plane or are coaxial/collinear. By definition, a sigma bond is formed by overlapping atomic orbitals that are in line with the internuclear axis. The s-orbital is spherical in shape and is said to be non-directional. P- orbitals have a dumbbell shape, and in order to form a sigma bond, p-orbital must lie on the internuclear axis. A pi bond is formed if there are two same p-orbitals, that are perpendicular to the axis. The lateral overlap leads to the formation of the pi bond.
The axis given to us is the Z axis. All the three p-orbitals are perpendicular to each other. On the z axis, $ {p_x} $ and $ {p_y} $ will surely be perpendicular to the axis, but also will be perpendicular to each other. Both have different symmetry and the shoulder-to-shoulder overlap will not occur. The overlap can be shown as below:

Hence as we can see no overlap occurs, because of the dissimilar symmetry.
The correct answer is option (D).
Note:
If s orbital combines with a p orbital perpendicular to the plane, no bond formation takes place and this forms a NBMO (non-bonding molecular orbital). Similarly with two p-orbitals, one in axis and one perpendicular to the axis, for example $ {p_x}\& {p_y} $ orbitals on x-axis, will lead to a formation of NBMO.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




