
Let ABCD be a unit square. Draw a quadrant of a circle with A as centre and B, D as end points of the arc. Similarly, draw a quadrant of a circle with B as centre and A, C as end points of the arc. Inscribe a circle $ \Gamma $ touching the arc AC internally, the arc BD internally and also touching the side AB. Find the radius of the circle $ \Gamma . $
Answer
578.7k+ views
Hint: In this question, we will construct a figure, by using the given information, now to find the radius of the circle, we will construct OE in the circle. Then by applying Pythagoras’ theorem in the right-angled triangle, we will get our required answer, i.e., the radius of the circle $ \Gamma . $
Complete step-by-step answer:
We need to draw a figure, where ABCD is a unit square. A quadrant of a circle with A as centre and B, D as end points of the arc is there. Similarly, another quadrant of a circle with B as centre and A, C as end points of the arc should be there. The circle $ \Gamma $ inscribed in the square, touching the arc AC internally, the arc BD internally and also touching the side AB, we also need to find the radius of the circle $ \Gamma . $
Let us construct a figure, using the above information.
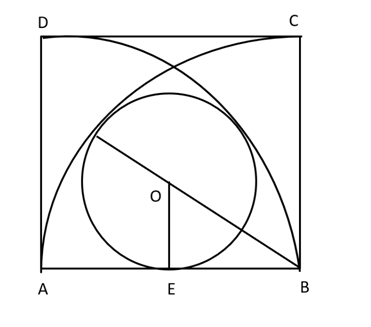
Here,we have taken O as the centre of the circle $ \Gamma . $ And, by symmetry OE is the perpendicular bisector of AB, i.e., \[OE \bot AB.\]
So, \[BE = \dfrac{{AB}}{2} = \dfrac{1}{2}\] (Since, ABCD is a unit square,\[\therefore AB = 1\] )
Now, if r is the radius of $ \Gamma , $ from the figure, we get that \[OB = 1 - r,\]and \[OE = r.\]
On using Pythagoras' theorem in the triangle OEB, we get
\[
{\left( {OB} \right)^2} = {\left( {OE} \right)^2} + {\left( {BE} \right)^2} \\
{\left( {1 - r} \right)^2} = {r^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)^2} \\
{1^2} - 2r + {r^2} = {r^2} + \dfrac{1}{4} \\
1 - 2r = \dfrac{1}{4} \\
4 - 8r = 1 \\
8r = 3 \\
\Rightarrow r = \dfrac{3}{8} \\
\]
Thus, the radius of the circle $ \Gamma $ is $ \dfrac{3}{8}. $
Note: In the question, we have been given a symbol, $ \Gamma $ . Let us know about this symbol in detail, this symbol is a gamma alphabet, in uppercase it is denoted as $ \Gamma $ while in lowercase it is denoted as $ \gamma . $ The lowercase symbol as a gamma sign is much more popular than the uppercase one.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We need to draw a figure, where ABCD is a unit square. A quadrant of a circle with A as centre and B, D as end points of the arc is there. Similarly, another quadrant of a circle with B as centre and A, C as end points of the arc should be there. The circle $ \Gamma $ inscribed in the square, touching the arc AC internally, the arc BD internally and also touching the side AB, we also need to find the radius of the circle $ \Gamma . $
Let us construct a figure, using the above information.

Here,we have taken O as the centre of the circle $ \Gamma . $ And, by symmetry OE is the perpendicular bisector of AB, i.e., \[OE \bot AB.\]
So, \[BE = \dfrac{{AB}}{2} = \dfrac{1}{2}\] (Since, ABCD is a unit square,\[\therefore AB = 1\] )
Now, if r is the radius of $ \Gamma , $ from the figure, we get that \[OB = 1 - r,\]and \[OE = r.\]
On using Pythagoras' theorem in the triangle OEB, we get
\[
{\left( {OB} \right)^2} = {\left( {OE} \right)^2} + {\left( {BE} \right)^2} \\
{\left( {1 - r} \right)^2} = {r^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)^2} \\
{1^2} - 2r + {r^2} = {r^2} + \dfrac{1}{4} \\
1 - 2r = \dfrac{1}{4} \\
4 - 8r = 1 \\
8r = 3 \\
\Rightarrow r = \dfrac{3}{8} \\
\]
Thus, the radius of the circle $ \Gamma $ is $ \dfrac{3}{8}. $
Note: In the question, we have been given a symbol, $ \Gamma $ . Let us know about this symbol in detail, this symbol is a gamma alphabet, in uppercase it is denoted as $ \Gamma $ while in lowercase it is denoted as $ \gamma . $ The lowercase symbol as a gamma sign is much more popular than the uppercase one.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




