
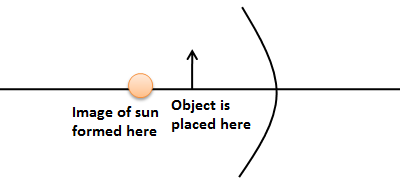
Light from the sun strikes the concave mirror pictured below. The image of the sun is formed at the point indicated.
When we place an object closer to the mirror than this point, what are the characteristics of the image formed (Size is compared to object)?
A. Larger, real, inverted
B. Smaller, real, inverted
C. Smaller, virtual, upright
D. Larger, virtual, upright

Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: The concave mirror forms both type of images: real image and virtual image. The real image forms when it is formed on the same side of the concave mirror. Draw the ray diagram of the concave mirror when the object is placed closer to the mirror. From the ray diagram, identify the magnification of the image.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the concave mirror forms both types of images: real image and virtual image. Since the rays reflected from the inner surface of the concave mirror converge at the point indicated in the figure, the point must be the focus of the mirror.
Now, we have given that the object is placed between this point and the plane of the mirror. We know that when we place the object between the focus and plane of the concave mirror, the image of the object forms behind the concave mirror. Let’s draw the ray diagram for this situation as shown in the figure below.
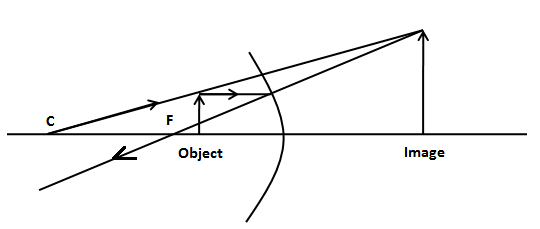
Thus, in the above figure, we can see that the image is formed above the principle axis. We know that the image formed above the principal axis is referred to as an erect or upright image. Also, this image is not formed by the converging of rays reflected from the mirror rather it is formed by back tracing the reflected ray. Therefore, the image is a virtual image. In the above ray diagram, we can see that the image is larger than the object.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
If the object is placed at the left of the focus, the image of the object will form on the same side of the mirror. This image is known as a real image since it is formed by focusing the reflected rays from the mirror. To answer these types of questions, students should know the properties of the spherical mirrors.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the concave mirror forms both types of images: real image and virtual image. Since the rays reflected from the inner surface of the concave mirror converge at the point indicated in the figure, the point must be the focus of the mirror.
Now, we have given that the object is placed between this point and the plane of the mirror. We know that when we place the object between the focus and plane of the concave mirror, the image of the object forms behind the concave mirror. Let’s draw the ray diagram for this situation as shown in the figure below.

Thus, in the above figure, we can see that the image is formed above the principle axis. We know that the image formed above the principal axis is referred to as an erect or upright image. Also, this image is not formed by the converging of rays reflected from the mirror rather it is formed by back tracing the reflected ray. Therefore, the image is a virtual image. In the above ray diagram, we can see that the image is larger than the object.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
If the object is placed at the left of the focus, the image of the object will form on the same side of the mirror. This image is known as a real image since it is formed by focusing the reflected rays from the mirror. To answer these types of questions, students should know the properties of the spherical mirrors.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE




