
Let ‘s’ denote the semiperimeter of a triangle ABC in which \[BC = a\] , \[CA = b\] , \[AB = c\] . If the circle touches the sides BC, CA, AB at D, E, F respectively, prove that \[BD = s - b\] .
Answer
552.9k+ views
Hint: We know that the semi perimeter of a triangle is given by \[s = \dfrac{{a + b + c}}{2}\] , where ‘a’ ‘b’ and ‘c’ are the length of sides of the triangle. We know the theorem that the length of tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal. Using this theorem we can solve the above theorem and we will draw a diagram using the given data in the above problem.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s draw the diagram for the given data.
\[BC = a\] , \[CA = b\] , \[AB = c\] .
Also the circle touches the sides BC, CA, AB at D, E, F respectively.
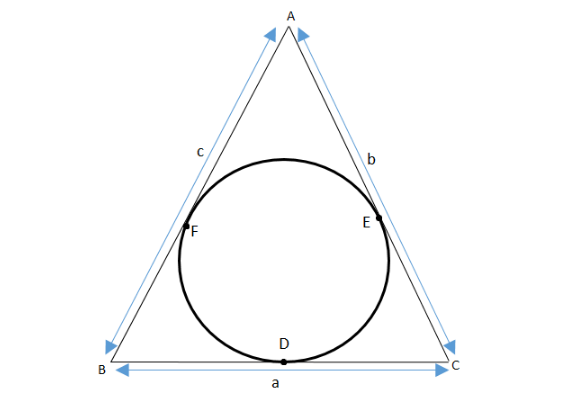
So the semi-perimeter is given according to the question is
\[s = \dfrac{{a + b + c}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2s = a + b + c\] .
B is an external point and BD and BF are tangents and from an external point the tangents drawn to a circle are equal in length.
That is,
\[BD = BF - - - (1)\] .
(The length of tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal.)
Similarly we have,
\[AF = AE - - - (2)\] and \[CD = CE - - - (3)\] .
Also given ‘s’ is semi perimeter
\[s = \dfrac{{AB + AC + BC}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2s = AB + AC + BC{\text{ }} - - - (4)\]
From the diagram we have,
\[AB = AF + FB\]
\[AC = AE + EC\]
\[BC = BD + DC\]
Substituting these in equation (1) we have,
\[ \Rightarrow 2s = AF + FB + AE + EC + BD + DC{\text{ }}\]
Now using equation (1), (2) and (3) we have,
\[ \Rightarrow 2s = 2AE + 2EC + 2BD\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2s = 2(AE + EC + BD)\]
\[ \Rightarrow s = AE + EC + BD\]
But \[AE + EC = AC\] . (See in the above diagram)
\[ \Rightarrow s = AC + BD\]
But we know that \[AC = b\]
\[ \Rightarrow s = b + BD\]
\[ \Rightarrow s - b = BD\]
Rearranging we have,
\[ \Rightarrow BD = s - b\] .
Hence proved.
Note: We know that if we want perimeter we add all the side lengths of a given dimension. We know that the perimeter of a triangle is \[P = a + b + c\] , where ‘a’, ‘b’ and ‘c’ are the length of sides of the triangle. Since they asked for a semi we took half of the perimeter. To solve we need to remember particular theorems.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s draw the diagram for the given data.
\[BC = a\] , \[CA = b\] , \[AB = c\] .
Also the circle touches the sides BC, CA, AB at D, E, F respectively.

So the semi-perimeter is given according to the question is
\[s = \dfrac{{a + b + c}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2s = a + b + c\] .
B is an external point and BD and BF are tangents and from an external point the tangents drawn to a circle are equal in length.
That is,
\[BD = BF - - - (1)\] .
(The length of tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal.)
Similarly we have,
\[AF = AE - - - (2)\] and \[CD = CE - - - (3)\] .
Also given ‘s’ is semi perimeter
\[s = \dfrac{{AB + AC + BC}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2s = AB + AC + BC{\text{ }} - - - (4)\]
From the diagram we have,
\[AB = AF + FB\]
\[AC = AE + EC\]
\[BC = BD + DC\]
Substituting these in equation (1) we have,
\[ \Rightarrow 2s = AF + FB + AE + EC + BD + DC{\text{ }}\]
Now using equation (1), (2) and (3) we have,
\[ \Rightarrow 2s = 2AE + 2EC + 2BD\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2s = 2(AE + EC + BD)\]
\[ \Rightarrow s = AE + EC + BD\]
But \[AE + EC = AC\] . (See in the above diagram)
\[ \Rightarrow s = AC + BD\]
But we know that \[AC = b\]
\[ \Rightarrow s = b + BD\]
\[ \Rightarrow s - b = BD\]
Rearranging we have,
\[ \Rightarrow BD = s - b\] .
Hence proved.
Note: We know that if we want perimeter we add all the side lengths of a given dimension. We know that the perimeter of a triangle is \[P = a + b + c\] , where ‘a’, ‘b’ and ‘c’ are the length of sides of the triangle. Since they asked for a semi we took half of the perimeter. To solve we need to remember particular theorems.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Find the sum of series 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + + 100 class 9 maths CBSE

Distinguish between Conventional and nonconventional class 9 social science CBSE

Find the greatest fivedigit number which is a perfect class 9 maths CBSE

Find the mode and median of the data 13 16 12 14 1-class-9-maths-CBSE




