
What is the Lewis dot structure of $B{{H}_{3}}$? How many lone pair electrons are in this molecule? How many bonding pairs of electrons are in this molecule? How many lone pairs electrons are at the central atom?
Answer
562.8k+ views
Hint: The Lewis dot structure is also known as the electron dot structure. To answer this question we should be aware of the concept of Lewis dot structure. This concept was the basis of VSEPR theory too.
Complete answer:
Lewis dot structure is a representation of the arrangement of electrons around each atom of a compound or a molecule. This is why it is also known as electron dot structure.
Firstly, let's write the number of valence electron in boron and fluorine:
Boron = 5 = $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{1}}$
Hydrogen = 1 = $1{{s}^{1}}$
The number of valence electrons in B + the number of valence electron in 1$\times $3
3 + 1 $\times $ 3
3 + 3
6
The boron is more electronegative than hydrogen. So, the boron is the central atom.
Now let's draw the $B{{H}_{3}}$.
The boron has three valence electrons and the hydrogen has only one valence electron around it.
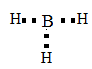
Then, join the electron and make bonds.
According to electron dot structure the arrangement of electrons around each atom of a compound or a molecule should be shown.
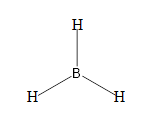
From the above discussion we can say that there are no lone pairs in the molecule and on the central atom. The number of bonding pairs are 3.
Note: There are six valence electrons that are engulfed in bonding. So half of it is three. There is no lone pair as there are no unpaired electrons. Lewis dot structure too has many limitations but certain limitations are overcome by VSEPR theory. The Lewis dot structure was a stepping stone for VSEPR theory.
Complete answer:
Lewis dot structure is a representation of the arrangement of electrons around each atom of a compound or a molecule. This is why it is also known as electron dot structure.
Firstly, let's write the number of valence electron in boron and fluorine:
Boron = 5 = $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{1}}$
Hydrogen = 1 = $1{{s}^{1}}$
The number of valence electrons in B + the number of valence electron in 1$\times $3
3 + 1 $\times $ 3
3 + 3
6
The boron is more electronegative than hydrogen. So, the boron is the central atom.
Now let's draw the $B{{H}_{3}}$.
The boron has three valence electrons and the hydrogen has only one valence electron around it.
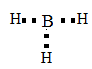
Then, join the electron and make bonds.

According to electron dot structure the arrangement of electrons around each atom of a compound or a molecule should be shown.
From the above discussion we can say that there are no lone pairs in the molecule and on the central atom. The number of bonding pairs are 3.
Note: There are six valence electrons that are engulfed in bonding. So half of it is three. There is no lone pair as there are no unpaired electrons. Lewis dot structure too has many limitations but certain limitations are overcome by VSEPR theory. The Lewis dot structure was a stepping stone for VSEPR theory.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




