
Let us assume that a particle of mass $2m$ is being projected at an angle of \[45{}^\circ \] with horizontal velocity of \[20\sqrt{2}m{{s}^{-1}}\]. After \[1s\], an explosion takes place and the particle is cracked into two equal pieces. Because of the explosion one part will come to rest. What will be the maximum height reached by the other part. Take \[g=10m{{s}^{-2}}\],
\[\begin{align}
& A.50m \\
& B.25m \\
& C.40m \\
& D.35m \\
\end{align}\]
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: Find the height moved by the particle in one second. Find the velocity of the particle after one second and the angle with the horizontal is to be calculated. The initial and final velocities of the particle is to be found. And the final height will be found by the equation of maximum height. Total height will be the sum of both the heights.
Complete step by step solution:
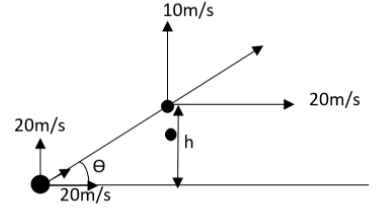
The height moved by the particle in \[1s\]can be found by the equation,
\[h=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}g{{t}^{2}}\]
As mentioned in the question,
The initial velocity can be shown as,
\[u=20m{{s}^{-1}}\]
The time taken will be written as,
\[t=1s\]
And the acceleration due to gravity will be,
\[g=10m{{s}^{-2}}\]
Substituting the values in it will give,
\[h=20\times 1+\dfrac{1}{2}\times 10\times {{1}^{2}}=15m\]
After one second, the vertical speed will become \[v\]. Let us perform newton’s first equation of motion.
That is,
\[v-u=-gt\]
Substituting the values in it,
\[\begin{align}
& v-20=-10\times 1 \\
& v=10m{{s}^{-1}} \\
\end{align}\]
The angle \[\theta \] at a height \[h\] with the horizontal can be written as,
\[\begin{align}
& \tan \theta =\dfrac{10}{20}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
& \sin \theta =\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}} \\
\end{align}\]
Before the explosion, the velocity of the particle will be,
\[{{v}_{e}}=\sqrt{{{10}^{2}}+{{20}^{2}}}=\sqrt{500}=10\sqrt{5}\]
And after the explosion the mass of the particle becomes half of the original value.
Therefore in accordance with conservation of momentum, the velocity will become twice. That is,
\[{{v}_{e}}^{\prime }=20\sqrt{5}\]
The height travelled after explosion will be found as,
\[{h}'=\dfrac{{{\left( {{v}_{e}}^{\prime } \right)}^{2}}{{\sin }^{2}}\theta }{2g}\]
Substituting the values in it will give,
\[{h}'=\dfrac{{{\left( 20\sqrt{5} \right)}^{2}}\times \dfrac{1}{5}}{2\times 10}=20cm\]
Hence the total height will be the sum of both the heights.
That is,
\[H=20+15=35cm\]
The answer has been mentioned as option D.
Note:
The conservation law of momentum says that the total momentum of a body before and after a collision will be similar. The initial momentum of the body before the collision will be the same as the final momentum of the body after the collision. Momentum is a vector quantity having both direction as well as magnitude.
Complete step by step solution:

The height moved by the particle in \[1s\]can be found by the equation,
\[h=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}g{{t}^{2}}\]
As mentioned in the question,
The initial velocity can be shown as,
\[u=20m{{s}^{-1}}\]
The time taken will be written as,
\[t=1s\]
And the acceleration due to gravity will be,
\[g=10m{{s}^{-2}}\]
Substituting the values in it will give,
\[h=20\times 1+\dfrac{1}{2}\times 10\times {{1}^{2}}=15m\]
After one second, the vertical speed will become \[v\]. Let us perform newton’s first equation of motion.
That is,
\[v-u=-gt\]
Substituting the values in it,
\[\begin{align}
& v-20=-10\times 1 \\
& v=10m{{s}^{-1}} \\
\end{align}\]
The angle \[\theta \] at a height \[h\] with the horizontal can be written as,
\[\begin{align}
& \tan \theta =\dfrac{10}{20}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
& \sin \theta =\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}} \\
\end{align}\]
Before the explosion, the velocity of the particle will be,
\[{{v}_{e}}=\sqrt{{{10}^{2}}+{{20}^{2}}}=\sqrt{500}=10\sqrt{5}\]
And after the explosion the mass of the particle becomes half of the original value.
Therefore in accordance with conservation of momentum, the velocity will become twice. That is,
\[{{v}_{e}}^{\prime }=20\sqrt{5}\]
The height travelled after explosion will be found as,
\[{h}'=\dfrac{{{\left( {{v}_{e}}^{\prime } \right)}^{2}}{{\sin }^{2}}\theta }{2g}\]
Substituting the values in it will give,
\[{h}'=\dfrac{{{\left( 20\sqrt{5} \right)}^{2}}\times \dfrac{1}{5}}{2\times 10}=20cm\]
Hence the total height will be the sum of both the heights.
That is,
\[H=20+15=35cm\]
The answer has been mentioned as option D.
Note:
The conservation law of momentum says that the total momentum of a body before and after a collision will be similar. The initial momentum of the body before the collision will be the same as the final momentum of the body after the collision. Momentum is a vector quantity having both direction as well as magnitude.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




