
Let us assume the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of earth is $10m{{s}^{-2}}$ and at the surface of mars it is $4.0m{{s}^{-2}}$. A $60kg$ passenger comes from the Earth to Mars in a spaceship which is moving with a fixed velocity. Let us neglect all other bodies in the sky. Which part of the diagram best indicates the weight that is the resultant gravitational force, of the passenger as a function of time?
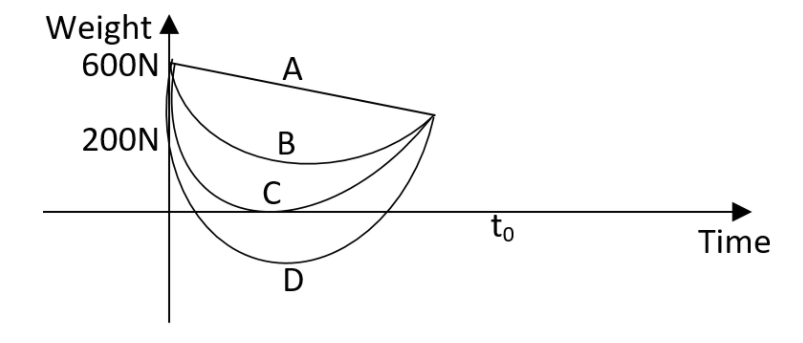
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D

Answer
575.4k+ views
Hint: The acceleration due to gravity is found by taking the ratio of the product of the gravitational constant and the mass of the earth to the square of the radius of the earth. As the gravitational constant and mass of the earth is a constant, the square of the radius will be inversely proportional to the acceleration due to gravity. This all will help you in answering this question.
Complete step by step answer:
The acceleration due to gravity is found by taking the ratio of the product of the gravitational constant and the mass of the earth to the square of the radius of the earth. This can be written as,
$g=\dfrac{GM}{{{R}^{2}}}$
Where $G$be gravitational constant, $M$ be the mass of the earth and $R$ be the radius of earth. From this we can say that,
$g\propto \dfrac{1}{{{R}^{2}}}$
This means that the graph will not be a straight line. The graph will be a curve. And also at the point where force due to Earth which is equivalent to the force due to Mars. Therefore at that point,
$F=0$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Gravitational acceleration is defined as the free fall acceleration of a body in vacuum without any force. This will be the constant gain in speed because of the force of gravitational attraction. The acceleration due to gravity will be a vector quantity depending on the magnitude as well as direction.
Complete step by step answer:
The acceleration due to gravity is found by taking the ratio of the product of the gravitational constant and the mass of the earth to the square of the radius of the earth. This can be written as,
$g=\dfrac{GM}{{{R}^{2}}}$
Where $G$be gravitational constant, $M$ be the mass of the earth and $R$ be the radius of earth. From this we can say that,
$g\propto \dfrac{1}{{{R}^{2}}}$
This means that the graph will not be a straight line. The graph will be a curve. And also at the point where force due to Earth which is equivalent to the force due to Mars. Therefore at that point,
$F=0$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Gravitational acceleration is defined as the free fall acceleration of a body in vacuum without any force. This will be the constant gain in speed because of the force of gravitational attraction. The acceleration due to gravity will be a vector quantity depending on the magnitude as well as direction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




