
Let $f:\mathbb{R}\to \mathbb{R}$ be any function defining $g:\mathbb{R}\to \mathbb{R}$ by $g\left( x \right)=\left| f\left( x \right) \right|$ for all $x\in \mathbb{R}$ then g is
A. onto if f is into
B. one-one if f is one-one
C. continuous if f is continuous
D. differentiable if f is differentiable
Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint: The domain of the given function $g\left( x \right)=\left| f\left( x \right) \right|$ is real as $f:\mathbb{R}\to \mathbb{R}$. We try to form the modulus function and find the continuity of the curve. We assume the function $y=f\left( x \right)$ and put the values in the main function g. We show that $g\left( x \right)=\left| f\left( x \right) \right|$ is continuous as long as $f:\mathbb{R}\to \mathbb{R}$ and the domain of g is in real values.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the function $g\left( x \right)=\left| f\left( x \right) \right|$, the main function is the modulus function.
Let’s check the continuity of $\left| y \right|$ for $y:\mathbb{R}\to \mathbb{R}$ where $y=f\left( x \right)$.
$\forall y\in \mathbb{R}$, we can put the graph of the modulus function as
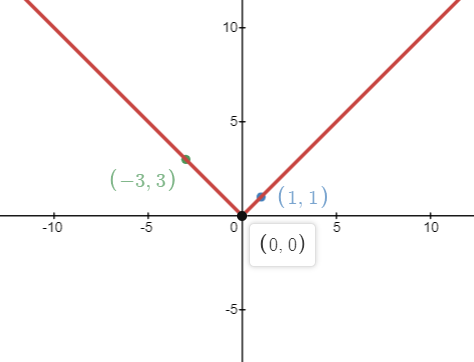
The graph of modulus is continuous itself. So, the condition for $\left| y \right|$ to be continuous $y\in \mathbb{R}$.
If there exists some y where $y\notin \mathbb{R}$, then $\left| y \right|$ is discontinuous.
Now it’s given that $f:\mathbb{R}\to \mathbb{R}$. So, the range of f is only real. So, all values of $y=f\left( x \right)$ are accounted for in the real value range.
So, $g\left( x \right)=\left| f\left( x \right) \right|$ is also continuous as $g:\mathbb{R}\to \mathbb{R}$.
The correct option is C.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: The relation between continuity and differentiability is that if a function is differentiable then the function is definitely continuous. But the opposite is not always true. So, if we show that $y=f\left( x \right)$ is continuous, its differentiability is only known when we have the exact function. Now if we assume that $y=f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}$, then we can see that the function f is not one-one but the function g is one-one. So, all the other options were not considered. In case of the modulus function whatever be the function of the outer always remains continuous.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the function $g\left( x \right)=\left| f\left( x \right) \right|$, the main function is the modulus function.
Let’s check the continuity of $\left| y \right|$ for $y:\mathbb{R}\to \mathbb{R}$ where $y=f\left( x \right)$.
$\forall y\in \mathbb{R}$, we can put the graph of the modulus function as

The graph of modulus is continuous itself. So, the condition for $\left| y \right|$ to be continuous $y\in \mathbb{R}$.
If there exists some y where $y\notin \mathbb{R}$, then $\left| y \right|$ is discontinuous.
Now it’s given that $f:\mathbb{R}\to \mathbb{R}$. So, the range of f is only real. So, all values of $y=f\left( x \right)$ are accounted for in the real value range.
So, $g\left( x \right)=\left| f\left( x \right) \right|$ is also continuous as $g:\mathbb{R}\to \mathbb{R}$.
The correct option is C.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: The relation between continuity and differentiability is that if a function is differentiable then the function is definitely continuous. But the opposite is not always true. So, if we show that $y=f\left( x \right)$ is continuous, its differentiability is only known when we have the exact function. Now if we assume that $y=f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}$, then we can see that the function f is not one-one but the function g is one-one. So, all the other options were not considered. In case of the modulus function whatever be the function of the outer always remains continuous.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




