
Lateral displacement of the emergent ray of light increases with,
A. Increase in angle of incidence
B. Decrease in refractive index of medium
C. Increase in the wavelength of light
D. None
Answer
606.6k+ views
Hint: In refraction through a medium, emergent ray is parallel to the incident ray but appears slightly shifted and this shift in the position of the emergent ray, as compared to the incident ray is called Lateral displacement.
Complete step by step answer:
Lateral displacement: The perpendicular distance between the incident ray and the emergent ray is defined as lateral shift. This shift depends upon the angle of incidence, the angle of refraction and the thickness of the medium.
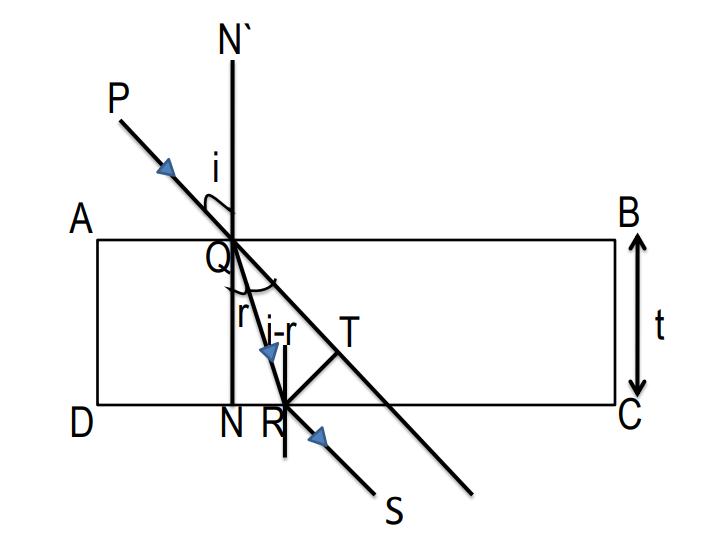
Mathematically, lateral shift is given by,
\[{{S}_{lateral}}=\dfrac{t}{\cos r}\sin (i-r)\]
Where,
\[{{S}_{lateral}}\] = lateral shift
t = thickness of medium
i = angle of incidence
r = angle of refraction
By the above formula we observe that the lateral displacement of the emergent ray of light increases with increase in angle of incidence.
Hence, the correct option is A, i.e., Increase in angle of incidence.
Additional Information:
Refraction occurs when light crosses two boundaries. Basically, a wave front is good representation here, not the ray representation. Ray is just a line drawn perpendicular to the wave front. When a wave front hits the glass at oblique angle, part of the wave enters glass and slows down. Gradually remaining part of the wave front enters glass and slows down. Wave front changes angle just because of entering partly in glass and partly in air.
Note: Students should analyse the factors affecting the lateral displacement by the formula given above i.e., lateral displacement increases with the refractive index of the medium so option B is incorrect and it decreases with the wavelength so option C is also incorrect.
Complete step by step answer:
Lateral displacement: The perpendicular distance between the incident ray and the emergent ray is defined as lateral shift. This shift depends upon the angle of incidence, the angle of refraction and the thickness of the medium.

Mathematically, lateral shift is given by,
\[{{S}_{lateral}}=\dfrac{t}{\cos r}\sin (i-r)\]
Where,
\[{{S}_{lateral}}\] = lateral shift
t = thickness of medium
i = angle of incidence
r = angle of refraction
By the above formula we observe that the lateral displacement of the emergent ray of light increases with increase in angle of incidence.
Hence, the correct option is A, i.e., Increase in angle of incidence.
Additional Information:
Refraction occurs when light crosses two boundaries. Basically, a wave front is good representation here, not the ray representation. Ray is just a line drawn perpendicular to the wave front. When a wave front hits the glass at oblique angle, part of the wave enters glass and slows down. Gradually remaining part of the wave front enters glass and slows down. Wave front changes angle just because of entering partly in glass and partly in air.
Note: Students should analyse the factors affecting the lateral displacement by the formula given above i.e., lateral displacement increases with the refractive index of the medium so option B is incorrect and it decreases with the wavelength so option C is also incorrect.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




