
What is the limit as x approaches infinity of $\dfrac{1}{x}$?
Answer
529.5k+ views
Hint: Here we will use the graphical method to determine the value of the limit. Assume the required limit as L. Now, to find the value of \[\displaystyle \lim_{x \to \infty }\left( \dfrac{1}{x} \right)\], first draw the graph of the rectangular hyperbola $\dfrac{1}{x}$. Check the value of function as x tends to infinity. If this value is a finite number then that will be our answer.
Complete step by step answer:
Here we have been asked to find the limit of the function $\dfrac{1}{x}$ as the domain value, i.e. x, tends to infinity. Let us assume the limit value as L so mathematically we have,
\[\Rightarrow L=\displaystyle \lim_{x \to \infty }\left( \dfrac{1}{x} \right)\]
Now, let us find the limit value of the function using the graphical method. We can clearly see that the given function is an equation of a rectangular hyperbola. So, the graph of the rectangular hyperbola \[f\left( x \right)=\dfrac{1}{x}\] can be shown as: -
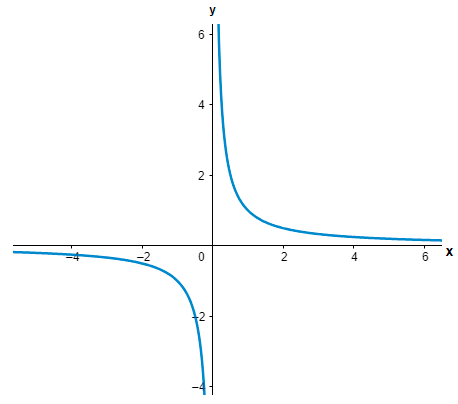
From the above graph we can see that as x tends to infinity, the value of the function tends to 0. So we have,
\[\Rightarrow L=\left( \dfrac{1}{\infty } \right)=0\]
Clearly 0 is a finite number, hence we can conclude that the limit of the given function is equal to 0.
Note: You must remember the graph of the rectangular hyperbola to solve the above question. Remember that infinity is not a real number so the value of x cannot be infinity exactly but only tends to infinity. Note that the function is not continuous at x = 0. In addition, also remember the graph of the functions like: $\ln x$, ${{e}^{x}}$, trigonometric and inverse trigonometric functions.
Complete step by step answer:
Here we have been asked to find the limit of the function $\dfrac{1}{x}$ as the domain value, i.e. x, tends to infinity. Let us assume the limit value as L so mathematically we have,
\[\Rightarrow L=\displaystyle \lim_{x \to \infty }\left( \dfrac{1}{x} \right)\]
Now, let us find the limit value of the function using the graphical method. We can clearly see that the given function is an equation of a rectangular hyperbola. So, the graph of the rectangular hyperbola \[f\left( x \right)=\dfrac{1}{x}\] can be shown as: -

From the above graph we can see that as x tends to infinity, the value of the function tends to 0. So we have,
\[\Rightarrow L=\left( \dfrac{1}{\infty } \right)=0\]
Clearly 0 is a finite number, hence we can conclude that the limit of the given function is equal to 0.
Note: You must remember the graph of the rectangular hyperbola to solve the above question. Remember that infinity is not a real number so the value of x cannot be infinity exactly but only tends to infinity. Note that the function is not continuous at x = 0. In addition, also remember the graph of the functions like: $\ln x$, ${{e}^{x}}$, trigonometric and inverse trigonometric functions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




