
Let $h(x) = {e^{ - x}} + kx,$ where $k$ is any constant. For what value(s) of $k$ does $h$ have, no critical points?
A. $k > 0$
B. $k = 0$
C. $k < 0$
D. $k \leqslant 0$
E. $k > 0$
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: At critical points $f'(x) = 0$
Differentiate the equation given in the question and equate it to zero to solve the question.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
We have, $h(x) = {e^{ - x}} + kx$,$k$is constant
At critical point, $\dfrac{d}{{dx}}[h(x)] = 0$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{d}{{dx}}({e^{ - x}} + kx) = 0$
$\because \dfrac{d}{{dx}}{e^{ax}} = a{e^{ax}}$ and $\dfrac{d}{{dx}}{x^n} = n{x^{n - 1}}$
We get
$\dfrac{d}{{dx}}({e^{ - x}} + kx) = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}({e^{ - x}}) + \dfrac{d}{{dx}}kx$
$ = - {e^{ - x}} + k(1)$ (Since differentiation is distinctive over addition)
$ \Rightarrow - {e^{ - x}} + k = 0$
$ \Rightarrow k = {e^{ - x}}.$
From the graph of ${e^{ - x}}$, we can observe that ${e^{ - x}} > 0$ for all the values of $x.$
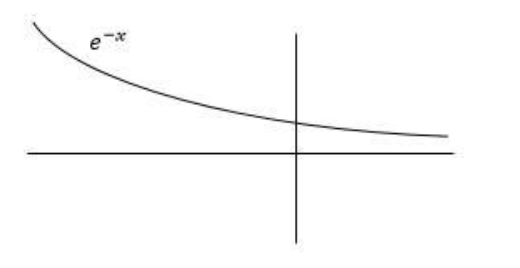
$ \Rightarrow k = {e^{ - x}} > 0$
$ \Rightarrow k > 0$
Therefore, at $k > 0$, we will get critical points.
Thus, for $k \leqslant 0$, we will not get critical points.
Therefore, the answer is D. $k \leqslant 0$
Note:
To solve such a type of question you need to know the range of basic functions like trigonometric functions, logarithmic function and exponential function. Also, you need to understand the concept of inequality knowing the graphs of basic function will always help you.
Differentiate the equation given in the question and equate it to zero to solve the question.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
We have, $h(x) = {e^{ - x}} + kx$,$k$is constant
At critical point, $\dfrac{d}{{dx}}[h(x)] = 0$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{d}{{dx}}({e^{ - x}} + kx) = 0$
$\because \dfrac{d}{{dx}}{e^{ax}} = a{e^{ax}}$ and $\dfrac{d}{{dx}}{x^n} = n{x^{n - 1}}$
We get
$\dfrac{d}{{dx}}({e^{ - x}} + kx) = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}({e^{ - x}}) + \dfrac{d}{{dx}}kx$
$ = - {e^{ - x}} + k(1)$ (Since differentiation is distinctive over addition)
$ \Rightarrow - {e^{ - x}} + k = 0$
$ \Rightarrow k = {e^{ - x}}.$
From the graph of ${e^{ - x}}$, we can observe that ${e^{ - x}} > 0$ for all the values of $x.$

$ \Rightarrow k = {e^{ - x}} > 0$
$ \Rightarrow k > 0$
Therefore, at $k > 0$, we will get critical points.
Thus, for $k \leqslant 0$, we will not get critical points.
Therefore, the answer is D. $k \leqslant 0$
Note:
To solve such a type of question you need to know the range of basic functions like trigonometric functions, logarithmic function and exponential function. Also, you need to understand the concept of inequality knowing the graphs of basic function will always help you.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




