
Magnification produced by a concave mirror is:
a. Is always less than one
b. Is always more than one
c. Always equal to one
d. May less than or equal to or greater than one
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: Magnification is defined as the ratio of the size of the image formed by the spherical mirror to the size of the object.Generally magnification is denoted by $m$. Magnification could be positive or negative depending upon the position of the object and the position of the image formed and height measured as negative for downwards and positive for upwards.
Formula for magnification:
$m = \dfrac{I}{O}$, where height of the image is $I$ and height of the object $O$.
Complete answer:
Magnification of the concave mirror depends on the position and erect and inversion of the image and object. We’ll try to understand the concept using two diagrams which can explain us better.
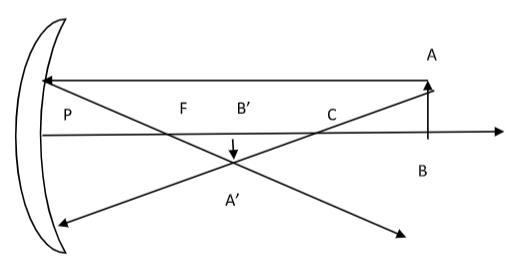
The diagram shows the image formation by concave mirror when the object is placed beyond the centre of curvature C. In this figure the object is AB and the image formed is A’B’. We can observe that the image formed is inverted in nature,therefore the size of the image is taken as negative because of inversion and the size of the object as positive because it is above the principal axis.
So, magnification is:
$m = \dfrac{{ \pm I}}{{ \pm O}}$, sign of the image and object size is based on erection and inversion.
Hence, the correct answer is option (d).
Note: Formula for magnification can also be given as:
$m = \dfrac{f}{{f - u}}$, where f is the focal length and u is the distance of the object measured from pole P.
Some of the uses of concave mirror are:
Used as reflectors in cinema projectors, used to construct reflecting type astronomical telescopes,as parabolic mirrors in search lights.
Formula for magnification:
$m = \dfrac{I}{O}$, where height of the image is $I$ and height of the object $O$.
Complete answer:
Magnification of the concave mirror depends on the position and erect and inversion of the image and object. We’ll try to understand the concept using two diagrams which can explain us better.

The diagram shows the image formation by concave mirror when the object is placed beyond the centre of curvature C. In this figure the object is AB and the image formed is A’B’. We can observe that the image formed is inverted in nature,therefore the size of the image is taken as negative because of inversion and the size of the object as positive because it is above the principal axis.
So, magnification is:
$m = \dfrac{{ \pm I}}{{ \pm O}}$, sign of the image and object size is based on erection and inversion.
Hence, the correct answer is option (d).
Note: Formula for magnification can also be given as:
$m = \dfrac{f}{{f - u}}$, where f is the focal length and u is the distance of the object measured from pole P.
Some of the uses of concave mirror are:
Used as reflectors in cinema projectors, used to construct reflecting type astronomical telescopes,as parabolic mirrors in search lights.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 12 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Prove that a parallelogram circumscribing a circle-class-12-maths-CBSE

How is the angle of emergence e related to the angle class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between lanthanoids and actinoids class 12 chemistry CBSE

Derive Lens Makers formula for a convex lens class 12 physics CBSE




