
Lucas test is given by an alcohol within $5$ minutes. $0.22g$ of which liberates $56m{L_{}}$ of $C{H_4}$ at STP on treating with $C{H_3}MgCl$.The structure of alcohol is:
A.
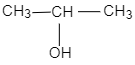
B.
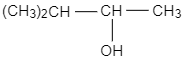
C.
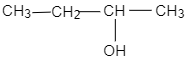
D.


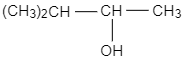


Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: The Lucas test in alcohols is a test for differentiating between primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols. It is basically based on the difference in reactivity of the three types of alcohols with hydrogen halides via an $SN_1$reaction:
$ROH + HCl \to RCl + {H_2}O$
Complete step by step solution:
Lucas test is given by all of the given alcohols within $5$ minutes as all given are secondary alcohols .Exact structure of the alcohol can be known by molecular mass or formula of alcohol which will be acquired as follows:
Let molecular mass of alcohol be $M$.
So the following equation is formed as,
$22400/56$=$0.22/M$
Or, $(5622400 \times 0.22)/56$=$88$
The general formula of alcohols is ${C_n}{H_{2n + 1}}OH$ .The molecular mass $88$ corresponds to the value of $n = 5$ Thus, the secondary alcohol is ${(C{H_3})_2}CHCH(OH)C{H_3}$.
So, the correct answer is B.
Additional information:
Lucas reagent is a solution of anhydrous zinc chloride which is concentrated in hydrochloric acid. Zinc chloride is used in this reagent as zinc chloride forms a complex with oxygen or alcohol and it converts the hydroxyl group to a better leaving group and helps in forming chloroalkane. Basically it converts the alcohols to the alkyl chlorides.This solution is used to classify alcohols of low molecular weight. This reaction is a replacement in which the chloride replaces a hydroxyl group during reaction. A positive test is shown by a change from clear and colorless to turbid color, signing formation of a chloroalkane. The best results for this test are detected in tertiary alcohols because they form their own alkyl halides fastest due to their higher stability of the intermediate tertiary carbocation. The test was stated in $1930$ and this became a standard method in organic chemistry. The test has now since become somewhat outdated with the availability of various spectroscopic and chromatographic methods of analysis. But the test was named after Howard Lucas.
Note: The different reactivity reflects the different way of formation of the corresponding carbocation’s. Tertiary carbocations are far more stable than secondary carbocations, and primary carbocations are the least stable (due to hyper conjugation).
$ROH + HCl \to RCl + {H_2}O$
Complete step by step solution:
Lucas test is given by all of the given alcohols within $5$ minutes as all given are secondary alcohols .Exact structure of the alcohol can be known by molecular mass or formula of alcohol which will be acquired as follows:
Let molecular mass of alcohol be $M$.
So the following equation is formed as,
$22400/56$=$0.22/M$
Or, $(5622400 \times 0.22)/56$=$88$
The general formula of alcohols is ${C_n}{H_{2n + 1}}OH$ .The molecular mass $88$ corresponds to the value of $n = 5$ Thus, the secondary alcohol is ${(C{H_3})_2}CHCH(OH)C{H_3}$.
So, the correct answer is B.
Additional information:
Lucas reagent is a solution of anhydrous zinc chloride which is concentrated in hydrochloric acid. Zinc chloride is used in this reagent as zinc chloride forms a complex with oxygen or alcohol and it converts the hydroxyl group to a better leaving group and helps in forming chloroalkane. Basically it converts the alcohols to the alkyl chlorides.This solution is used to classify alcohols of low molecular weight. This reaction is a replacement in which the chloride replaces a hydroxyl group during reaction. A positive test is shown by a change from clear and colorless to turbid color, signing formation of a chloroalkane. The best results for this test are detected in tertiary alcohols because they form their own alkyl halides fastest due to their higher stability of the intermediate tertiary carbocation. The test was stated in $1930$ and this became a standard method in organic chemistry. The test has now since become somewhat outdated with the availability of various spectroscopic and chromatographic methods of analysis. But the test was named after Howard Lucas.
Note: The different reactivity reflects the different way of formation of the corresponding carbocation’s. Tertiary carbocations are far more stable than secondary carbocations, and primary carbocations are the least stable (due to hyper conjugation).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




