
Longest phase of meiosis is
a. Prophase l
b. Prophase II
c. Anaphase I
d. Metaphase II
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: Meiosis is the special type of cell division that occurs in the reproductive organs in order to produce the reproductive cells such as gametes or eggs, and the daughter cells which are formed in the meiosis contains only one set or haploid set of chromosomes.
Complete answer:
Meiosis occurs in two rounds, that is meiosis I and meiosis II.
Before Meiosis to start, there is a preparatory phase called interphase occurs and it contains G1, S, G2 phase, mostly G2 takes place only in the mitotic division, absent in meiosis, and after interphase meiosis I occurs and Later Meiosis II occurs.
Both phases of meiosis contain 4 stages where they also divided into I and II.
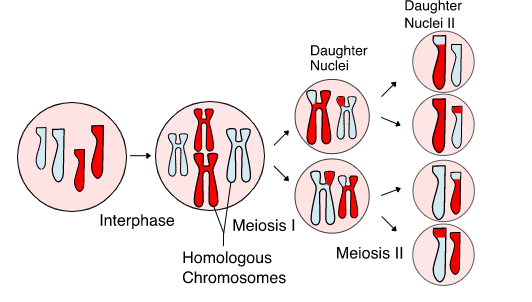
Meiosis I
> Prophase I: It is the longest phase in the meiosis, where it contains so many substages which includes,
Leptotene: In this phase, individual chromosomes, each consisting of 2 sister chromatids, become individuals that form the visible strands in the nucleus.
- Zygotene: Synapsis or pairing of homologous chromosomes takes place.
- Pachytene: In this stage chromosomal recombination/crossing over occurs and chiasmata formed in this stage.
- Diplotene: Uncoiling occurs except at the site of chiasmata.
- Diakinesis: Further condensation of Chromosomes occurs, this stage resembles the prometaphase of mitosis.
> Metaphase I: In this phase, the homologous chromosomes align along an equatorial plane, and kinetochore microtubules are formed, which form spindles at poles, which attached to respective kinetochore.
> Anaphase I: Pulling of the homologous chromosomes occurs by shortening of kinetochore microtubule, and cell elongation also takes place in this phase.
> Telophase I: First meiosis ends in this phase, where chromosomes arrive at the poles, each daughter cell has half the number of chromosomes to which the parent cells are formed.
After Meiosis I cells enter interkinesis, which is considered as a resting phase.
Then Meiosis II takes place where all phases occur similar to the Meiosis I, but it involves the equational segregation takes place, and forms haploid cells, and the meiosis completed.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Meiosis I is consider as reductional division because here diploid is reduced to haploid, whereas Meiosis II is an equatorial division, where it is similar like mitosis, by the end of meiosis finally 4 new haploid daughter cells are formed.
Complete answer:
Meiosis occurs in two rounds, that is meiosis I and meiosis II.
Before Meiosis to start, there is a preparatory phase called interphase occurs and it contains G1, S, G2 phase, mostly G2 takes place only in the mitotic division, absent in meiosis, and after interphase meiosis I occurs and Later Meiosis II occurs.
Both phases of meiosis contain 4 stages where they also divided into I and II.

Meiosis I
> Prophase I: It is the longest phase in the meiosis, where it contains so many substages which includes,
Leptotene: In this phase, individual chromosomes, each consisting of 2 sister chromatids, become individuals that form the visible strands in the nucleus.
- Zygotene: Synapsis or pairing of homologous chromosomes takes place.
- Pachytene: In this stage chromosomal recombination/crossing over occurs and chiasmata formed in this stage.
- Diplotene: Uncoiling occurs except at the site of chiasmata.
- Diakinesis: Further condensation of Chromosomes occurs, this stage resembles the prometaphase of mitosis.
> Metaphase I: In this phase, the homologous chromosomes align along an equatorial plane, and kinetochore microtubules are formed, which form spindles at poles, which attached to respective kinetochore.
> Anaphase I: Pulling of the homologous chromosomes occurs by shortening of kinetochore microtubule, and cell elongation also takes place in this phase.
> Telophase I: First meiosis ends in this phase, where chromosomes arrive at the poles, each daughter cell has half the number of chromosomes to which the parent cells are formed.
After Meiosis I cells enter interkinesis, which is considered as a resting phase.
Then Meiosis II takes place where all phases occur similar to the Meiosis I, but it involves the equational segregation takes place, and forms haploid cells, and the meiosis completed.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Meiosis I is consider as reductional division because here diploid is reduced to haploid, whereas Meiosis II is an equatorial division, where it is similar like mitosis, by the end of meiosis finally 4 new haploid daughter cells are formed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




