
Let I be the moment of inertia, of a uniform square plate about an axis AB that passes through its center and is parallel to two of its sides. CD is a line in the plane of the plate that passes through the center of the plate and makes an angle $\theta $ with AB as shown in the figure. The moment of inertia of the plate about the axis CD is then equal to
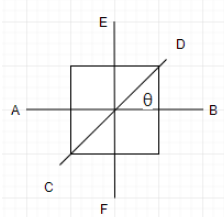
A: $I$
B: $I{{\sin }^{2}}\theta $
C: $I{{\cos }^{2}}\theta $
D: $I{{\cos }^{2}}\dfrac{\theta }{2}$

Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint:The moment of inertia of a point mass with respect to an axis is defined as the product of the mass with the distance from the axis. So in our question, we have to define the point around which the body rotates when torque acts on it.
Formulas used:
If axis AB is perpendicular to CD and an axis passing through centre of square and perpendicular to the plane is XY, then
${{I}_{XY}}={{I}_{AB}}+{{I}_{CD}}$
Complete step by step answer:
We can modify the figure as follows:
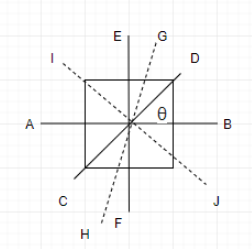
From the figure, we can deduce that Axis AB is perpendicular to EF and axis GH passes through the centre of square and perpendicular to the plane.
Hence, ${{I}_{GH}}={{I}_{AB}}+{{I}_{EF}}$
$\Rightarrow {{I}_{GH}}=2{{I}_{AB}}=2I$ (since ${{I}_{AB}}={{I}_{EF}}$)
Using the similar reason, we can say that
$\begin{align}
& {{I}_{GH}}={{I}_{CD}}+{{I}_{IJ}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{I}_{GH}}=2{{I}_{CD}} \\
& \therefore {{I}_{CD}}=\dfrac{2I}{2}=I \\
\end{align}$
IJ is an axis perpendicular to CD
The moment of inertia of a square plate about an axis on its plane is the same about the axis which is also in the same plane but perpendicular to the former.
Hence option A is the correct answer among the given options.
Note:Moment of inertia is also termed as rotational inertia or angular mass. Sometimes the question might be phrased using these terms. The students have to understand that it is the moment of inertia and proceed accordingly.
Formulas used:
If axis AB is perpendicular to CD and an axis passing through centre of square and perpendicular to the plane is XY, then
${{I}_{XY}}={{I}_{AB}}+{{I}_{CD}}$
Complete step by step answer:
We can modify the figure as follows:

From the figure, we can deduce that Axis AB is perpendicular to EF and axis GH passes through the centre of square and perpendicular to the plane.
Hence, ${{I}_{GH}}={{I}_{AB}}+{{I}_{EF}}$
$\Rightarrow {{I}_{GH}}=2{{I}_{AB}}=2I$ (since ${{I}_{AB}}={{I}_{EF}}$)
Using the similar reason, we can say that
$\begin{align}
& {{I}_{GH}}={{I}_{CD}}+{{I}_{IJ}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{I}_{GH}}=2{{I}_{CD}} \\
& \therefore {{I}_{CD}}=\dfrac{2I}{2}=I \\
\end{align}$
IJ is an axis perpendicular to CD
The moment of inertia of a square plate about an axis on its plane is the same about the axis which is also in the same plane but perpendicular to the former.
Hence option A is the correct answer among the given options.
Note:Moment of inertia is also termed as rotational inertia or angular mass. Sometimes the question might be phrased using these terms. The students have to understand that it is the moment of inertia and proceed accordingly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




