
Let \[f\] be an odd function defined on the set of real numbers such that for \[x \geqslant 0\], \[f(x) = 3\sin x + 4\cos x\]. Then \[f(x)\] at \[x = \dfrac{{ - 11\pi }}{6}\] is equal to
A. \[\dfrac{{ - 3}}{2} - 2\sqrt 3 \]
B. \[\dfrac{3}{2} - 2\sqrt 3 \]
C. \[\dfrac{3}{2} + 2\sqrt 3 \]
D. \[\dfrac{{ - 3}}{2} + 2\sqrt 3 \]
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: Here we use the concept of odd functions which is \[f( - x) = - f(x)\] and solve for the value at given x. We break the angle in such a way that it is added or subtracted from \[2\pi \].
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have \[f(x) = 3\sin x + 4\cos x\]
Also, we know any function is an odd function if it satisfies \[f( - x) = - f(x)\].
Now we have to find the value of the function at point \[x = \dfrac{{ - 11\pi }}{6}\]
We have to find the value of \[f(\dfrac{{ - 11\pi }}{6})\]
Since, f is an odd function, therefore, we can use the concept \[f( - x) = - f(x)\]. Substitute \[x = \dfrac{{ - 11\pi }}{6}\].
\[ \Rightarrow f(\dfrac{{ - 11\pi }}{6}) = - f(\dfrac{{11\pi }}{6})\]
Now we can break the angle inside the function as
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{11\pi }}{6} = \dfrac{{12\pi - \pi }}{6}\]
Separating the fraction into two parts
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{11\pi }}{6} = \dfrac{{12\pi }}{6} - \dfrac{\pi }{6}\]
Cancel out common factors from numerator and denominator
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{11\pi }}{6} = 2\pi - \dfrac{\pi }{6}\]
Therefore, we can write
\[f(\dfrac{{ - 11\pi }}{6}) = - f(2\pi - \dfrac{\pi }{6})\]
Now we know \[f(x) = 3\sin x + 4\cos x\]
Put \[x = 2\pi - \dfrac{\pi }{6}\]
\[ \Rightarrow f(\dfrac{{11\pi }}{6}) = 3\sin \left( {2\pi - \dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right) + 4\cos \left( {2\pi - \dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right)\] … (1)
Now we will use the quadrant graph to convert the angles.
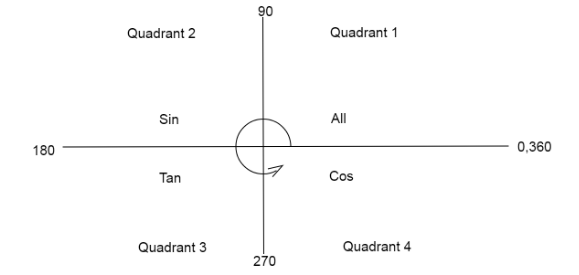
Here we denote \[2\pi = {360^ \circ },\pi = {180^ \circ }\]
Now we calculate the values of both the functions on RHS of the equation using the quadrant diagram.
For \[\sin \left( {2\pi - \dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right)\], we are subtracting from \[2\pi \]which goes into the fourth quadrant where sin function is negative.
So, the value of \[\sin \left( {2\pi - \dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right) = - \sin (\dfrac{\pi }{6}) = - \dfrac{1}{2}\] … (2)
For \[\cos \left( {2\pi - \dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right)\], we are subtracting from \[2\pi \]which goes into the fourth quadrant where the cos function is positive.
So, the value of \[\cos \left( {2\pi - \dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right) = \cos (\dfrac{\pi }{6}) = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\] … (3)
Substitute the values from equation (2) and equation (3) in equation (1)
\[ \Rightarrow f(x) = 3(\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}) + 4(\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2})\]
Multiply the terms in the bracket.
\[
\Rightarrow f(\dfrac{{11\pi }}{6}) = \dfrac{{ - 3}}{2} + \dfrac{{4\sqrt 3 }}{2} \\
\Rightarrow f(\dfrac{{11\pi }}{6}) = \dfrac{{ - 3}}{2} + 2\sqrt 3 \\
\]
So now \[f( - \dfrac{{11\pi }}{6}) = - f(\dfrac{{11\pi }}{6})\]
Therefore,
\[
\Rightarrow f( - \dfrac{{11\pi }}{6}) = - [\dfrac{{ - 3}}{2} + 2\sqrt 3 ] \\
\Rightarrow f( - \dfrac{{11\pi }}{6}) = \dfrac{3}{2} - 2\sqrt 3 \\
\]
So, option B is correct.
Note: Students are likely to make mistakes while calculating the values from the quadrant diagram, keep in mind that we always move anti-clockwise as we add the angles, so when we subtract the angle we move backwards or clockwise to see which quadrant our function lies in.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have \[f(x) = 3\sin x + 4\cos x\]
Also, we know any function is an odd function if it satisfies \[f( - x) = - f(x)\].
Now we have to find the value of the function at point \[x = \dfrac{{ - 11\pi }}{6}\]
We have to find the value of \[f(\dfrac{{ - 11\pi }}{6})\]
Since, f is an odd function, therefore, we can use the concept \[f( - x) = - f(x)\]. Substitute \[x = \dfrac{{ - 11\pi }}{6}\].
\[ \Rightarrow f(\dfrac{{ - 11\pi }}{6}) = - f(\dfrac{{11\pi }}{6})\]
Now we can break the angle inside the function as
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{11\pi }}{6} = \dfrac{{12\pi - \pi }}{6}\]
Separating the fraction into two parts
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{11\pi }}{6} = \dfrac{{12\pi }}{6} - \dfrac{\pi }{6}\]
Cancel out common factors from numerator and denominator
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{11\pi }}{6} = 2\pi - \dfrac{\pi }{6}\]
Therefore, we can write
\[f(\dfrac{{ - 11\pi }}{6}) = - f(2\pi - \dfrac{\pi }{6})\]
Now we know \[f(x) = 3\sin x + 4\cos x\]
Put \[x = 2\pi - \dfrac{\pi }{6}\]
\[ \Rightarrow f(\dfrac{{11\pi }}{6}) = 3\sin \left( {2\pi - \dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right) + 4\cos \left( {2\pi - \dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right)\] … (1)
Now we will use the quadrant graph to convert the angles.

Here we denote \[2\pi = {360^ \circ },\pi = {180^ \circ }\]
Now we calculate the values of both the functions on RHS of the equation using the quadrant diagram.
For \[\sin \left( {2\pi - \dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right)\], we are subtracting from \[2\pi \]which goes into the fourth quadrant where sin function is negative.
So, the value of \[\sin \left( {2\pi - \dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right) = - \sin (\dfrac{\pi }{6}) = - \dfrac{1}{2}\] … (2)
For \[\cos \left( {2\pi - \dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right)\], we are subtracting from \[2\pi \]which goes into the fourth quadrant where the cos function is positive.
So, the value of \[\cos \left( {2\pi - \dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right) = \cos (\dfrac{\pi }{6}) = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\] … (3)
Substitute the values from equation (2) and equation (3) in equation (1)
\[ \Rightarrow f(x) = 3(\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}) + 4(\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2})\]
Multiply the terms in the bracket.
\[
\Rightarrow f(\dfrac{{11\pi }}{6}) = \dfrac{{ - 3}}{2} + \dfrac{{4\sqrt 3 }}{2} \\
\Rightarrow f(\dfrac{{11\pi }}{6}) = \dfrac{{ - 3}}{2} + 2\sqrt 3 \\
\]
So now \[f( - \dfrac{{11\pi }}{6}) = - f(\dfrac{{11\pi }}{6})\]
Therefore,
\[
\Rightarrow f( - \dfrac{{11\pi }}{6}) = - [\dfrac{{ - 3}}{2} + 2\sqrt 3 ] \\
\Rightarrow f( - \dfrac{{11\pi }}{6}) = \dfrac{3}{2} - 2\sqrt 3 \\
\]
So, option B is correct.
Note: Students are likely to make mistakes while calculating the values from the quadrant diagram, keep in mind that we always move anti-clockwise as we add the angles, so when we subtract the angle we move backwards or clockwise to see which quadrant our function lies in.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




