
Let f: R$ \to $R and g: R$ \to $R be respectively given by f(x) = |x| + 1 and g(x) =${x^2} + 1$. Define h: R$ \to $R by
h(x) = \[\left\{ \begin{gathered}
\max {\text{ }}\left\{ {f\left( x \right),g\left( x \right)} \right\}{\text{ if }}x \leqslant 0 \\
\min {\text{ }}\left\{ {f\left( x \right),g\left( x \right)} \right\}{\text{ if }}x > 0 \\
\end{gathered} \right.\].
Then number of points at which h(x) is not differentiable is
Answer
597k+ views
Hint: In this question find the meeting points of function f(x) and function g(x) and also remember to use the graphical representation of the given functions, use this information to approach towards the solution of the question.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the given information we have function f(x) = |x| + 1 and g(x) = ${x^2} + 1$ where f: R$ \to $R and g: R$ \to $R
So for function f(x) = |x|+1 = \[\left\{ \begin{gathered}
f\left( x \right) = x + 1{\text{ for }}x \geqslant 0 \\
f\left( x \right) = - x + 1{\text{ for }}x < 0 \\
\end{gathered} \right.\]
For the function g(x) = ${x^2} + 1$ we know that for $x \geqslant 0$ and for x < 0 the function g(x) = ${x^2} + 1$
Finding the meeting point for function f(x) and function g(x)
When x < 0
Function f(x) = - x + 1 and function g(x) = ${x^2} + 1$
We know that at the meeting point of two function f(x) = g(x)
Therefore ${x^2} + 1$ = - x + 1
$ \Rightarrow $${x^2} + x = 1 - 1$
$ \Rightarrow $x (x+1) = 0
Since x can’t be 0 therefore x = - 1
For x = -1, y = 2
Therefore the function f(x) and function g(x) for x < 0 will meet at (-1, 2)
For $x \geqslant 0$
Function f(x) = x + 1 and function g(x) = ${x^2} + 1$
We know that at the meeting point f(x) = g(x)
Therefore x + 1 = ${x^2} + 1$
$ \Rightarrow $${x^2} - x = 1 - 1$
$ \Rightarrow $x(x – 1) = 0
Therefore x = 0, 1
For x = 0, y = 1
And for x =1, y = 2
Therefore function f(x) and function g(x) for $x \geqslant 0$ will meet at (0, 1) and (1, 2)
The graphical representation of the above equation is given below
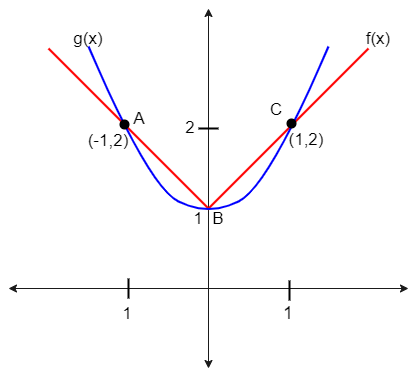
For function h(x) we know that h(x) = \[\left\{ \begin{gathered}
\max {\text{ }}\left\{ {f\left( x \right),g\left( x \right)} \right\}{\text{ if }}x \leqslant 0 \\
\min {\text{ }}\left\{ {f\left( x \right),g\left( x \right)} \right\}{\text{ if }}x > 0 \\
\end{gathered} \right.\]

Here green shows the representation of h(x) function
We know that for \[x \leqslant 0\]the function h(x) is maximum so in the above graph
For x < -1 function g(x) is showing the maximum value
For – 1 < x < 0 function f(x) is showing the maximum value
Also for x > 0 the function h(x) is minimum do by the above graph
For 0 < x < 1 function g(x) is showing the minimum value
And for x > 1 function f(x) is showing the minimum value
So by the above statement we can say that function h(x) is not differentiable at (0, 1), (-1, 2) and (1, 2)
Hence the number of points at which h(x) is not differentiable at 3 points.
Note: In the above solution we used a term “function” which can be explained as a relation between the set of inputs and the set of possible outputs of those inputs. A function is represented as f: X $ \to $Y Here X and Y are the two types of variables i.e. independent and dependent variables, thus this function defines the relationship between X and Y.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the given information we have function f(x) = |x| + 1 and g(x) = ${x^2} + 1$ where f: R$ \to $R and g: R$ \to $R
So for function f(x) = |x|+1 = \[\left\{ \begin{gathered}
f\left( x \right) = x + 1{\text{ for }}x \geqslant 0 \\
f\left( x \right) = - x + 1{\text{ for }}x < 0 \\
\end{gathered} \right.\]
For the function g(x) = ${x^2} + 1$ we know that for $x \geqslant 0$ and for x < 0 the function g(x) = ${x^2} + 1$
Finding the meeting point for function f(x) and function g(x)
When x < 0
Function f(x) = - x + 1 and function g(x) = ${x^2} + 1$
We know that at the meeting point of two function f(x) = g(x)
Therefore ${x^2} + 1$ = - x + 1
$ \Rightarrow $${x^2} + x = 1 - 1$
$ \Rightarrow $x (x+1) = 0
Since x can’t be 0 therefore x = - 1
For x = -1, y = 2
Therefore the function f(x) and function g(x) for x < 0 will meet at (-1, 2)
For $x \geqslant 0$
Function f(x) = x + 1 and function g(x) = ${x^2} + 1$
We know that at the meeting point f(x) = g(x)
Therefore x + 1 = ${x^2} + 1$
$ \Rightarrow $${x^2} - x = 1 - 1$
$ \Rightarrow $x(x – 1) = 0
Therefore x = 0, 1
For x = 0, y = 1
And for x =1, y = 2
Therefore function f(x) and function g(x) for $x \geqslant 0$ will meet at (0, 1) and (1, 2)
The graphical representation of the above equation is given below

For function h(x) we know that h(x) = \[\left\{ \begin{gathered}
\max {\text{ }}\left\{ {f\left( x \right),g\left( x \right)} \right\}{\text{ if }}x \leqslant 0 \\
\min {\text{ }}\left\{ {f\left( x \right),g\left( x \right)} \right\}{\text{ if }}x > 0 \\
\end{gathered} \right.\]

Here green shows the representation of h(x) function
We know that for \[x \leqslant 0\]the function h(x) is maximum so in the above graph
For x < -1 function g(x) is showing the maximum value
For – 1 < x < 0 function f(x) is showing the maximum value
Also for x > 0 the function h(x) is minimum do by the above graph
For 0 < x < 1 function g(x) is showing the minimum value
And for x > 1 function f(x) is showing the minimum value
So by the above statement we can say that function h(x) is not differentiable at (0, 1), (-1, 2) and (1, 2)
Hence the number of points at which h(x) is not differentiable at 3 points.
Note: In the above solution we used a term “function” which can be explained as a relation between the set of inputs and the set of possible outputs of those inputs. A function is represented as f: X $ \to $Y Here X and Y are the two types of variables i.e. independent and dependent variables, thus this function defines the relationship between X and Y.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




