
Let $f:\left[ {0,4\pi } \right] \to \left[ {0,\pi } \right]$ be defined by $f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos x} \right)$ . The number of points $x \in \left[ {0,4\pi } \right]$ satisfying the equation $f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{10 - x}}{{10}}$ is.
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: The number of points of satisfaction is the points of intersection between the two given functions.
Try to draw the graph of both given functions and graphically find the point of intersection.
Intersection points are the points where the graph of both given functions cut each other.
The slope of a straight line $Ax + By + C = 0$, is given by the derivative of the equation of the line with respect to x.
For the function $f\left( x \right):x \to y$, the domain of the function is the set of all possible values of $x$ for which the function is defined. The range of the function is the set of all output values of the function at $x$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Step 1: Draw a graph of $f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos x} \right)$
To draw the graph of $f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos x} \right)$ , we will use both the functions $\cos x$ and ${\cos ^{ - 1}}x$.
Let us consider the graph of the trigonometric function $f\left( x \right) = \cos x$
Let $y = f\left( x \right)$
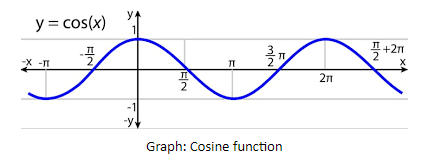
The function $\cos x$ is defined on all the real values of the $x$. Thus,
Domain: $\mathbb{R}$ , where $\mathbb{R}$ is the set of real numbers.
The maximum output value of the function $\cos x$ is +1 and the minimum output value is -1, and all other values of $\cos x$ lie between +1 and -1. Thus,
Range: $\left[ { - 1,1} \right]$
Now, let us consider the graph of the inverse trigonometric function \[f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}x\] :
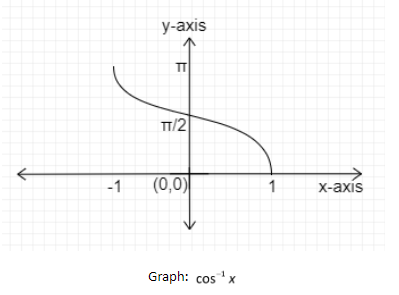
It is taking the values from +1 to -1. So, Domain = $\left[ { - 1,1} \right]$
The output values of the function are from 0 to $\pi $. So, Range = $\left[ {0,\pi } \right]$
Now draw the Graph of $f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos x} \right)$
Given that the function is defined for $f:\left[ {0,4\pi } \right] \to \left[ {0,\pi } \right]$
For the interval $x \in \left[ {0,\pi } \right]$
From the above graph of the function $f\left( x \right) = \cos x$ , the output values for the interval $\left[ {0,\pi } \right]$ is between -1 and +1. The output value of$\cos x$ is the input value of ${\cos ^{ - 1}}x$ .
And from the above graph of the function $f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}x$ , the output values for the interval $\left[ { - 1, + 1} \right]$ is 0 to $\pi $. Thus,
$f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos x} \right) = x$
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right) = x$
( Let $y = f\left( x \right)$
Differentiation $\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}$ gives the slope of the function.
i.e. $y = x$, a straight line with slope $\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = 1$)
The range for the interval $x \in \left[ {0,\pi } \right]$ is $f\left( x \right) \in \left[ {0,\pi } \right]$
Thus the graph of $f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos x} \right)$ in the interval $x \in \left[ {0,\pi } \right]$ is a straight line with slope 1.
For the interval $x \in \left[ {\pi ,2\pi } \right]$
From the above graph of the function $f\left( x \right) = \cos x$ , the output values for the interval $\left[ {\pi ,2\pi } \right]$ is between -1 and 0.
In $f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos x} \right)$ , the domain is the range of \[\cos x\] , but for the domain$ \in \left[ { - 1,0} \right]$ , the function ${\cos ^{ - 1}}x$ is not defined.
Therefore, using the property of the cosine function $\cos x = \cos \left( {2\pi - x} \right)$
$f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos x} \right)$
Therefore, $f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos \left( {2\pi - x} \right)} \right) = 2\pi - x$
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right) = 2\pi - x$
(Let $y = f\left( x \right)$
Differentiation $\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}$ gives the slope of the function.
i.e. $y = 2\pi - x$, a straight line with slope $\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = - 1$)
For $x = \pi ,$
$f\left( x \right) = 2\pi - \pi = \pi $
For $x = 2\pi ,$
$f\left( x \right) = 2\pi - 2\pi = 0$
The range for the interval $x \in \left[ {\pi ,2\pi } \right]$ is $f\left( x \right) \in \left[ {0,\pi } \right]$
Thus the graph of $f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos x} \right)$ in the interval $x \in \left[ {\pi ,2\pi } \right]$ is a straight line with slope -1.
Therefore, the drawn graph of $f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos x} \right)$ is the following:
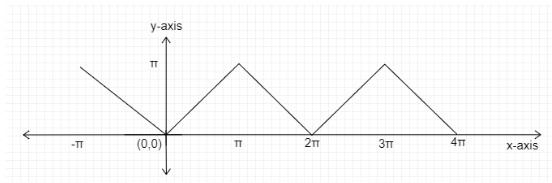
Graph: $f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos x} \right)$
Step 2: Draw graph of $f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{10 - x}}{{10}}$
We have drawn the graph of one given function. Now let’s draw the function of other given functions to find the intersection points between them.
$f\left( x \right) = 1 - \dfrac{x}{{10}}$
Point $10 \simeq 3\pi $
Let $y = f\left( x \right)$
Differentiation $\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}$ gives the slope of the function. Thus,
The slope of the line $f\left( x \right) = 1 - \dfrac{x}{{10}}$, is $\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = - 1$
Therefore, the drawn graph $f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{10 - x}}{{10}}$ is the following:
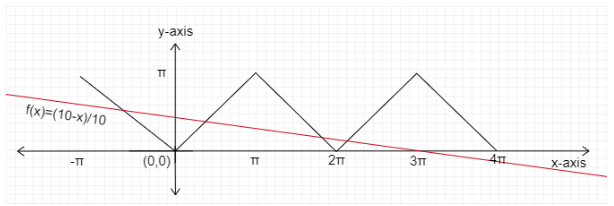
Graph: $f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{10 - x}}{{10}}$
Step 3: Count the point of intersection from the graph:
For $x \in \left[ {0,4\pi } \right]$
Function $f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos x} \right)$ and $f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{10 - x}}{{10}}$ intersects each other 3 points shown as below:
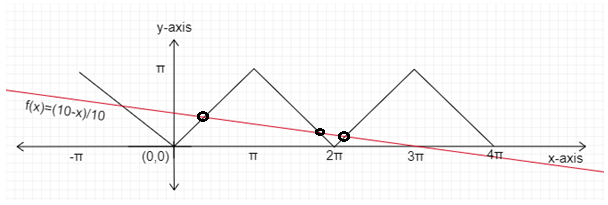
Final answer: At 3 points function $f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos x} \right)$ satisfies $f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{10 - x}}{{10}}$ in the interval $x \in \left[ {0,4\pi } \right]$
Note: Following graphs will be useful in future reference.
Graph of the sine function.
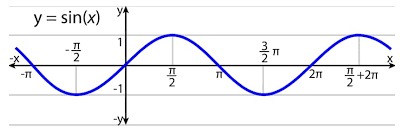
The function $\sin x$ is defined on all the real values of the $x$. Thus,
Domain: $\mathbb{R}$ , where $\mathbb{R}$ is the set of real numbers.
The maximum output value of the function $\sin x$ is +1 and the minimum output value is -1, and all other values of $\sin x$ lie between +1 and -1. Thus,
Range: $\left[ { - 1,1} \right]$
The graph of $\sin x$ and $\cos x$ is shifted by $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$. Thus, we can also interchange between sine and cosine function as well by using the relation: $\sin x = \cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2} - x} \right)$ or $\cos x = \sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2} - x} \right)$ .
Graph of sine inverse function.
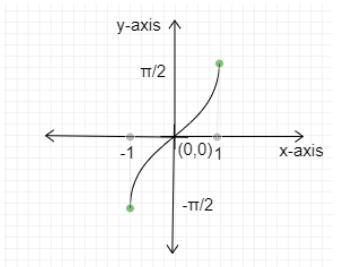
It is taking the values from +1 to -1. So, Domain = $\left[ { - 1,1} \right]$
The output values of the function are from $ - \dfrac{\pi }{2}$ to $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$. So, Range = $\left[ { - \dfrac{\pi }{2},\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right]$
Try to draw the graph of both given functions and graphically find the point of intersection.
Intersection points are the points where the graph of both given functions cut each other.
The slope of a straight line $Ax + By + C = 0$, is given by the derivative of the equation of the line with respect to x.
For the function $f\left( x \right):x \to y$, the domain of the function is the set of all possible values of $x$ for which the function is defined. The range of the function is the set of all output values of the function at $x$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Step 1: Draw a graph of $f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos x} \right)$
To draw the graph of $f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos x} \right)$ , we will use both the functions $\cos x$ and ${\cos ^{ - 1}}x$.
Let us consider the graph of the trigonometric function $f\left( x \right) = \cos x$
Let $y = f\left( x \right)$

The function $\cos x$ is defined on all the real values of the $x$. Thus,
Domain: $\mathbb{R}$ , where $\mathbb{R}$ is the set of real numbers.
The maximum output value of the function $\cos x$ is +1 and the minimum output value is -1, and all other values of $\cos x$ lie between +1 and -1. Thus,
Range: $\left[ { - 1,1} \right]$
Now, let us consider the graph of the inverse trigonometric function \[f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}x\] :

It is taking the values from +1 to -1. So, Domain = $\left[ { - 1,1} \right]$
The output values of the function are from 0 to $\pi $. So, Range = $\left[ {0,\pi } \right]$
Now draw the Graph of $f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos x} \right)$
Given that the function is defined for $f:\left[ {0,4\pi } \right] \to \left[ {0,\pi } \right]$
For the interval $x \in \left[ {0,\pi } \right]$
From the above graph of the function $f\left( x \right) = \cos x$ , the output values for the interval $\left[ {0,\pi } \right]$ is between -1 and +1. The output value of$\cos x$ is the input value of ${\cos ^{ - 1}}x$ .
And from the above graph of the function $f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}x$ , the output values for the interval $\left[ { - 1, + 1} \right]$ is 0 to $\pi $. Thus,
$f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos x} \right) = x$
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right) = x$
( Let $y = f\left( x \right)$
Differentiation $\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}$ gives the slope of the function.
i.e. $y = x$, a straight line with slope $\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = 1$)
The range for the interval $x \in \left[ {0,\pi } \right]$ is $f\left( x \right) \in \left[ {0,\pi } \right]$
Thus the graph of $f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos x} \right)$ in the interval $x \in \left[ {0,\pi } \right]$ is a straight line with slope 1.
For the interval $x \in \left[ {\pi ,2\pi } \right]$
From the above graph of the function $f\left( x \right) = \cos x$ , the output values for the interval $\left[ {\pi ,2\pi } \right]$ is between -1 and 0.
In $f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos x} \right)$ , the domain is the range of \[\cos x\] , but for the domain$ \in \left[ { - 1,0} \right]$ , the function ${\cos ^{ - 1}}x$ is not defined.
Therefore, using the property of the cosine function $\cos x = \cos \left( {2\pi - x} \right)$
$f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos x} \right)$
Therefore, $f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos \left( {2\pi - x} \right)} \right) = 2\pi - x$
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right) = 2\pi - x$
(Let $y = f\left( x \right)$
Differentiation $\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}$ gives the slope of the function.
i.e. $y = 2\pi - x$, a straight line with slope $\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = - 1$)
For $x = \pi ,$
$f\left( x \right) = 2\pi - \pi = \pi $
For $x = 2\pi ,$
$f\left( x \right) = 2\pi - 2\pi = 0$
The range for the interval $x \in \left[ {\pi ,2\pi } \right]$ is $f\left( x \right) \in \left[ {0,\pi } \right]$
Thus the graph of $f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos x} \right)$ in the interval $x \in \left[ {\pi ,2\pi } \right]$ is a straight line with slope -1.
Therefore, the drawn graph of $f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos x} \right)$ is the following:

Graph: $f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos x} \right)$
Step 2: Draw graph of $f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{10 - x}}{{10}}$
We have drawn the graph of one given function. Now let’s draw the function of other given functions to find the intersection points between them.
$f\left( x \right) = 1 - \dfrac{x}{{10}}$
| $x$ | $0$ | $10$ |
| $y$ | $1$ | $0$ |
Point $10 \simeq 3\pi $
Let $y = f\left( x \right)$
Differentiation $\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}$ gives the slope of the function. Thus,
The slope of the line $f\left( x \right) = 1 - \dfrac{x}{{10}}$, is $\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = - 1$
Therefore, the drawn graph $f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{10 - x}}{{10}}$ is the following:

Graph: $f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{10 - x}}{{10}}$
Step 3: Count the point of intersection from the graph:
For $x \in \left[ {0,4\pi } \right]$
Function $f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos x} \right)$ and $f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{10 - x}}{{10}}$ intersects each other 3 points shown as below:

Final answer: At 3 points function $f\left( x \right) = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\cos x} \right)$ satisfies $f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{10 - x}}{{10}}$ in the interval $x \in \left[ {0,4\pi } \right]$
Note: Following graphs will be useful in future reference.
Graph of the sine function.

The function $\sin x$ is defined on all the real values of the $x$. Thus,
Domain: $\mathbb{R}$ , where $\mathbb{R}$ is the set of real numbers.
The maximum output value of the function $\sin x$ is +1 and the minimum output value is -1, and all other values of $\sin x$ lie between +1 and -1. Thus,
Range: $\left[ { - 1,1} \right]$
The graph of $\sin x$ and $\cos x$ is shifted by $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$. Thus, we can also interchange between sine and cosine function as well by using the relation: $\sin x = \cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2} - x} \right)$ or $\cos x = \sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2} - x} \right)$ .
Graph of sine inverse function.

It is taking the values from +1 to -1. So, Domain = $\left[ { - 1,1} \right]$
The output values of the function are from $ - \dfrac{\pi }{2}$ to $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$. So, Range = $\left[ { - \dfrac{\pi }{2},\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right]$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




