
$\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)$ has much higher boiling point than $\left( {{\text{P}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)$ because:
A. $\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)$has much higher molecular mass.
B.$\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)$ forms hydrogen bonds.
C.$\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)$ contains ionic bond while $\left( {{\text{P}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)$ contains covalent bonds.
D. $\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)$undergoes umbrella inversion
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: We know that hydrogen bond is a type of bond that is present in molecules and this bond is also written as H – bond. To understand a hydrogen bond we consider a molecule that has an H atom say HA. In the molecule HA, A is a strongly electronegative element and H atom linked with A by a normal covalent bond. Electron pairs that are present in the molecule will be shared between H and A atom. Thus H will be partially positive and A will be partially negative. HA molecule thus behaves as a dipole that is represented by \[\mathop {\text{H}}\limits^{{\text{ $\delta$ + }}} - \mathop {\text{A}}\limits^{{\text{$\delta$ }} - } \]. Now another molecule say HB also forms dipole \[\mathop {\text{H}}\limits^{{\text{$\delta$ + }}} - \mathop {\text{B}}\limits^{{\text{$\delta$ }} - } \] that is brought near \[\mathop {\text{H}}\limits^{{\text{$\delta$ + }}} - \mathop {\text{A}}\limits^{{\text{$\delta$ }} - } \]. These two dipoles are linked by a type of bond which is also called hydrogen bond. Hydrogen bond between two molecule is shown as follows:
\[\mathop {\text{H}}\limits^{{\text{$\delta$ + }}} - \mathop {\text{A}}\limits^{{\text{$\delta$ }} - } ........\mathop {\text{H}}\limits^{{\text{$\delta$ + }}} - \mathop {\text{B}}\limits^{{\text{$\delta$ }} - } \]
Complete step by step answer:
As we know that ammonia $\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)$ molecule is smaller than phosphine $\left( {{\text{P}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)$ molecule. The dispersion force of ammonia molecules is smaller than the phosphine molecule.
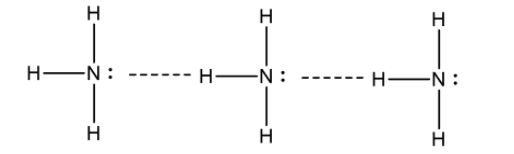
${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ molecule has a strong hydrogen bond between N and H atoms. This leads to intermolecular force and thus has a greater attraction between ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ . Due to this reason ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ has much higher boiling point than ${\text{P}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$. Hydrogen bond between ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ molecule is shown is as follows:
Hence, the option B is the correct answer
Note:
Hydrogen bonds are classified as intramolecular H bonding and intermolecular hydrogen bonding. In intramolecular hydrogen bonding H occurs between a single molecule and in inter molecule hydrogen bonding H occurs between a more similar or different molecule.
\[\mathop {\text{H}}\limits^{{\text{$\delta$ + }}} - \mathop {\text{A}}\limits^{{\text{$\delta$ }} - } ........\mathop {\text{H}}\limits^{{\text{$\delta$ + }}} - \mathop {\text{B}}\limits^{{\text{$\delta$ }} - } \]
Complete step by step answer:
As we know that ammonia $\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)$ molecule is smaller than phosphine $\left( {{\text{P}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)$ molecule. The dispersion force of ammonia molecules is smaller than the phosphine molecule.
${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ molecule has a strong hydrogen bond between N and H atoms. This leads to intermolecular force and thus has a greater attraction between ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ . Due to this reason ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ has much higher boiling point than ${\text{P}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$. Hydrogen bond between ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ molecule is shown is as follows:

Hence, the option B is the correct answer
Note:
Hydrogen bonds are classified as intramolecular H bonding and intermolecular hydrogen bonding. In intramolecular hydrogen bonding H occurs between a single molecule and in inter molecule hydrogen bonding H occurs between a more similar or different molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




