
Let three points A (2, 3, 4) B (3, 4, 2) and C (4, 2, 3) in space are given. A point D in space is such that it is at a distance of $\sqrt 6 $ units from 3 given points. Then volume of tetrahedron ABCD is:
A) 1
B) $\sqrt 3 $
C) $\sqrt {13} $
D) 2
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: Given the point D is equidistant from all points A, B and C. So the distance AD=BD=CD=$\sqrt 6 $units. So using this find the coordinates of D. To calculate the volume of tetrahedron find the absolute value of the triple product and divide it by 6.
Complete step-by-step answer:
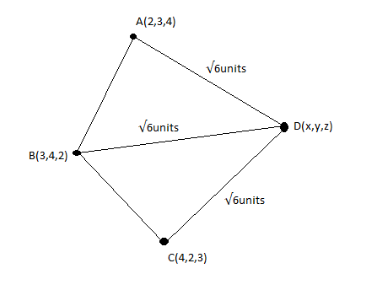
We are given that three points A (2, 3, 4) B (3, 4, 2) and C (4, 2, 3) are in space and a point D in space is equidistant from A, B, C and the distance between D and these three points is $\sqrt 6 $units.
Therefore, AD=BD=CD=$\sqrt 6 $units.
Distance between two points with three coordinates x, y, z is $\sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{z_2} - {z_1}} \right)}^2}} $
Let the coordinates of D be (x, y, z)
AD=BD
$\sqrt {{{\left( {2 - x} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {3 - y} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {4 - z} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {{{\left( {3 - x} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {4 - y} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {2 - z} \right)}^2}} $
Cancel the square root on both sides.
$
{\left( {2 - x} \right)^2} + {\left( {3 - y} \right)^2} + {\left( {4 - z} \right)^2} = {\left( {3 - x} \right)^2} + {\left( {4 - y} \right)^2} + {\left( {2 - z} \right)^2} \\
4 - 4x + {x^2} + 9 - 6y + {y^2} + 16 - 8z + {z^2} = 9 - 6x + {x^2} + 16 - 8y + {y^2} + 4 - 4z + {z^2} \\
- 4x - 6y - 8z = - 6x - 8y - 4z \\
4x + 6y + 8z = 6x + 8y + 4z \\
2x + 3y + 4z = 3x + 4y + 2z \\
x + y = 2z \\
$
BD=CD
$\sqrt {{{\left( {3 - x} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {4 - y} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {2 - z} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {{{\left( {4 - x} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {2 - y} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {3 - z} \right)}^2}} $
Cancel the square root on both sides.
$
{\left( {3 - x} \right)^2} + {\left( {4 - y} \right)^2} + {\left( {2 - z} \right)^2} = {\left( {4 - x} \right)^2} + {\left( {2 - y} \right)^2} + {\left( {3 - z} \right)^2} \\
9 - 6x + {x^2} + 16 - 8y + {y^2} + 4 - 4z + {z^2} = 16 - 8x + {x^2} + 4 - 4y + {y^2} + 9 - 6z + {z^2} \\
- 6x - 8y - 4z = - 8x - 4y - 6z \\
6x + 8y + 4z = 8x + 4y + 6z \\
3x + 4y + 2z = 4x + 2y + 3z \\
x + z = 2y \\
$
AD=CD
$\sqrt {{{\left( {2 - x} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {3 - y} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {4 - z} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {{{\left( {4 - x} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {2 - y} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {3 - z} \right)}^2}} $
Cancel the square root on both sides.
\[
{\left( {2 - x} \right)^2} + {\left( {3 - y} \right)^2} + {\left( {4 - z} \right)^2} = {\left( {4 - x} \right)^2} + {\left( {2 - y} \right)^2} + {\left( {3 - z} \right)^2} \\
4 - 4x + {x^2} + 9 - 6y + {y^2} + 16 - 8z + {z^2} = 16 - 8x + {x^2} + 4 - 4y + {y^2} + 9 - 6z + {z^2} \\
- 4x - 6y - 8z = - 8x - 4y - 6z \\
4x + 6y + 8z = 8x + 4y + 6z \\
2x + 3y + 4z = 4x + 2y + 3z \\
y + z = 2y \\
\]
$
x + y = 2z \\
x + z = 2y \\
y + z = 2x \\
$
Solving the above equations we get D(x, y, z) = (2, 2, 2)
A(2, 3, 4), B(3, 4, 2), C(4, 2, 3), D(2, 2, 2) form a tetrahedron.
Volume of tetrahedron ABCD is \[\dfrac{1}{6}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{u_1}}&{{u_2}}&{{u_3}} \\
{{v_1}}&{{v_2}}&{{v_3}} \\
{{w_1}}&{{w_2}}&{{w_3}}
\end{array}} \right|\]
\[
\left( {{u_1},{u_2},{u_3}} \right) = \left( {1,1, - 2} \right) \\
\left( {{v_1},{v_2},{v_3}} \right) = \left( {2, - 1, - 1} \right) \\
\left( {{w_1},{w_2},{w_3}} \right) = \left( {0, - 1, - 2} \right) \\
\]
Volume of the tetrahedron is \[\dfrac{1}{6}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{u_1}}&{{u_2}}&{{u_3}} \\
{{v_1}}&{{v_2}}&{{v_3}} \\
{{w_1}}&{{w_2}}&{{w_3}}
\end{array}} \right|\]
\[
= \dfrac{1}{6}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
1&1&{ - 2} \\
2&{ - 1}&{ - 1} \\
0&{ - 1}&{ - 2}
\end{array}} \right| \\
= \dfrac{1}{6}\left[ {1 - \left( { - 4} \right) - 2\left( { - 2} \right)} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{6}\left( {4 + 4 + 4} \right) \\
= \dfrac{{12}}{6} = 2 \\
\]
Volume of the tetrahedron is 2 cube units, Option D is correct.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: In geometry, a tetrahedron also known as a triangular pyramid is a polyhedron with four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertices. Prism and Pyramids of Egypt are examples of tetrahedrons.
Complete step-by-step answer:

We are given that three points A (2, 3, 4) B (3, 4, 2) and C (4, 2, 3) are in space and a point D in space is equidistant from A, B, C and the distance between D and these three points is $\sqrt 6 $units.
Therefore, AD=BD=CD=$\sqrt 6 $units.
Distance between two points with three coordinates x, y, z is $\sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{z_2} - {z_1}} \right)}^2}} $
Let the coordinates of D be (x, y, z)
AD=BD
$\sqrt {{{\left( {2 - x} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {3 - y} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {4 - z} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {{{\left( {3 - x} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {4 - y} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {2 - z} \right)}^2}} $
Cancel the square root on both sides.
$
{\left( {2 - x} \right)^2} + {\left( {3 - y} \right)^2} + {\left( {4 - z} \right)^2} = {\left( {3 - x} \right)^2} + {\left( {4 - y} \right)^2} + {\left( {2 - z} \right)^2} \\
4 - 4x + {x^2} + 9 - 6y + {y^2} + 16 - 8z + {z^2} = 9 - 6x + {x^2} + 16 - 8y + {y^2} + 4 - 4z + {z^2} \\
- 4x - 6y - 8z = - 6x - 8y - 4z \\
4x + 6y + 8z = 6x + 8y + 4z \\
2x + 3y + 4z = 3x + 4y + 2z \\
x + y = 2z \\
$
BD=CD
$\sqrt {{{\left( {3 - x} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {4 - y} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {2 - z} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {{{\left( {4 - x} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {2 - y} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {3 - z} \right)}^2}} $
Cancel the square root on both sides.
$
{\left( {3 - x} \right)^2} + {\left( {4 - y} \right)^2} + {\left( {2 - z} \right)^2} = {\left( {4 - x} \right)^2} + {\left( {2 - y} \right)^2} + {\left( {3 - z} \right)^2} \\
9 - 6x + {x^2} + 16 - 8y + {y^2} + 4 - 4z + {z^2} = 16 - 8x + {x^2} + 4 - 4y + {y^2} + 9 - 6z + {z^2} \\
- 6x - 8y - 4z = - 8x - 4y - 6z \\
6x + 8y + 4z = 8x + 4y + 6z \\
3x + 4y + 2z = 4x + 2y + 3z \\
x + z = 2y \\
$
AD=CD
$\sqrt {{{\left( {2 - x} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {3 - y} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {4 - z} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {{{\left( {4 - x} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {2 - y} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {3 - z} \right)}^2}} $
Cancel the square root on both sides.
\[
{\left( {2 - x} \right)^2} + {\left( {3 - y} \right)^2} + {\left( {4 - z} \right)^2} = {\left( {4 - x} \right)^2} + {\left( {2 - y} \right)^2} + {\left( {3 - z} \right)^2} \\
4 - 4x + {x^2} + 9 - 6y + {y^2} + 16 - 8z + {z^2} = 16 - 8x + {x^2} + 4 - 4y + {y^2} + 9 - 6z + {z^2} \\
- 4x - 6y - 8z = - 8x - 4y - 6z \\
4x + 6y + 8z = 8x + 4y + 6z \\
2x + 3y + 4z = 4x + 2y + 3z \\
y + z = 2y \\
\]
$
x + y = 2z \\
x + z = 2y \\
y + z = 2x \\
$
Solving the above equations we get D(x, y, z) = (2, 2, 2)
A(2, 3, 4), B(3, 4, 2), C(4, 2, 3), D(2, 2, 2) form a tetrahedron.
Volume of tetrahedron ABCD is \[\dfrac{1}{6}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{u_1}}&{{u_2}}&{{u_3}} \\
{{v_1}}&{{v_2}}&{{v_3}} \\
{{w_1}}&{{w_2}}&{{w_3}}
\end{array}} \right|\]
\[
\left( {{u_1},{u_2},{u_3}} \right) = \left( {1,1, - 2} \right) \\
\left( {{v_1},{v_2},{v_3}} \right) = \left( {2, - 1, - 1} \right) \\
\left( {{w_1},{w_2},{w_3}} \right) = \left( {0, - 1, - 2} \right) \\
\]
Volume of the tetrahedron is \[\dfrac{1}{6}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{u_1}}&{{u_2}}&{{u_3}} \\
{{v_1}}&{{v_2}}&{{v_3}} \\
{{w_1}}&{{w_2}}&{{w_3}}
\end{array}} \right|\]
\[
= \dfrac{1}{6}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
1&1&{ - 2} \\
2&{ - 1}&{ - 1} \\
0&{ - 1}&{ - 2}
\end{array}} \right| \\
= \dfrac{1}{6}\left[ {1 - \left( { - 4} \right) - 2\left( { - 2} \right)} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{6}\left( {4 + 4 + 4} \right) \\
= \dfrac{{12}}{6} = 2 \\
\]
Volume of the tetrahedron is 2 cube units, Option D is correct.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: In geometry, a tetrahedron also known as a triangular pyramid is a polyhedron with four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertices. Prism and Pyramids of Egypt are examples of tetrahedrons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




