
Let the tangents PA and PB are drawn from P(0,-2) to the circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2x-4y=0$. The area of the triangle PAB is
[a] $\dfrac{2\sqrt{15}}{17}$
[b] $\dfrac{4\sqrt{15}}{\sqrt{17}}$
[c] $\dfrac{24\sqrt{15}}{17}$
[d] $\dfrac{24\sqrt{15}}{\sqrt{17}}$
Answer
570.9k+ views
Hint: Use the fact that the equation of the chord of contact of tangents of the circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0$ from the point $P\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ is given by $x{{x}_{1}}+y{{y}_{1}}+g\left( x+{{x}_{1}} \right)+f\left( y+{{y}_{1}} \right)+c=0$. Solve the equation of the chord of contact and the circle and hence find the coordinates of A and B. Use the fact that the area of the triangle formed by the points $A\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right),B\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right),C\left( {{x}_{3}},{{y}_{3}} \right)$ is given by $\Delta =\dfrac{1}{2}\left| \begin{matrix}
{{x}_{1}} & {{y}_{1}} & 1 \\
{{x}_{2}} & {{y}_{2}} & 1 \\
{{x}_{3}} & {{y}_{3}} & 1 \\
\end{matrix} \right|$
. Hence find the area of the triangle PAB.
Complete step by step answer:
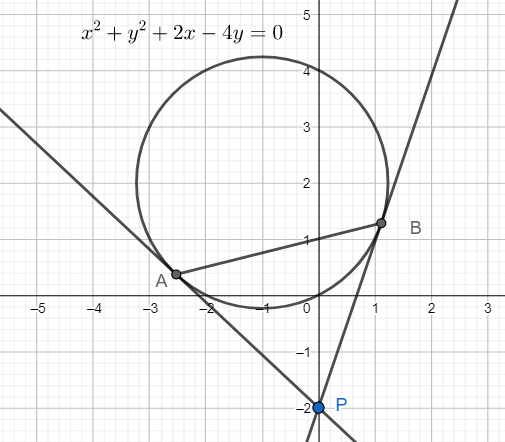
Equation of the circle is ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2x-4y=0$
We know that the equation of the chord of contact of the tangents of the circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0$ from the point $P\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ is given by $x{{x}_{1}}+y{{y}_{1}}+\left( x+{{x}_{1}} \right)+f\left( y+{{y}_{1}} \right)+c=0$
Hence the equation of AB is
$\begin{align}
& x\left( 0 \right)+y\left( -2 \right)+\left( x+0 \right)-2\left( y-2 \right)=0 \\
& x-4y+4=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=4y-4 \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the value of x in the equation of the circle, we get
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( 4y-4 \right)}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2\left( 4y-4 \right)-4y=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 16{{y}^{2}}+16-32y+{{y}^{2}}+8y-8-4y=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 17{{y}^{2}}-28y+8=0 \\
\end{align}$
Let the roots of this expression be ${{y}_{1}},{{y}_{2}}$
Hence, we have ${{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}=\dfrac{28}{17},{{y}_{1}}{{y}_{2}}=\dfrac{8}{17}$
Also, we have $A\equiv \left( 4{{y}_{1}}-4,{{y}_{1}} \right),B\equiv \left( 4{{y}_{2}}-4,{{y}_{2}} \right)$
We know that the area of the triangle $\Delta ABC$ formed by the points $A\left( {{x}_{,1}},{{y}_{1}} \right),B\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right),C\left( {{x}_{3}},{{y}_{3}} \right)$ is given by $\Delta =\dfrac{1}{2}\left| \begin{matrix}
{{x}_{1}} & {{y}_{1}} & 1 \\
{{x}_{2}} & {{y}_{2}} & 1 \\
{{x}_{3}} & {{y}_{3}} & 1 \\
\end{matrix} \right|$ which we expand by row operations and third column to have $\Delta =\dfrac{1}{2}\left| \begin{matrix}
{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} & {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \\
{{x}_{3}}-{{x}_{1}} & {{y}_{3}}-{{y}_{1}} \\
\end{matrix} \right|$
Hence, we have
$ar\left( \Delta PAB \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\left| \begin{matrix}
4{{y}_{1}}-4-0 & {{y}_{1}}+2 \\
4{{y}_{2}}-4-0 & {{y}_{2}}+2 \\
\end{matrix} \right|$
Hence, we have
\[ar\left( \Delta PAB \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\left| \left( 4{{y}_{1}}-4 \right)\left( {{y}_{2}}+2 \right)-\left( 4{{y}_{2}}-4 \right)\left( {{y}_{1}}+2 \right) \right|\]
Taking 4 common inside modulus sign, we get
$ar\left( \Delta PAB \right)=2\left| \left( {{y}_{1}}-1 \right)\left( {{y}_{2}}+2 \right)-\left( {{y}_{2}}-1 \right)\left( {{y}_{1}}+2 \right) \right|$
Expanding the terms inside the modulus sign, we get
$\begin{align}
& ar\left( \Delta PAB \right)=2\left| {{y}_{1}}{{y}_{2}}+2{{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}}-2-{{y}_{1}}{{y}_{2}}-2{{y}_{2}}+{{y}_{1}}+2 \right| \\
& =6\left| {{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}} \right| \\
\end{align}$
We know that ${{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}-4ab$
Hence, we have
${{\left( {{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( {{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}-4{{y}_{1}}{{y}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{28}^{2}}}{{{17}^{2}}}-\dfrac{32}{17}=\dfrac{{{28}^{2}}-17\times 32}{{{17}^{2}}}=\dfrac{240}{{{17}^{2}}}$
Taking square root on both sides, we get
$\left| {{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}} \right|=\dfrac{4\sqrt{15}}{17}$
Hence, we have
$ar\left( \Delta PAB \right)=6\left( \dfrac{4\sqrt{15}}{17} \right)=\dfrac{24\sqrt{15}}{17}$
So, the correct answer is “Option c”.
Note: [1] This question can also be solved directly using Pythagoras theorem and trigonometry without the use of analytical geometry. However the calculations will be more tedious to perform. Hence the method should be avoided as it is more prone to calculation mistakes.
{{x}_{1}} & {{y}_{1}} & 1 \\
{{x}_{2}} & {{y}_{2}} & 1 \\
{{x}_{3}} & {{y}_{3}} & 1 \\
\end{matrix} \right|$
. Hence find the area of the triangle PAB.
Complete step by step answer:

Equation of the circle is ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2x-4y=0$
We know that the equation of the chord of contact of the tangents of the circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0$ from the point $P\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ is given by $x{{x}_{1}}+y{{y}_{1}}+\left( x+{{x}_{1}} \right)+f\left( y+{{y}_{1}} \right)+c=0$
Hence the equation of AB is
$\begin{align}
& x\left( 0 \right)+y\left( -2 \right)+\left( x+0 \right)-2\left( y-2 \right)=0 \\
& x-4y+4=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=4y-4 \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the value of x in the equation of the circle, we get
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( 4y-4 \right)}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2\left( 4y-4 \right)-4y=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 16{{y}^{2}}+16-32y+{{y}^{2}}+8y-8-4y=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 17{{y}^{2}}-28y+8=0 \\
\end{align}$
Let the roots of this expression be ${{y}_{1}},{{y}_{2}}$
Hence, we have ${{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}=\dfrac{28}{17},{{y}_{1}}{{y}_{2}}=\dfrac{8}{17}$
Also, we have $A\equiv \left( 4{{y}_{1}}-4,{{y}_{1}} \right),B\equiv \left( 4{{y}_{2}}-4,{{y}_{2}} \right)$
We know that the area of the triangle $\Delta ABC$ formed by the points $A\left( {{x}_{,1}},{{y}_{1}} \right),B\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right),C\left( {{x}_{3}},{{y}_{3}} \right)$ is given by $\Delta =\dfrac{1}{2}\left| \begin{matrix}
{{x}_{1}} & {{y}_{1}} & 1 \\
{{x}_{2}} & {{y}_{2}} & 1 \\
{{x}_{3}} & {{y}_{3}} & 1 \\
\end{matrix} \right|$ which we expand by row operations and third column to have $\Delta =\dfrac{1}{2}\left| \begin{matrix}
{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} & {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \\
{{x}_{3}}-{{x}_{1}} & {{y}_{3}}-{{y}_{1}} \\
\end{matrix} \right|$
Hence, we have
$ar\left( \Delta PAB \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\left| \begin{matrix}
4{{y}_{1}}-4-0 & {{y}_{1}}+2 \\
4{{y}_{2}}-4-0 & {{y}_{2}}+2 \\
\end{matrix} \right|$
Hence, we have
\[ar\left( \Delta PAB \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\left| \left( 4{{y}_{1}}-4 \right)\left( {{y}_{2}}+2 \right)-\left( 4{{y}_{2}}-4 \right)\left( {{y}_{1}}+2 \right) \right|\]
Taking 4 common inside modulus sign, we get
$ar\left( \Delta PAB \right)=2\left| \left( {{y}_{1}}-1 \right)\left( {{y}_{2}}+2 \right)-\left( {{y}_{2}}-1 \right)\left( {{y}_{1}}+2 \right) \right|$
Expanding the terms inside the modulus sign, we get
$\begin{align}
& ar\left( \Delta PAB \right)=2\left| {{y}_{1}}{{y}_{2}}+2{{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}}-2-{{y}_{1}}{{y}_{2}}-2{{y}_{2}}+{{y}_{1}}+2 \right| \\
& =6\left| {{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}} \right| \\
\end{align}$
We know that ${{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}-4ab$
Hence, we have
${{\left( {{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( {{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}-4{{y}_{1}}{{y}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{28}^{2}}}{{{17}^{2}}}-\dfrac{32}{17}=\dfrac{{{28}^{2}}-17\times 32}{{{17}^{2}}}=\dfrac{240}{{{17}^{2}}}$
Taking square root on both sides, we get
$\left| {{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}} \right|=\dfrac{4\sqrt{15}}{17}$
Hence, we have
$ar\left( \Delta PAB \right)=6\left( \dfrac{4\sqrt{15}}{17} \right)=\dfrac{24\sqrt{15}}{17}$
So, the correct answer is “Option c”.
Note: [1] This question can also be solved directly using Pythagoras theorem and trigonometry without the use of analytical geometry. However the calculations will be more tedious to perform. Hence the method should be avoided as it is more prone to calculation mistakes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




