
Lower carboxylic acid are soluble in water due to:
A: low molecular weight
B: hydrogen bonding
C: dissociation into ions
D: easy hydrolysis
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: Carboxylic acids are basically the derivatives of hydrocarbons in which carboxyl group \[\left( {C\left( { = O} \right)OH} \right)\] replaces one or more hydrogen atoms in the hydrocarbon. The general formula for a carboxylic acid molecule is \[R-COOH\], where R refers to an alkyl group.
Complete Step by step answer:
- Carboxylic acids are polar in nature due to the presence of hydroxyl groups. Carboxylic acids consist of the carboxyl group (\[COOH{\text{ }}or{\text{ }}C{O_2}H\]).
- The carboxyl group contains a carbonyl group (\[C = O\]) which is a hydrogen bond acceptor and a hydroxyl group (\[O--H\]) which is a hydrogen bond donor. Therefore like alcohols, in carboxylic acids also, the hydrogen bonds are formed owing to the existence of covalent bonds between oxygen atom and hydrogen atom in the hydroxyl group (\[O--H\]). Oxygen is highly electronegative and thus, attracts the electrons towards itself in \[O--H\] bonds.
- As the proton in the hydrogen atom nucleus slightly screens the action of the oxygen which pulls the electrons away from hydrogen, it results into a net positive charge over the hydrogen atom. As a result, there is a net negative charge on the oxygen atom which creates an imbalance of charge over the hydroxyl group. Thus, the overall hydroxyl group is considered to be polar as (similar to magnet) it possesses two opposite charges on each end.
- The net positive hydrogen atom can attract the negative electron clouds readily from the oxygen atom in a carbonyl group placed adjacent to it. Unlike Van der Waals’ forces, hydrogen bond involves a permanent imbalance of charges and hence, results in permanent dipole attractions.
- The diagram below demonstrates hydrogen bonding in carboxylic acid (ethanoic acid) molecules. Each ethanoic acid molecule is capable of forming double hydrogen bonded dimers.
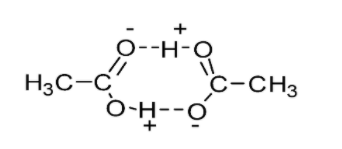
Hydrogen bonds are developed between the individual molecules of acid and the water molecules when carboxylic acid is added to water. These interactions make the carboxylic acids soluble in water. Lower carboxylic acids (up to four carbon atoms) are readily soluble in water due to hydrogen bonding.
Hence, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: Higher carboxylic acids are not readily soluble in water owing to increasing hydrophobicity of the alkyl chain. These longer chain acids would rather be soluble in less polar solvents like ethers or alcohols.
Complete Step by step answer:
- Carboxylic acids are polar in nature due to the presence of hydroxyl groups. Carboxylic acids consist of the carboxyl group (\[COOH{\text{ }}or{\text{ }}C{O_2}H\]).
- The carboxyl group contains a carbonyl group (\[C = O\]) which is a hydrogen bond acceptor and a hydroxyl group (\[O--H\]) which is a hydrogen bond donor. Therefore like alcohols, in carboxylic acids also, the hydrogen bonds are formed owing to the existence of covalent bonds between oxygen atom and hydrogen atom in the hydroxyl group (\[O--H\]). Oxygen is highly electronegative and thus, attracts the electrons towards itself in \[O--H\] bonds.
- As the proton in the hydrogen atom nucleus slightly screens the action of the oxygen which pulls the electrons away from hydrogen, it results into a net positive charge over the hydrogen atom. As a result, there is a net negative charge on the oxygen atom which creates an imbalance of charge over the hydroxyl group. Thus, the overall hydroxyl group is considered to be polar as (similar to magnet) it possesses two opposite charges on each end.
- The net positive hydrogen atom can attract the negative electron clouds readily from the oxygen atom in a carbonyl group placed adjacent to it. Unlike Van der Waals’ forces, hydrogen bond involves a permanent imbalance of charges and hence, results in permanent dipole attractions.
- The diagram below demonstrates hydrogen bonding in carboxylic acid (ethanoic acid) molecules. Each ethanoic acid molecule is capable of forming double hydrogen bonded dimers.

Hydrogen bonds are developed between the individual molecules of acid and the water molecules when carboxylic acid is added to water. These interactions make the carboxylic acids soluble in water. Lower carboxylic acids (up to four carbon atoms) are readily soluble in water due to hydrogen bonding.
Hence, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: Higher carboxylic acids are not readily soluble in water owing to increasing hydrophobicity of the alkyl chain. These longer chain acids would rather be soluble in less polar solvents like ethers or alcohols.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




