
Who made the first law of Thermodynamics?
Answer
499.5k+ views
Hint: Thermodynamics: The term Thermodynamics comprises heat, temperature and work. Basically it explains the relationship between these three parameters of a matter. It also explains how thermal energy can be converted into other forms of energy and vice-versa and its effects on matters.
Example of Thermodynamics: Thermosteel bottles to maintain the temperature of the liquid whether it's hot or cold. Melting ice cubes into liquids, Using microwaves for cooking purposes etc.
Complete step by step solution:
First Law of Thermodynamics: According to the first law of thermodynamics, in an isolated system, energy can neither be created nor it can be destroyed. This law is also known as “Energy Conservation Law”. This law was made by scientist Rudolf Clausius in \[1850\].
Additional information:
Other laws of Thermodynamics:
Second Law: According to the second law of thermodynamics the entropy of an isolated system always increases.
Third Law of Thermodynamics: According to the third law of thermodynamics, as the temperature of a system approaches absolute zero, the entropy of a system approaches a constant value.
According to energy conservation law, energy can neither be created nor it can be destroyed. Only it can be transferred from one form to another form of energy but the total amount of energy always remains the same.
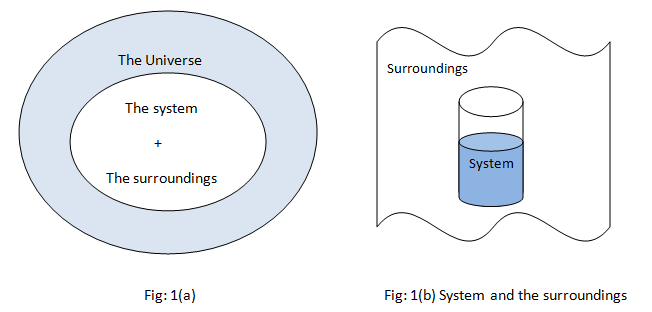
All the observations are made into the systems and the remaining part other than observations included into the surrounding. Various changes take place into the systems but it does not affect the entire universe, for practical purposes only surroundings can interact with the system as shown in fig 1(b).
Note: The second law is made by scientists Rudolf Clausius and William Thomson and the third law is made by scientist Walther Nernst during \[1906-1912\] while entropy can be explained as a measure of thermal energy per unit temperature of a system.
Example of Thermodynamics: Thermosteel bottles to maintain the temperature of the liquid whether it's hot or cold. Melting ice cubes into liquids, Using microwaves for cooking purposes etc.
Complete step by step solution:
First Law of Thermodynamics: According to the first law of thermodynamics, in an isolated system, energy can neither be created nor it can be destroyed. This law is also known as “Energy Conservation Law”. This law was made by scientist Rudolf Clausius in \[1850\].
Additional information:
Other laws of Thermodynamics:
Second Law: According to the second law of thermodynamics the entropy of an isolated system always increases.
Third Law of Thermodynamics: According to the third law of thermodynamics, as the temperature of a system approaches absolute zero, the entropy of a system approaches a constant value.
According to energy conservation law, energy can neither be created nor it can be destroyed. Only it can be transferred from one form to another form of energy but the total amount of energy always remains the same.

All the observations are made into the systems and the remaining part other than observations included into the surrounding. Various changes take place into the systems but it does not affect the entire universe, for practical purposes only surroundings can interact with the system as shown in fig 1(b).
Note: The second law is made by scientists Rudolf Clausius and William Thomson and the third law is made by scientist Walther Nernst during \[1906-1912\] while entropy can be explained as a measure of thermal energy per unit temperature of a system.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




