
Let the tangent at point P of the curve ${{x}^{2m}}{{y}^{\dfrac{n}{2}}}={{a}^{\dfrac{4m+n}{2}}}$ meets the x-axis and the y-axis at A and B, respectively. If $AP:PB=\dfrac{n}{\lambda m}$, where P lies between A and B, then find the value of $\lambda $
[a] 4
[b] 3
[c] -4
[d] -3
Answer
575.1k+ views
Hint: Take logarithm on both sides of the equation and differentiate with respect to x, Hence find the expression for $\dfrac{dy}{dx}$. Hence find the slope of the tangent at a point $P\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ on the given curve and hence find the equation of the tangent. Determine the coordinates of points of intersection of the tangent with the axis. Hence determine the ratio in which P divides AB.
Alternatively form the equation of the family of the curves whose tangent at point P meets x-axis at A and B and satisfies AP: PB $=\dfrac{n}{\lambda m}$. Solve the differential equation and compare with the given equation. Hence find the value of $\lambda $.
Complete step-by-step answer:
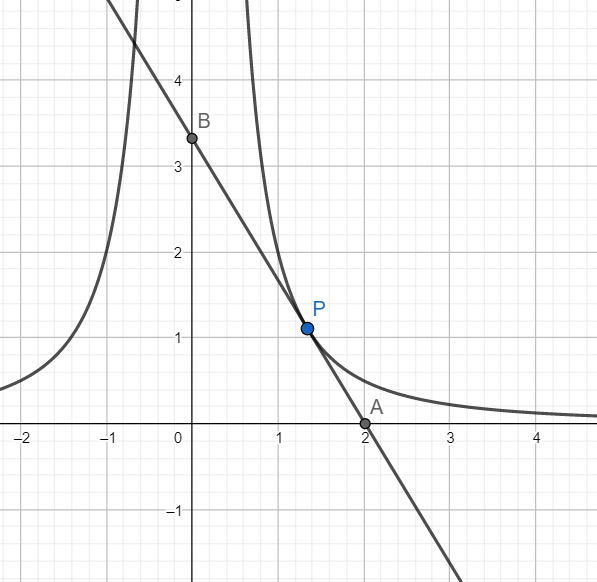
We have ${{x}^{2m}}{{y}^{\dfrac{n}{2}}}={{a}^{\dfrac{4m+n}{2}}}$
Taking log on both sides, we get
$\log \left( {{x}^{2m}}{{y}^{\dfrac{n}{2}}} \right)=\log \left( {{a}^{\dfrac{4m+n}{2}}} \right)$
Using $\log mn=\log m+\log n$ and $\log \left( {{a}^{n}} \right)=n\log a$, we get
$2m\log x+\dfrac{n}{2}\log y=\dfrac{4m+n}{2}\log a$
Differentiating both sides of the equation, we get
$2m\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{n}{2}\dfrac{1}{y}\dfrac{dy}{dx}=0$
Subtracting $\dfrac{2m}{x}$ from both sides of the equation, we get
$\dfrac{n}{2y}\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{-2m}{x}$
Multiplying both sides of the equation by $\dfrac{2y}{n}$, we get
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{-4my}{nx}$
Hence the slope of the tangent at $\text{ }P\left( {{x}_{1}},{{ y }_{1}} \right)$ is given by $m={{\left. \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right|}_{x={{x}_{1}},y={{ y }_{1}}}}=\dfrac{-4m{{y}_{1}}}{n{{x}_{1}}}$
Hence the equation of the tangent is given by
$y-{{y}_{1}}=\dfrac{-4m{{y}_{1}}}{n{{x}_{1}}}\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)$
At point A, we have y = 0
Hence, we have
$\begin{align}
& -{{y}_{1}}=\dfrac{-4m{{y}_{1}}}{n{{x}_{1}}}\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow n{{x}_{1}}=4m\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Dividing both sides by 4m, we get
$x-{{x}_{1}}=\dfrac{n{{x}_{1}}}{4m}$
Adding ${{x}_{1}}$ on both sides, we get
$x=\dfrac{n+4m}{4m}{{x}_{1}}$
At point B, we have x=0.
Hence, we have
$y-{{y}_{1}}=\dfrac{-4m{{y}_{1}}}{n{{x}_{1}}}\left( -{{x}_{1}} \right)=\dfrac{4m{{y}_{1}}}{n}$
Adding ${{y}_{1}}$ on both sides of the equation, we get
$y=\left( \dfrac{4m}{n}+1 \right){{y}_{1}}=\dfrac{4m+n}{n}{{y}_{1}}$
Let P divides AB in the ratio of $k:1$
Hence, we have
$P\equiv \left( \dfrac{k\times 0+\dfrac{4m+n}{4m}{{x}_{1}}}{k+1},\dfrac{k\times \dfrac{4m+n}{n}{{y}_{1}}}{k+1} \right)$
But $\text{ }P\equiv \left({{ x }_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$
Hence, we have
$\dfrac{4m+n}{4m\left( k+1 \right)}=1$
Multiplying both sides by k+1, we get
$k+1=\dfrac{4m+n}{4m}$
Subtracting 1 from both sides, we get
$k=\dfrac{4m+n}{4m}-1=\dfrac{n}{4m}$
Hence the ratio in which P divides AB is $\dfrac{n}{4m}$
Hence $\lambda =4$
Hence option [a] is correct
So, the correct answer is “Option [a]”.
Note: Alternative Method: Best method
Equation of the tangent at point $P\left( x,y \right)$ is given by
$Y-y=\dfrac{dy}{dx}\left( X-x \right)$
At point A, we have Y = 0
Hence $-y=\dfrac{dy}{dx}\left( X-x \right)$
Hence, we have
$X=x+\dfrac{-y}{\dfrac{dy}{dx}}$
Since P divides AB in the ratio $\dfrac{n}{\lambda m}$, we have
$x=\dfrac{\lambda m\left( x-\dfrac{y}{\dfrac{dy}{dx}} \right)}{n+\lambda m}$
Multiplying both sides by $n+\lambda m$, we get
$\left( n+\lambda m \right)x=\lambda m\left( x-\dfrac{y}{\dfrac{dy}{dx}} \right)$
Dividing both sides by$\lambda m$ , we get
$\dfrac{n+\lambda m}{\lambda m}x=x-\dfrac{y}{\dfrac{dy}{dx}}$
Subtracting x from both sides, we get
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{n}{\lambda m}x=-\dfrac{y}{\dfrac{dy}{dx}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{n}{\lambda m}x=-y\dfrac{dx}{dy} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{y}=-\dfrac{\lambda m}{n}\dfrac{dx}{x} \\
\end{align}$
Integrating both sides, we get
$\log y=-\dfrac{\lambda m}{n}\log x+\log C$
Hence, we have
$\log \left( y{{x}^{\dfrac{\lambda m}{n}}} \right)=\log C$
Hence, we have
$y{{x}^{\dfrac{\lambda m}{n}}}=C$
Raising power to $\dfrac{n}{2}$ on both sides of the equation, we get
${{y}^{\dfrac{n}{2}}}{{x}^{\dfrac{\lambda m}{2}}}={{C}^{\dfrac{n}{2}}}=C'$
Comparing the equation, with the given equation, we get
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{\lambda }{2}=2 \\
& \Rightarrow \lambda =4 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the value of $\lambda $ is 4
Alternatively form the equation of the family of the curves whose tangent at point P meets x-axis at A and B and satisfies AP: PB $=\dfrac{n}{\lambda m}$. Solve the differential equation and compare with the given equation. Hence find the value of $\lambda $.
Complete step-by-step answer:

We have ${{x}^{2m}}{{y}^{\dfrac{n}{2}}}={{a}^{\dfrac{4m+n}{2}}}$
Taking log on both sides, we get
$\log \left( {{x}^{2m}}{{y}^{\dfrac{n}{2}}} \right)=\log \left( {{a}^{\dfrac{4m+n}{2}}} \right)$
Using $\log mn=\log m+\log n$ and $\log \left( {{a}^{n}} \right)=n\log a$, we get
$2m\log x+\dfrac{n}{2}\log y=\dfrac{4m+n}{2}\log a$
Differentiating both sides of the equation, we get
$2m\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{n}{2}\dfrac{1}{y}\dfrac{dy}{dx}=0$
Subtracting $\dfrac{2m}{x}$ from both sides of the equation, we get
$\dfrac{n}{2y}\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{-2m}{x}$
Multiplying both sides of the equation by $\dfrac{2y}{n}$, we get
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{-4my}{nx}$
Hence the slope of the tangent at $\text{ }P\left( {{x}_{1}},{{ y }_{1}} \right)$ is given by $m={{\left. \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right|}_{x={{x}_{1}},y={{ y }_{1}}}}=\dfrac{-4m{{y}_{1}}}{n{{x}_{1}}}$
Hence the equation of the tangent is given by
$y-{{y}_{1}}=\dfrac{-4m{{y}_{1}}}{n{{x}_{1}}}\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)$
At point A, we have y = 0
Hence, we have
$\begin{align}
& -{{y}_{1}}=\dfrac{-4m{{y}_{1}}}{n{{x}_{1}}}\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow n{{x}_{1}}=4m\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Dividing both sides by 4m, we get
$x-{{x}_{1}}=\dfrac{n{{x}_{1}}}{4m}$
Adding ${{x}_{1}}$ on both sides, we get
$x=\dfrac{n+4m}{4m}{{x}_{1}}$
At point B, we have x=0.
Hence, we have
$y-{{y}_{1}}=\dfrac{-4m{{y}_{1}}}{n{{x}_{1}}}\left( -{{x}_{1}} \right)=\dfrac{4m{{y}_{1}}}{n}$
Adding ${{y}_{1}}$ on both sides of the equation, we get
$y=\left( \dfrac{4m}{n}+1 \right){{y}_{1}}=\dfrac{4m+n}{n}{{y}_{1}}$
Let P divides AB in the ratio of $k:1$
Hence, we have
$P\equiv \left( \dfrac{k\times 0+\dfrac{4m+n}{4m}{{x}_{1}}}{k+1},\dfrac{k\times \dfrac{4m+n}{n}{{y}_{1}}}{k+1} \right)$
But $\text{ }P\equiv \left({{ x }_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$
Hence, we have
$\dfrac{4m+n}{4m\left( k+1 \right)}=1$
Multiplying both sides by k+1, we get
$k+1=\dfrac{4m+n}{4m}$
Subtracting 1 from both sides, we get
$k=\dfrac{4m+n}{4m}-1=\dfrac{n}{4m}$
Hence the ratio in which P divides AB is $\dfrac{n}{4m}$
Hence $\lambda =4$
Hence option [a] is correct
So, the correct answer is “Option [a]”.
Note: Alternative Method: Best method
Equation of the tangent at point $P\left( x,y \right)$ is given by
$Y-y=\dfrac{dy}{dx}\left( X-x \right)$
At point A, we have Y = 0
Hence $-y=\dfrac{dy}{dx}\left( X-x \right)$
Hence, we have
$X=x+\dfrac{-y}{\dfrac{dy}{dx}}$
Since P divides AB in the ratio $\dfrac{n}{\lambda m}$, we have
$x=\dfrac{\lambda m\left( x-\dfrac{y}{\dfrac{dy}{dx}} \right)}{n+\lambda m}$
Multiplying both sides by $n+\lambda m$, we get
$\left( n+\lambda m \right)x=\lambda m\left( x-\dfrac{y}{\dfrac{dy}{dx}} \right)$
Dividing both sides by$\lambda m$ , we get
$\dfrac{n+\lambda m}{\lambda m}x=x-\dfrac{y}{\dfrac{dy}{dx}}$
Subtracting x from both sides, we get
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{n}{\lambda m}x=-\dfrac{y}{\dfrac{dy}{dx}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{n}{\lambda m}x=-y\dfrac{dx}{dy} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{y}=-\dfrac{\lambda m}{n}\dfrac{dx}{x} \\
\end{align}$
Integrating both sides, we get
$\log y=-\dfrac{\lambda m}{n}\log x+\log C$
Hence, we have
$\log \left( y{{x}^{\dfrac{\lambda m}{n}}} \right)=\log C$
Hence, we have
$y{{x}^{\dfrac{\lambda m}{n}}}=C$
Raising power to $\dfrac{n}{2}$ on both sides of the equation, we get
${{y}^{\dfrac{n}{2}}}{{x}^{\dfrac{\lambda m}{2}}}={{C}^{\dfrac{n}{2}}}=C'$
Comparing the equation, with the given equation, we get
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{\lambda }{2}=2 \\
& \Rightarrow \lambda =4 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the value of $\lambda $ is 4
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 11 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




