
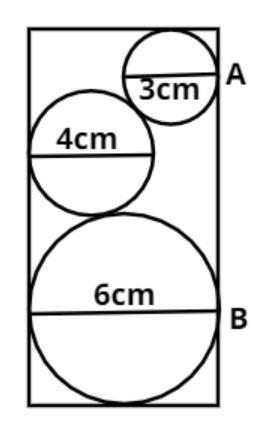
What is the length of AB in the below given figure?

Answer
598.5k+ views
Hint: In this particular types of question use the concept of Pythagoras theorem i.e. ${\left( {{\text{hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{base}}} \right)^2}$ and use that the distance between the center of the two circle if they touch each other is the sum of the respective radii so use this concept to reach the solution of the question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given data:
Diameter of bigger circle = 6cm, therefore radius = 3cm
Diameter of the middle circle = 4 cm, therefore radius = 2cm
Diameter of the upper circle = 3 cm, therefore radius = 1.5cm.
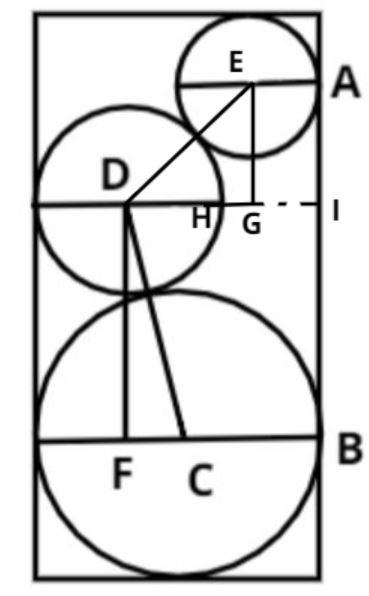
Let C, D and F be the center of the bigger, middle and upper circles respectively.
Draw perpendicular from the center of the middle circle to the lower circle as shown, let it cut the lower circle at point F
So, angle DFC = 90 degrees.
So distance CF = radius of the bigger circle – radius of the middle circle
Therefore, CF = 3 – 2 = 1cm.
Now join C and D as shown.
As C and D bot are centers so the distance CD = sum of the radius of the bigger and middle circles.
Therefore, CD = 3 + 2 = 5cm.
Now extend the diameter of the middle circle towards RHS and draw the perpendicular on this line from the center of the upper circle as shown; let it cut the line at point G.
So, angle EGD = 90 degrees.
Now from figure, GH = HI – GI
Now HI = 6 – 4 = 2cm, and GI = radius of the upper circle = 1.5cm.
Therefore, GH = 2 – 1.5 = 0.5cm
Therefore, DG = GH + DH = 0.5 + 2 = 2.5cm
And ED is distance between the centers of the upper and middle circle so,
ED = 1.5 + 2 = 3.5cm
Now in triangle DFC apply Pythagoras theorem we have,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{base}}} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{DC}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{DF}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{FC}}} \right)^2}$
Now substitute the values we have,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {\text{5}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{DF}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {\text{1}} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{DF}}} \right)^2} = 25 - 1 = 24$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{\text{DF}}} \right) = \sqrt {24} = 2\sqrt 6 $ Cm
Now in triangle DEG apply Pythagoras theorem we have,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{base}}} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{ED}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{GE}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{DG}}} \right)^2}$
Now substitute the values we have,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{3}}{\text{.5}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{EG}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {2.5} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{EG}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{3}}{\text{.5}}} \right)^2} - {\left( {2.5} \right)^2} = 6$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{\text{EG}}} \right) = \sqrt 6 $
So the distance AB = DF + EG = $2\sqrt 6 + \sqrt 6 = 3\sqrt 6 $ Cm.
So this is the required answer.
Note – Whenever we face such types of questions the key concept we have to remember is that to solve this problem construction is the key, so construct the diagram as above and calculate all the values required to solve the right triangles in the figure so that we can apply Pythagoras theorem and calculate the distance of DF and EG, effectively AB.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Given data:
Diameter of bigger circle = 6cm, therefore radius = 3cm
Diameter of the middle circle = 4 cm, therefore radius = 2cm
Diameter of the upper circle = 3 cm, therefore radius = 1.5cm.
Let C, D and F be the center of the bigger, middle and upper circles respectively.
Draw perpendicular from the center of the middle circle to the lower circle as shown, let it cut the lower circle at point F
So, angle DFC = 90 degrees.
So distance CF = radius of the bigger circle – radius of the middle circle
Therefore, CF = 3 – 2 = 1cm.
Now join C and D as shown.
As C and D bot are centers so the distance CD = sum of the radius of the bigger and middle circles.
Therefore, CD = 3 + 2 = 5cm.
Now extend the diameter of the middle circle towards RHS and draw the perpendicular on this line from the center of the upper circle as shown; let it cut the line at point G.
So, angle EGD = 90 degrees.
Now from figure, GH = HI – GI
Now HI = 6 – 4 = 2cm, and GI = radius of the upper circle = 1.5cm.
Therefore, GH = 2 – 1.5 = 0.5cm
Therefore, DG = GH + DH = 0.5 + 2 = 2.5cm
And ED is distance between the centers of the upper and middle circle so,
ED = 1.5 + 2 = 3.5cm
Now in triangle DFC apply Pythagoras theorem we have,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{base}}} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{DC}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{DF}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{FC}}} \right)^2}$
Now substitute the values we have,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {\text{5}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{DF}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {\text{1}} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{DF}}} \right)^2} = 25 - 1 = 24$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{\text{DF}}} \right) = \sqrt {24} = 2\sqrt 6 $ Cm
Now in triangle DEG apply Pythagoras theorem we have,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{base}}} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{ED}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{GE}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{DG}}} \right)^2}$
Now substitute the values we have,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{3}}{\text{.5}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{EG}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {2.5} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{EG}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{3}}{\text{.5}}} \right)^2} - {\left( {2.5} \right)^2} = 6$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{\text{EG}}} \right) = \sqrt 6 $
So the distance AB = DF + EG = $2\sqrt 6 + \sqrt 6 = 3\sqrt 6 $ Cm.
So this is the required answer.
Note – Whenever we face such types of questions the key concept we have to remember is that to solve this problem construction is the key, so construct the diagram as above and calculate all the values required to solve the right triangles in the figure so that we can apply Pythagoras theorem and calculate the distance of DF and EG, effectively AB.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




