
Let $ A=\left[ x:x\in R,|x|<1 \right];B=\left[ x:x\in R,|x-1|\ge 1 \right] $ and $ A\cup B=R-D $ then the set D is
A. $ \left[ x:1 < x\le 2 \right] $
B. $ \left[ x:1\le x < 2 \right] $
C. $ \left[ x:1\le x\le 2 \right] $
D. None of these
Answer
510.3k+ views
Hint: We will first find the domain of ‘x’ In set ‘A’ and Set ‘B’ which are the elements of sets, from where we will find out the $ A\cup B $ , which will help us to find the set D by comparing the result we got from $ A\cup B $ and $ R-D $ .
Complete step by step answer:
Moving ahead with the question in step wise manner,
We need to find out the value of set D, so let us first find out the set A and Set B elements, so first in set A we are given with the info $ A=\left[ x:x\in R,|x|< 1 \right] $ to get the domain of ‘x’ we need to simplify $ |x|< 1 $ by using the mode property. So we have $ |x|< 1 $ by simplifying it using the mode inequality we will get;
$ -1 < x < 1 $ .
Similarly simplifying the set B we have $ B=\left[ x:x\in R,|x-1|\ge 1 \right] $ , so to find the elements of set B, we need to simplify $ |x-1|\ge 1 $ , which on simplifying using property of mode we will get;
$ \begin{align}
& |x-1|\ge 1 \\
& x\ge 2\cup x\le 0 \\
\end{align} $
So we got set A and set B which are equal to $ -1 < x < 1 $ and $ x\ge 2\cup x\le 0 $ .
So now we need to find out the $ A\cup B $ . So let us draw it on the number line and find out the union of both sets, so let us plot the number line and mark the points $ -1,0,1 $ and 2 as shown in figure.
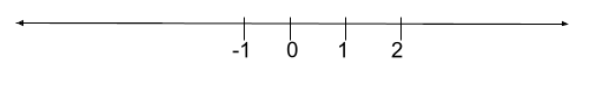
As we can see, if we take the union of two sets A and B then all numbers get covered on the number line except the numbers from 1 to 2, including 1 and excluding 2. We can also say that $ A\cup B=R-[1,2) $ so by comparing it with $ R-D $ we can say that set D is $ [1,2) $ which can also be written as $ 1\le x < 2 $ .
So set D is $ 1\le x < 2 $ .
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: As in the set B the number 2 is included, so in the set $A\cup B$ the number will be included, same is with 1; as in set A number 1 is not included in set so it will be not present in the number line, hence we can say that in the number line $A\cup B$ all number will be there except the number 2 which is included and the number 1 will be not be counted in $A\cup B$ because it is not in set A.
Complete step by step answer:
Moving ahead with the question in step wise manner,
We need to find out the value of set D, so let us first find out the set A and Set B elements, so first in set A we are given with the info $ A=\left[ x:x\in R,|x|< 1 \right] $ to get the domain of ‘x’ we need to simplify $ |x|< 1 $ by using the mode property. So we have $ |x|< 1 $ by simplifying it using the mode inequality we will get;
$ -1 < x < 1 $ .
Similarly simplifying the set B we have $ B=\left[ x:x\in R,|x-1|\ge 1 \right] $ , so to find the elements of set B, we need to simplify $ |x-1|\ge 1 $ , which on simplifying using property of mode we will get;
$ \begin{align}
& |x-1|\ge 1 \\
& x\ge 2\cup x\le 0 \\
\end{align} $
So we got set A and set B which are equal to $ -1 < x < 1 $ and $ x\ge 2\cup x\le 0 $ .
So now we need to find out the $ A\cup B $ . So let us draw it on the number line and find out the union of both sets, so let us plot the number line and mark the points $ -1,0,1 $ and 2 as shown in figure.

As we can see, if we take the union of two sets A and B then all numbers get covered on the number line except the numbers from 1 to 2, including 1 and excluding 2. We can also say that $ A\cup B=R-[1,2) $ so by comparing it with $ R-D $ we can say that set D is $ [1,2) $ which can also be written as $ 1\le x < 2 $ .
So set D is $ 1\le x < 2 $ .
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: As in the set B the number 2 is included, so in the set $A\cup B$ the number will be included, same is with 1; as in set A number 1 is not included in set so it will be not present in the number line, hence we can say that in the number line $A\cup B$ all number will be there except the number 2 which is included and the number 1 will be not be counted in $A\cup B$ because it is not in set A.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




