
Large intestine in man mainly carries out
A. Absorption of water
B. Assimilation
C. Digestion of fats
D. Digestion of carbohydrates
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: Large intestine is the last part of the gastrointestinal tract, where the final step of digestion takes place. Here, in the large intestine, the liquid unwanted digested food from the small intestine is converted to semi-solid faeces (by the reduction in volume).
Complete answer:
The large intestine also known as the large bowel consists of the colon, cecum, rectum, and anal canal. Its main function is to absorb water from the final undigested food in the form of liquid, passed on to the large intestine by the small intestine. Apart from this large intestine perform the following functions:
- Water absorption
- Absorption of electrolytes and vitamins
- Forming of faeces
- Elimination of digestive waste from the body in the form of faeces through the rectum.
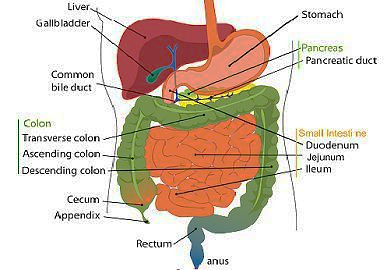
Figure 1: Digestive system
Additional Information:
1) The large intestine as the name suggests is larger in diameter than the small intestine. But in length, the small intestine is longer than the large intestine.
2) The large intestine is larger in diameter than the small intestine, having a diameter of 2.5 inches and a length of 5 feet which is shorter in length than the small intestine.
3) Large intestine does not have any folds or villi or payer patches, it is fixed and shows less motility. 4) Thus, the large intestine is not involved in digestion.
Also, this is the only part of the digestive system where no hormones are secreted or used.
Note: Large intestine irrespective of sex performs the function of absorption of water, vitamins and electrolytes from the completely digested food and removes the unwanted food waste in the form of faeces. Assimilation is the process of absorption and digestion of food or nutrients. Assimilation of nutrients, digestion of fats, and digestion of carbohydrates take place in the small intestine.
Complete answer:
The large intestine also known as the large bowel consists of the colon, cecum, rectum, and anal canal. Its main function is to absorb water from the final undigested food in the form of liquid, passed on to the large intestine by the small intestine. Apart from this large intestine perform the following functions:
- Water absorption
- Absorption of electrolytes and vitamins
- Forming of faeces
- Elimination of digestive waste from the body in the form of faeces through the rectum.

Figure 1: Digestive system
Additional Information:
1) The large intestine as the name suggests is larger in diameter than the small intestine. But in length, the small intestine is longer than the large intestine.
2) The large intestine is larger in diameter than the small intestine, having a diameter of 2.5 inches and a length of 5 feet which is shorter in length than the small intestine.
3) Large intestine does not have any folds or villi or payer patches, it is fixed and shows less motility. 4) Thus, the large intestine is not involved in digestion.
Also, this is the only part of the digestive system where no hormones are secreted or used.
Note: Large intestine irrespective of sex performs the function of absorption of water, vitamins and electrolytes from the completely digested food and removes the unwanted food waste in the form of faeces. Assimilation is the process of absorption and digestion of food or nutrients. Assimilation of nutrients, digestion of fats, and digestion of carbohydrates take place in the small intestine.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




