
Let $S$ be the focus of ${{y}^{2}}=4x$ and a point \[P\] is moving on the curve such that its abscissa is increasing at the rate of $4$ units per sec, then the rate of increase of projection of $SP$ on $x+y=1$ when \[P\] is at $\left( 4,4 \right)$ is:
A. $\sqrt{2}$
B. $-1$
C. $-\sqrt{2}$
D. $\dfrac{-3}{\sqrt{2}}$
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: First we will find the value of $a$by comparing the standard equation of parabola to the given equation of parabola in question. Then we will find the focus as $S\left( a,0 \right)$ then we will find the vertices of a point $P\left( a{{k}^{2}},2ak \right)$ and find the vector $\overrightarrow{SP}$ and we will find its projection on $x+y=1$ by applying the formula: \[pro{{j}_{b}}a=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}}{\left| \right|}\] and then we will apply the second condition that the rate of change of abscissa for finding the value of $\dfrac{dx}{dt}$ and put the values of $x$ from $\left( 4,4 \right)$ and then find the differentiation of projection and put the values there to get the answer.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s define what a parabola is. So basically a parabola is a U-shaped plane curve where any point is at an equal distance from a fixed point (known as the focus) and from a fixed straight line which is known as the directrix. The standard equation of parabola be ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$and the focal point or focus be $S$ which has the vertices: $\left( a,0 \right)$ .
Let’s find out the focal point that is $S\left( a,0 \right)$ , for that we have to find the value of $a$ , now we know that $a$ here stands for the value from the standard equation of parabola that is ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$.
We are given${{y}^{2}}=4x$ in the question now let’s compare it with the standard equation of parabola that is ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$, so we can see that: $4a=4\Rightarrow a=1$ .
Therefore, the focal point will be: $S\left( 1,0 \right)$ ,
Now, we know that any point $P$ on a parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ is of the form \[\left( a{{k}^{2}},2ak \right)\] . So, for our given parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4x$ the point $P$ is of the form: $\left( {{k}^{2}},2k \right)$ :
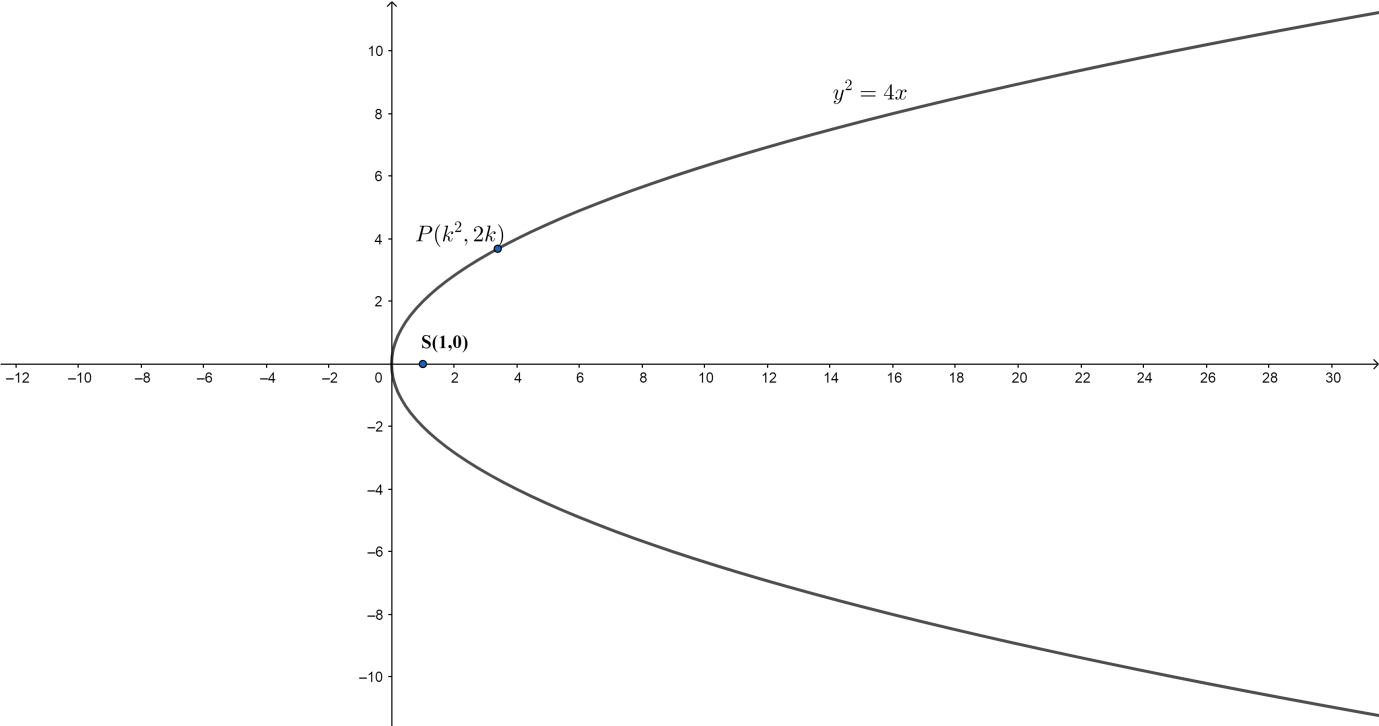
Now we have two points that are $S\left( 1,0 \right)$ and $P\left( {{k}^{2}},2k \right)$ , now $\overrightarrow{SP}=\left( {{k}^{2}}-1 \right)\widehat{i}+\left( 2k \right)\widehat{j}$
Now it is given that the projection of vector $\overrightarrow{a}$ on vector $\overrightarrow{b}$ will be: \[pro{{j}_{b}}a=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}}{\left| \right|}\]
Let, \[\overrightarrow{n}\] be the vector form of \[x+y=1\] that is $\widehat{i}+\widehat{j}=1$ .
Now the projection of vector on $\overrightarrow{SP}=\left( {{k}^{2}}-1 \right)\widehat{i}+\left( 2k \right)\widehat{j}$
\[\overrightarrow{n}\] : $y=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{SP}.\overrightarrow{n}}{\left| \overrightarrow{n} \right|}\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{\left( \left( 1-{{k}^{2}} \right).1 \right)+\left( 2k.1 \right)}{\sqrt{\left( {{1}^{2}}+{{1}^{2}} \right)}}\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{\left( 1-{{k}^{2}} \right)+2k}{\sqrt{2}}\text{ }......\text{Equation 1}\text{.}$
It is given that the rate of change of abscissa is $4$ units per sec: $\dfrac{dx}{dt}=4$ , and we have found that $P\left( {{k}^{2}},2k \right)$ , here $x={{k}^{2}}\Rightarrow \dfrac{dx}{dt}=2k.\dfrac{dk}{dt}$ , now, we have to find the rate of increase of projection at $\left( 4,4 \right)$ then $2k=4\Rightarrow k=2$ , therefore: $\dfrac{dx}{dt}=2k.\dfrac{dk}{dt}\Rightarrow 4=4.\dfrac{dk}{dt}\Rightarrow \dfrac{dk}{dt}=1\text{ }......\text{ Equation 2}$
Now, we know that to find the rate of increase of projection we will have to differentiate equation 1 that is: $y=\dfrac{\left( 1-{{k}^{2}} \right)+2k}{\sqrt{2}}\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=\left( \dfrac{-2k+2}{\sqrt{2}} \right)\dfrac{dk}{dt}$ now we will put the value of $k=2$ and $\dfrac{dk}{dt}=1$
Therefore,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=\left( \dfrac{-2k+2}{\sqrt{2}} \right)\dfrac{dk}{dt}\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=\left( \dfrac{-2\left( 2 \right)+2}{\sqrt{2}} \right)1\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=\left( \dfrac{-4+2}{\sqrt{2}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=-\sqrt{2} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the rate of increase of the projection will be $-\sqrt{2}$ .
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note:
In questions like this be careful while finding the dot product and converting the scalar equations into the vector equations, Students may make the mistakes in those parts. Also, to find the rate of change at a particular point, we will just put those points into the condition.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s define what a parabola is. So basically a parabola is a U-shaped plane curve where any point is at an equal distance from a fixed point (known as the focus) and from a fixed straight line which is known as the directrix. The standard equation of parabola be ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$and the focal point or focus be $S$ which has the vertices: $\left( a,0 \right)$ .
Let’s find out the focal point that is $S\left( a,0 \right)$ , for that we have to find the value of $a$ , now we know that $a$ here stands for the value from the standard equation of parabola that is ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$.
We are given${{y}^{2}}=4x$ in the question now let’s compare it with the standard equation of parabola that is ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$, so we can see that: $4a=4\Rightarrow a=1$ .
Therefore, the focal point will be: $S\left( 1,0 \right)$ ,
Now, we know that any point $P$ on a parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ is of the form \[\left( a{{k}^{2}},2ak \right)\] . So, for our given parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4x$ the point $P$ is of the form: $\left( {{k}^{2}},2k \right)$ :

Now we have two points that are $S\left( 1,0 \right)$ and $P\left( {{k}^{2}},2k \right)$ , now $\overrightarrow{SP}=\left( {{k}^{2}}-1 \right)\widehat{i}+\left( 2k \right)\widehat{j}$
Now it is given that the projection of vector $\overrightarrow{a}$ on vector $\overrightarrow{b}$ will be: \[pro{{j}_{b}}a=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}}{\left| \right|}\]
Let, \[\overrightarrow{n}\] be the vector form of \[x+y=1\] that is $\widehat{i}+\widehat{j}=1$ .
Now the projection of vector on $\overrightarrow{SP}=\left( {{k}^{2}}-1 \right)\widehat{i}+\left( 2k \right)\widehat{j}$
\[\overrightarrow{n}\] : $y=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{SP}.\overrightarrow{n}}{\left| \overrightarrow{n} \right|}\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{\left( \left( 1-{{k}^{2}} \right).1 \right)+\left( 2k.1 \right)}{\sqrt{\left( {{1}^{2}}+{{1}^{2}} \right)}}\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{\left( 1-{{k}^{2}} \right)+2k}{\sqrt{2}}\text{ }......\text{Equation 1}\text{.}$
It is given that the rate of change of abscissa is $4$ units per sec: $\dfrac{dx}{dt}=4$ , and we have found that $P\left( {{k}^{2}},2k \right)$ , here $x={{k}^{2}}\Rightarrow \dfrac{dx}{dt}=2k.\dfrac{dk}{dt}$ , now, we have to find the rate of increase of projection at $\left( 4,4 \right)$ then $2k=4\Rightarrow k=2$ , therefore: $\dfrac{dx}{dt}=2k.\dfrac{dk}{dt}\Rightarrow 4=4.\dfrac{dk}{dt}\Rightarrow \dfrac{dk}{dt}=1\text{ }......\text{ Equation 2}$
Now, we know that to find the rate of increase of projection we will have to differentiate equation 1 that is: $y=\dfrac{\left( 1-{{k}^{2}} \right)+2k}{\sqrt{2}}\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=\left( \dfrac{-2k+2}{\sqrt{2}} \right)\dfrac{dk}{dt}$ now we will put the value of $k=2$ and $\dfrac{dk}{dt}=1$
Therefore,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=\left( \dfrac{-2k+2}{\sqrt{2}} \right)\dfrac{dk}{dt}\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=\left( \dfrac{-2\left( 2 \right)+2}{\sqrt{2}} \right)1\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=\left( \dfrac{-4+2}{\sqrt{2}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=-\sqrt{2} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the rate of increase of the projection will be $-\sqrt{2}$ .
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note:
In questions like this be careful while finding the dot product and converting the scalar equations into the vector equations, Students may make the mistakes in those parts. Also, to find the rate of change at a particular point, we will just put those points into the condition.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




