
How long are infrared waves compared with waves of visible light?
Answer
538.2k+ views
Hint: The distance between two successive crests of a wave, or the distance between two successive troughs of a wave is known as wavelength. It is denoted by $\lambda $. Visible light waves and infrared rays are electromagnetic in nature.
Complete answer:
We know that the transverse waves which are created because of synchronized oscillations or vibrations between a magnetic field and the electric field are known as electromagnetic waves, also called EM waves. The EM waves travel through a speed of light in vacuum. EM waves can be refracted as well as reflected, and they also are carriers and transporters of energy.
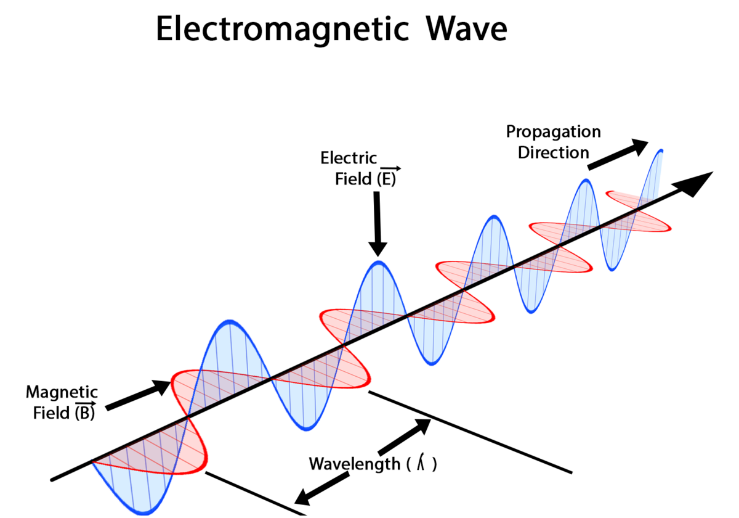
Now, the range of all the types of EM radiations is known as the electromagnetic spectrum. The two factors which decide the position of the EM wave on the electromagnetic spectrum are
1. Wavelength
2. Frequency of oscillations
The frequency of the waves in the electromagnetic spectrum ranges from below one hertz to above ${{10}^{25}}$ hertz. And hence the wavelength ranges from fraction of the size of the atomic nucleus to thousands of kilometers.
The electromagnetic spectrum is divided into different frequency bands and each frequency band has a different name. This is because different frequency bands have different sources and also, they differ in how they affect matter.
The order of the bands in the electromagnetic spectrum in decreasing order of wavelength or increasing order of frequency are
1. Radio waves
2. Microwaves
3. Infrared radiation
4. Visible light
5. Ultraviolet radiation
6. X-rays
7. Gamma rays
We know that the wavelength of infrared waves ranges from 700 nm to 1mm. The wavelength of visible light ranges from 400 nm to 700 nm.
So, infrared waves are longer than visible light waves by 0.0004 mm or ${{10}^{-4}}$m.
Note:
The relation between wavelength and frequency, in vacuum, can be defined by the
\[\lambda v=c\]
Where v is the frequency, $\lambda $ is the wavelength and c is the speed of light.
From this formula we can see that frequency and wavelength are inversely proportional. That means that when there is an increase in wavelength, the frequency decreases.
Complete answer:
We know that the transverse waves which are created because of synchronized oscillations or vibrations between a magnetic field and the electric field are known as electromagnetic waves, also called EM waves. The EM waves travel through a speed of light in vacuum. EM waves can be refracted as well as reflected, and they also are carriers and transporters of energy.

Now, the range of all the types of EM radiations is known as the electromagnetic spectrum. The two factors which decide the position of the EM wave on the electromagnetic spectrum are
1. Wavelength
2. Frequency of oscillations
The frequency of the waves in the electromagnetic spectrum ranges from below one hertz to above ${{10}^{25}}$ hertz. And hence the wavelength ranges from fraction of the size of the atomic nucleus to thousands of kilometers.
The electromagnetic spectrum is divided into different frequency bands and each frequency band has a different name. This is because different frequency bands have different sources and also, they differ in how they affect matter.
The order of the bands in the electromagnetic spectrum in decreasing order of wavelength or increasing order of frequency are
1. Radio waves
2. Microwaves
3. Infrared radiation
4. Visible light
5. Ultraviolet radiation
6. X-rays
7. Gamma rays
We know that the wavelength of infrared waves ranges from 700 nm to 1mm. The wavelength of visible light ranges from 400 nm to 700 nm.
So, infrared waves are longer than visible light waves by 0.0004 mm or ${{10}^{-4}}$m.
Note:
The relation between wavelength and frequency, in vacuum, can be defined by the
\[\lambda v=c\]
Where v is the frequency, $\lambda $ is the wavelength and c is the speed of light.
From this formula we can see that frequency and wavelength are inversely proportional. That means that when there is an increase in wavelength, the frequency decreases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




