
Let a vertical tower AB have its and A on the level ground. Let C be the midpoint of AB and P be a point on the ground such that \[AP = 2AB\]of \[\angle BPC = B,\] then \[\tan \beta \]is equal to
A. \[\dfrac{1}{4}\]
B. \[\dfrac{2}{9}\]
C. \[\dfrac{4}{9}\]
D. \[\dfrac{6}{7}\]
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: Draw the figure to get a clarity of the question. The term vertical means straight that it is a straight tower which has its end in the level ground. Again, level ground is nothing but a flat surface. Naming the diagram or figure helps out a lot in solving the question. So, name the figure properly and exactly according to the given condition. \[\tan \beta \] is the angle at the point C and point P and \[\tan \beta \] is nothing but perpendicularly divided by base.
Complete step by step solution:
Given:\[\angle BPC = \beta \]
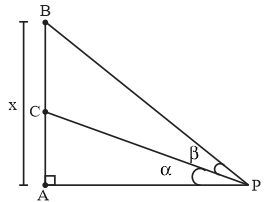
Let \[AB = x,\]
Then \[AP = 2AB = 2x\]
Now,
Triangle ABP is right angled triangle with BP as hypotenuse
Now, by Pythagoras theorem,
\[
B{P^2} = A{P^2} + A{B^2} \\
B{P^2} = {\left( {2x} \right)^2} + {x^2} \\
B{P^2} = 5{x^2} \\
\]
Therefore,
\[BP = \sqrt 5 \,\,x\]
Now, according to question we are told that C is mid-point of AB therefore
\[AC = \dfrac{1}{2}AB\]
Thus \[AC = \dfrac{x}{2}\]
Now,
\[\tan \alpha = \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{x}{2}} \right)}}{{\left( {2x} \right)}} = \dfrac{1}{4}\]
thus\[\tan \alpha = \dfrac{1}{4}\]
Now, we know from figure that in triangle APB,
\[\tan \left( {\alpha + \beta } \right) = \dfrac{x}{{2x}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
Therefore,
\[
\dfrac{{\tan \alpha + \tan \beta }}{{1 - \tan \alpha \times \tan \beta }} = \dfrac{1}{2} \\
\Rightarrow 2\left( {\tan \alpha + \tan \beta } \right) = 1 - \tan \alpha \tan \beta \\
\Rightarrow 2\left( {\dfrac{1}{4} + \tan \beta } \right) = 1 - \dfrac{1}{4}\tan \beta \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{9}{4}\tan \beta = \dfrac{1}{2} \\
\Rightarrow \tan \beta = \dfrac{2}{9} \\
\]
Thus, the angle made by triangle CPB is nothing \[\tan \beta \] and is equal to \[\dfrac{2}{9}\].
Hence the correct option is (2).
Note: In this type of question students often makes mistake while determining angle \[\beta \] as they always choose the wrong side as thus this is the reason why it is highly recommended to draw the diagram, also remember the standard formula, as \[\tan \left( {\alpha + \beta } \right)\] is not \[\tan \alpha + \tan \beta \] this is incorrect, use the correct formula to get the correct answer.
Complete step by step solution:
Given:\[\angle BPC = \beta \]

Let \[AB = x,\]
Then \[AP = 2AB = 2x\]
Now,
Triangle ABP is right angled triangle with BP as hypotenuse
Now, by Pythagoras theorem,
\[
B{P^2} = A{P^2} + A{B^2} \\
B{P^2} = {\left( {2x} \right)^2} + {x^2} \\
B{P^2} = 5{x^2} \\
\]
Therefore,
\[BP = \sqrt 5 \,\,x\]
Now, according to question we are told that C is mid-point of AB therefore
\[AC = \dfrac{1}{2}AB\]
Thus \[AC = \dfrac{x}{2}\]
Now,
\[\tan \alpha = \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{x}{2}} \right)}}{{\left( {2x} \right)}} = \dfrac{1}{4}\]
thus\[\tan \alpha = \dfrac{1}{4}\]
Now, we know from figure that in triangle APB,
\[\tan \left( {\alpha + \beta } \right) = \dfrac{x}{{2x}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
Therefore,
\[
\dfrac{{\tan \alpha + \tan \beta }}{{1 - \tan \alpha \times \tan \beta }} = \dfrac{1}{2} \\
\Rightarrow 2\left( {\tan \alpha + \tan \beta } \right) = 1 - \tan \alpha \tan \beta \\
\Rightarrow 2\left( {\dfrac{1}{4} + \tan \beta } \right) = 1 - \dfrac{1}{4}\tan \beta \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{9}{4}\tan \beta = \dfrac{1}{2} \\
\Rightarrow \tan \beta = \dfrac{2}{9} \\
\]
Thus, the angle made by triangle CPB is nothing \[\tan \beta \] and is equal to \[\dfrac{2}{9}\].
Hence the correct option is (2).
Note: In this type of question students often makes mistake while determining angle \[\beta \] as they always choose the wrong side as thus this is the reason why it is highly recommended to draw the diagram, also remember the standard formula, as \[\tan \left( {\alpha + \beta } \right)\] is not \[\tan \alpha + \tan \beta \] this is incorrect, use the correct formula to get the correct answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




