
Let us assume that you make a plot on log-log paper of ${{V}_{rms}}$ versus $T$ for an ideal gas. (Alternatively, you could plot in ${{V}_{rms}}$ versus $\ln T$ on ordinary graph paper). Represent that the plot is a straight line having slope $\dfrac{1}{2}$.
Answer
575.1k+ views
Hint: The rms velocity is found by taking the square root of the ratio of the thrice of the product of the universal gas constant and temperature to the mass of the gas. Take a log on both the sides and find the slope of the graph. This will help you in solving this question.
Complete step by step answer:
As we already know that the rms velocity is found by taking the square root of the ratio of the thrice of the product of the universal gas constant and temperature to the mass of the gas. This can be written as,
\[{{V}_{rms}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{3RT}{M}}\]
Do the log function on both the sides of the equation,
\[{{\log }_{e}}\left( {{V}_{rms}} \right)={{\log }_{e}}\left( \sqrt{\dfrac{3RT}{M}} \right)\]
This can be written as the sum like,
\[{{\log }_{e}}\left( {{V}_{rms}} \right)={{\log }_{e}}\left( \sqrt{T} \right)+{{\log }_{e}}\left( \sqrt{\dfrac{3R}{M}} \right)\]
The last term is a constant as all the terms in it are constant. Therefore we can write that,
\[{{\log }_{e}}\left( {{V}_{rms}} \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}{{\log }_{e}}\left({T} \right)+C\]
The general equation of the straight line graph can be shown as,
\[Y=mX+C\]
We can compare the both equations. Therefore we can find that,
\[\begin{align}
& \text{intercept}\to \text{C} \\
& \text{slope}=m\text{ }=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
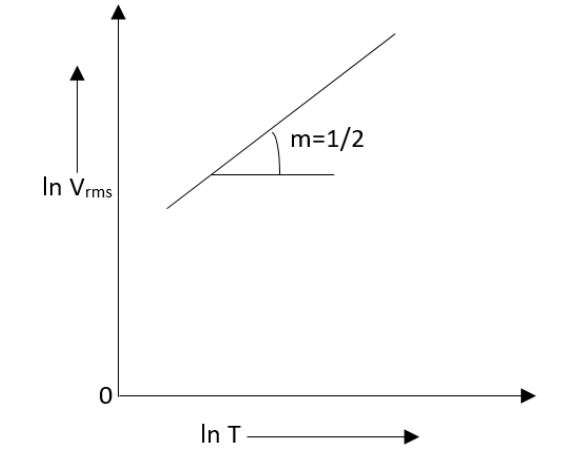
Therefore the graph will be a straight line with the slope mentioned as \[\dfrac{1}{2}\].
Hence the answer has been obtained.
Note: The rms velocity is the abbreviation of the root mean square velocity. It is defined as the square root of the mean of the square of the velocity. This velocity will be having the same units of velocity. This rms velocity has been used generally instead of the average velocity is that for a particular gas sample the resultant velocity is zero as the particles are moving in every direction.
Complete step by step answer:
As we already know that the rms velocity is found by taking the square root of the ratio of the thrice of the product of the universal gas constant and temperature to the mass of the gas. This can be written as,
\[{{V}_{rms}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{3RT}{M}}\]
Do the log function on both the sides of the equation,
\[{{\log }_{e}}\left( {{V}_{rms}} \right)={{\log }_{e}}\left( \sqrt{\dfrac{3RT}{M}} \right)\]
This can be written as the sum like,
\[{{\log }_{e}}\left( {{V}_{rms}} \right)={{\log }_{e}}\left( \sqrt{T} \right)+{{\log }_{e}}\left( \sqrt{\dfrac{3R}{M}} \right)\]
The last term is a constant as all the terms in it are constant. Therefore we can write that,
\[{{\log }_{e}}\left( {{V}_{rms}} \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}{{\log }_{e}}\left({T} \right)+C\]
The general equation of the straight line graph can be shown as,
\[Y=mX+C\]
We can compare the both equations. Therefore we can find that,
\[\begin{align}
& \text{intercept}\to \text{C} \\
& \text{slope}=m\text{ }=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
\end{align}\]

Therefore the graph will be a straight line with the slope mentioned as \[\dfrac{1}{2}\].
Hence the answer has been obtained.
Note: The rms velocity is the abbreviation of the root mean square velocity. It is defined as the square root of the mean of the square of the velocity. This velocity will be having the same units of velocity. This rms velocity has been used generally instead of the average velocity is that for a particular gas sample the resultant velocity is zero as the particles are moving in every direction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




