
List out the salient features of double helix structure of DNA.
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: The definition of the structure of a DNA molecule is the double helix. A DNA molecule is composed of two strands that wind like a twisted ladder around each other.
Complete Answer:
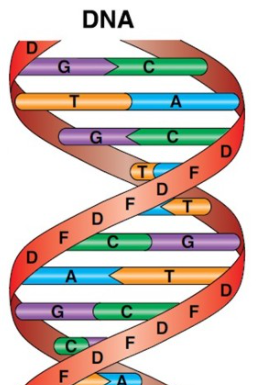
The backbone of each strand is composed of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) groups and phosphate groups.. One of four bases is added to each sugar: adenine (A), cytosine ( C), guanine ( G), or thymine ( T). Bonds between the bases, adenine forming a base pair with thymine and cytosine forming a base pair with guanine, hold the two strands together.
DNA's double helix has these characteristics:
- It comprises two strands of polynucleotides wrapped around one another.
- Each backbone consists of alternating groups of deoxyribose and phosphate.
- The phosphate group bonded to one deoxyribose 's 5 'carbon atom is bonded to the next 's 3' carbon covalently. The "antiparallel" are the two strands; that is, one strand runs 5' to 3' while the other runs 3' to 5'.
- The DNA strands are assembled in the direction of 5 "to 3" [More] and we "read" them the same way by convention.
- The purine or pyrimidine that is attached to each deoxyribose projects towards the helix axis. Each base forms hydrogen bonds, which form base pairs (also called nucleotide pairs) with the one immediately opposite it.
- The planes in which neighbouring base pairs are located are divided by 3.4 Å. In just over 10 nucleotide pairs, the double helix makes a complete turn, so each turn takes just a little more (35.7 Å to be exact) than the 34 Å.
- Inside each complete turn of the double helix, there are an average of 25 hydrogen bonds offering a binding stability almost as strong as what a covalent bond can provide. The helix 's diameter is 20 Å.
- The helix can be nearly any length; when fully extended, some DNA molecules are as much as 5 cm (2 inches) long. A major (wider) groove (from "34 A" to the top of the arrow) and a minor (narrower) groove (the one below) form the direction taken by the two backbones.
Note: Francis Crick and James D. Watson figured out this structure of DNA in 1953. It showed how DNA could be repeated and thus passed on from generation to generation, the molecule that Avery had shown to be the physical material of the genes.For this momentous work, they shared a Nobel Prize in 1962.
Complete Answer:
The backbone of each strand is composed of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) groups and phosphate groups.. One of four bases is added to each sugar: adenine (A), cytosine ( C), guanine ( G), or thymine ( T). Bonds between the bases, adenine forming a base pair with thymine and cytosine forming a base pair with guanine, hold the two strands together.
DNA's double helix has these characteristics:
- It comprises two strands of polynucleotides wrapped around one another.
- Each backbone consists of alternating groups of deoxyribose and phosphate.
- The phosphate group bonded to one deoxyribose 's 5 'carbon atom is bonded to the next 's 3' carbon covalently. The "antiparallel" are the two strands; that is, one strand runs 5' to 3' while the other runs 3' to 5'.
- The DNA strands are assembled in the direction of 5 "to 3" [More] and we "read" them the same way by convention.
- The purine or pyrimidine that is attached to each deoxyribose projects towards the helix axis. Each base forms hydrogen bonds, which form base pairs (also called nucleotide pairs) with the one immediately opposite it.
- The planes in which neighbouring base pairs are located are divided by 3.4 Å. In just over 10 nucleotide pairs, the double helix makes a complete turn, so each turn takes just a little more (35.7 Å to be exact) than the 34 Å.
- Inside each complete turn of the double helix, there are an average of 25 hydrogen bonds offering a binding stability almost as strong as what a covalent bond can provide. The helix 's diameter is 20 Å.
- The helix can be nearly any length; when fully extended, some DNA molecules are as much as 5 cm (2 inches) long. A major (wider) groove (from "34 A" to the top of the arrow) and a minor (narrower) groove (the one below) form the direction taken by the two backbones.

Note: Francis Crick and James D. Watson figured out this structure of DNA in 1953. It showed how DNA could be repeated and thus passed on from generation to generation, the molecule that Avery had shown to be the physical material of the genes.For this momentous work, they shared a Nobel Prize in 1962.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




